Abstract
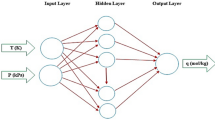
Biomass ashes are used for adsorption of herbicides from aqueous solution. A relationship between physicochemical properties of biomass ashes such as carbon–hydrogen–nitrogen content (CHN analysis), silica content and BET surface area with their adsorption capacity was established and modeled using artificial neural network. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) a commonly used herbicide is chosen a representative for this study. The artificial neural network model was trained, validated and tested using 35 data sets and was equipped with nine neuron hidden layers having tansig (tangent sigmoid) transfer function and an output layer with purelin (purely linear) transfer function. This model can be used to predict 2,4-D removal efficacy of any biomass ash by knowing its physicochemical properties like C, H, N, Si and BET surface area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi T, Abbasi SA (2010) Biomass energy and the environmental impacts associated with its production and utilization. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.11.006
Agbagla-Dohnani A, Nozière P, Gaillard-Martinie B, Puard M, Doreau M (2003) Effect of silica content on rice straw ruminal degradation. J Agric Sci 140:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859603003034
Brewer CE, Schmidt-Rohr K, Satrio JA, Brown RC (2009) Characterization of biochar from fast pyrolysis and gasification systems. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 28:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10378
Daneshvar N, Khataee AR, Djafarzadeh N (2006) The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of decolorization of textile dye solution containing C. I. Basic Yellow 28 by electrocoagulation process. J Hazard Mater 137:1788–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.042
Deokar SK, Mandavgane SA, Kulkarni BD (2016) Behaviour of biomass multicomponent ashes as adsorbents. Curr Sci 110:180–186. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v110/i2/180-186
Elgarahy AM, Elwakeel KZ, Elshoubaky GA, Mohammad SH (2019a) Untapped sepia shell-based composite for the sorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4247-1
Elgarahy AM, Elwakeel KZ, Elshoubaky GA, Mohammad SH (2019b) Microwave-accelerated sorption of cationic dyes onto green marine algal biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22704–22722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05417-2
Elwakeel KZ, Yousif AM (2010) Adsorption of malathion on thermally treated egg shell material. Water Sci Technol 61:1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.005
Elwakeel KZ, Aly MH, El-Howety MA, El-Fadaly E, Al-Said A (2018) Synthesis of chitosan@activated carbon beads with abundant amino groups for capture of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. J Polym Environ 26:3590–3602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1243-2
Heinimö J, Junginger M (2009) Production and trading of biomass for energy—an overview of the global status. Biomass Bioenergy 33:1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.05.017
International Code of Conduct on the Distribution and Use of Pesticides (2003) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/3/y4544e/y4544e00.htm
Kearns JP, Welborn LS, Summer RS, Knappe DRU (2014) 2,4-D adsorption to biochars; effect of preparation conditions on equilibrium capacity and comparison with commercial activated literature data. Water Res 60:20–28
Khataee A, Khani A (2009) Modeling of nitrate adsorption on granular activated carbon (GAC) using artificial neural network (ANN). Int J Chem React Eng. https://doi.org/10.2202/1542-6580.1870
Liese W, Zhu S, Li W, Zhang X, Wang Z (eds) (1992) The structure of bamboo in relation to its properties and utilization. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on industrial use of bamboo, Beijing, China, pp. 7–11
Lu J, Li J, Li Y, Chen B, Zao B (2012) Use of rice straw biochar simultaneously as the sustained release carrier of herbicides and soil amendment for their reduced leaching. J Agric Food Chem 60:6463–6470
Ragland K, Aerts D, Baker A (1991) Properties of wood for combustion analysis. Bioresour Technol 37:161–168
Selvam A, Nair NG, Singh P (1998) Synthesis and characterization of SiC whiskers from coconut shells. J Mater Sci Lett 17:57–60. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006597725455
Trivedi NS, Mandavgane SA (2018) Fundamentals of 2, 4 dichlorophenoxyacetic acid removal from aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Rev 47:337–354. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2018.1450765
Trivedi NS, Kharkar RA, Mandavgane SA (2016a) 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid adsorption on adsorbent prepared from groundnut shell: effect of preparation conditions on equilibrium adsorption capacity. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.07.022
Trivedi NS, Mandavgane SA, Kulkarni BD (2016b) Mustard plant ash: a source of micronutrient and an adsorbent for removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20087–20099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6202-7
Trivedi NS, Mandavgane SA, Mehetre S, Kulkarni BD (2016c) Characterization and valorization of biomass ashes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20243–20256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7227-7
Trivedi NS, Mandavgane SA, Chaurasia A (2018) Characterization and valorization of biomass char: a comparison with biomass ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3458–3467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0689-4
Trivedi NS, Trivedi NS, Kharkar RA, Mandavgane SA (2019) Use of wheat straw combustion residues for removal of chlorinated herbicide (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid). Waste Biomass Valoriz 10(5):1323–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0134-4
Turan NG, Mesci B, Ozgonenel O (2011a) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn(II) adsorption from leachate using a new biosorbent. Chem Eng J 173:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.042
Turan NG, Mesci B, Ozgonenel O (2011b) The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of adsorption of Cu(II) from industrial leachate by pumice. Chem Eng J 171:1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.005
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO, Geneva
Yakout AA, Shaker MA, Elwakeel KZ, Alshitari W (2019a) Lauryl sulfate@magnetic graphene oxide nanosorbent for fast methylene blue recovery from aqueous solutions. J Dispers Sci Technol 40:707–715. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1477604
Yakout AA, Shaker MA, Elwakeel KZ, Alshitari W (2019b) Response surface methodological optimization of batch Cu(II) sorption onto succinic acid functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles. Can J Chem 97:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjc-2018-0086
Yetilmezsoy K, Demirel S (2008) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling of Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by Antep pistachio (Pistacia Vera L.) shells. J Hazard Mater 153:1288–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.092
Acknowledgements
We thank the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), India, for providing us a research grant (Grant No. SB/S3/CE/077/2013) to undertake this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokhale, N.A., Trivedi, N.S., Mandavgane, S.A. et al. Biomass ashes as potent adsorbent for pesticide: prediction of adsorption capacity by artificial neural network. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 3209–3216 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02645-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02645-9