Abstract
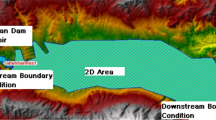
Dam ruptures can cause large water discharges over a short period of time, which constitutes a serious threat for downstream regions. In this context, the paper focuses on the risk assessment of the Sélingué reservoir-dam rupture’s scenario. Computational fluid dynamics “ANSYS FLUENT” code is used to simulate the environmental impact of its rupture. In order to assess potential risks for each zone, the evolution of physical parameters such as water flow, water volume and height is determined and briefly discussed. Possible environmental risks are also examined in terms of critical infrastructure protection. In order to better comprehend the simulation results, two zones are distinguished by their altitudes on the simulation profile. Water flow, volume and height in each zone have been determined as a function of time. Results show that the magnitude of the damage is strongly related to the distance between each zone and the dam. The extent of this damage in the parts nearest to the dam is approximately five to six times higher compared to the other zones. Furthermore, water level in the nearest zones is found to reach more than 1 m within just few hours after the rupture. We therefore suggest that the low-altitude areas of this reservoir dam should be urgently evacuated.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFP (2015) Rupture d’un barrage au Brésil _ 17 morts et 50 blessés. Sciences et Avenir
Alhassan HS (2009) Butterflies vs. hydropower: reflections on large dams in contemporary Africa. Water Altern 2(1):148–160
Amegashie BK, Quansah C, Agyare WA, Tamene L, Vlek PLG (2011) Sediment-bound nutrient export from five small reservoir catchments and its implications for the Sudan savanna zone of Ghana. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 16:61–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1770.2011.00459.x
Amnyattalab J, Rezaie H (2018) Study of the effect of seepage through the body of earth dam on its stability by predicting the affecting hydraulic factors using models of Brooks: Corey and van Genuchten (Case study of Nazluchay and Shahrchay earth dams). Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:2625–2636
Arfi R (2003) The effects of climate and hydrology on the trophic status of Sélingué Reservoir, Mali, West Africa. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 8:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1770.2003.00223.x
Biscarini C, Francesco SD, Manciola P (2010) CFD modelling approach for dam break flow studies. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14(4):705–718. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-6-6759-2009
Bonelli S, Nicot F (2013) Erosion in geomechanics applied to dams and levees, Wiley, Hoboken, ISBN: 9781848214095, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118577165
Boussinesq J (1903) Theorie analytique de la chaleur, Gauthier-V. Paris: Gauthier-Villars, vol 2
Concho Valley Council of Governments (CVCOG) (2012) Hazard mitigation plan update 2012
Foster M, Fell R, Spannagle M (2000) The statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents. Can Geotech J 37(5):1000–1024. https://doi.org/10.1139/t00-030
Ghemmour A, Chambon G, Naaim M (2008) Gravitary free surface flows used as a rheometrical tool : the case of viscoplastic fluids. In: CP1027, The XV th international congress on rheology, the society of rheology 80th annual meeting, vol 8, pp 1039–1042. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2964460
Google Earth (2019) [Online]. Available: https://earth.google.com/web/@11.6383017,-8.229789,343.64505597a,1032.26992133d,35y,0h,45t,0r/data=Cl0aWxJVCiQweGU1MjM5MjhlMzY5MDIzZDoweDc2NzQ5OWRkNDFmMmJmZWIZYPb8es9GJ0AhCvZf56Z1IMAqG1PDqWxpbmd1w6kgRGFtIEh5ZHJvbGVjdHJpYxgCIAEoAg
ICOLD (1995) Dam failures statistical analysis. Bulletin 099-1995, International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD), Paris
Issa RI (1986) Solution of the implicitly discretised fluid flow equations by operator-splitting. 62(1):40–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(86)90099-9
Issakhov A, Imanberdiyeva M (2019) Numerical simulation of the movement of water surface of dam break flow by VOF methods for various obstacles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 136:1030–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.03.034
Jandora J, Riha J (2009) The failure of embankment dams due to overtopping (Translation & review © František Aujeský & Roger Turland Cover & typography © Václav Houf) ISBN 978-80-214-3527-8
Jang DS, Jetli R, Acharya S (2007) Comparison of the piso, simpler, and simplec algorithms for the treatment of the pressure-velocity coupling in steady flow problems. Numer Heat Transf An Int J Comput Methodol 10:209–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407788608913517
L Province- AFP (2018) Actualités _ Birmanie _ plus de 50 000 personnes évacuées à cause de la rupture d’un barrage, La province
La Banque mondiale au Mali (2019). https://www.banquemondiale.org/fr/country/mali/overview
Larocque LA, Imran J, Chaudhry MH (2013) Experimental and numerical investigations of two-dimensional dam-break flows. J Hydraul Eng 139(6):569–579. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000705
Launder BE, Spalding DB (1972) Lectures in mathematical models of turbulence. London, New York, Academic Press, ISBN 0124380506
Moore D, Dore J, Gyawali D (2010) The world commission on dams + 10: revisiting the large dam controversy. Water Altern 3(2):3–13
Nagata N, Hosoda T, Nakato T, Muramoto Y (2005) Three-dimensional numerical model for flow and bed. J Hydraul Eng 131(12):1074–1087. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:12(1074)
Palmieri A, Shah F, Dinar A (2001) Economics of reservoir sedimentation and sustainable management of dams. J Environ Manage 61(2):149–163. https://doi.org/10.1006/jema.2000.0392
Patankar SV, Spalding DB (1983) A calculation procedure for heat, mass and momentum transfert in three-dimensional parabolic flows. Numer Predict Flow Heat Transf Turbul Combust. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-030937-8.50013-1
Radio-Canada R (2018) Rupture d’un barrage au Laos _ 3000 personnes à secourir _ ICI Radio-Canada. Radio-Canada
Reuters TM (2018) Un barrage cède au Kenya _ des dizaines de morts, emportés par les eaux. Ouest France with AFP
Sarkar S, Lakshmananf B (1991) Application of a reynolds stress turbulence model to the compressible shear layer. AIAA J 29(5):743–749. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.10649
Vorosmarty CJ, Meybeck M, Fekete B, Sharma K (1997) The potential impact of neo-Castorization on sediment transport by the global network of rivers. In: Human impact on erosion and sedimentation, Proceedings of the Rabat Symposium, no. 245
Vorosmarty CJ, Meybeck M, Fekete B, Sharma K, Green P, Syvitski JPM (2003) Anthropogenic sediment retention: major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob Planet Change 39:169–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8181(03)00023-7
Wisser D, Frolking S, Hagen S, Bierkens MFP (2013) Beyond peak reservoir storage? A global estimate of declining water storage capacity in large reservoirs. Water Resour Res 49:5732–5739. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrcr.20452
Wu TR, Liu PLF (2009) Numerical study on the three-dimensional dam-break bore interacting with a square cylinder. Nonlinear Wave Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812709042_0014
Yu D, Tang L, Chen C (2019) Three-dimensional numerical simulation of mud flow from a tailings dam failure across complex terrain. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-2019-298
Zhou JG, Causon DM, Mingham CG, Ingram DM (2004) Numerical prediction of dam-break flows in general geometries with complex bed topography. J Hydraul Eng 130(4):332–340. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2004)130:4(332)
Acknowledgements
The National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0601101) and the Open Fund Project for State Key Laboratory of Iron and Steel Industry Environmental Protection (No. 2016YZC04) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Shahid Hussain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drame, A.S., Zhang, Y. & Wang, L. Risk analysis of a dam rupture scenario on adjacent zones using ANSYS FLUENT: case study of Sélingué reservoir dam, Mali. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 965–978 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02885-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02885-9