Abstract
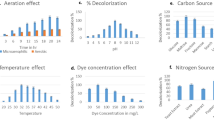
Triclosan, a commonly available pesticide, has emerged as a ubiquitous pollutant posing a major threat to the environment. Here we have isolated a wastewater microorganism, Pseudomonas aeruginosa KS2002, capable of converting triclosan to 2,4-dichlorophenol within 96 h of incubation. The confirmation of the end product was done using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and mass spectroscopy. Different minimal media were investigated to establish a suitable media supporting maximum triclosan degradation. Spectral analysis showed that this bacterial isolate degraded 99.89% ± 0.3 of 2 g/L of triclosan spiked in an M9 minimal salt medium. This isolate utilized fructose and glycerol as a co-substrate to enhance degradation process. The cell-free extract of Pseudomonas aeruginosa KS2002 showed the activity of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase enzyme (specific enzyme activity = 0.161 U/mg). In the presence of 3-fluorocatechol, a meta-cleavage enzyme inhibitor, triclosan degradation was ceased suggesting a meta-cleavage pathway for triclosan degradation. Keeping in view the observations recorded, we proposed a pathway for partial triclosan degradation using this isolate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai X, Acharya K (2017) Algae-mediated removal of selected pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from Lake Mead water. Sci Total Environ 581–582:734–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.192
Balmer ME, Poiger T, Droz C, Romanin K, Bergqvist PA, Muller MD, Buser HR (2004) Occurrence of methyl triclosan, a transformation product of the bactericide triclosan, in fish from various lakes in Switzerland. Environ Sci Technol 38:390–395. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030068p
Cherednichenko G, Zhang R, Bannister RA (2012) Triclosan impairs excitation—contraction coupling and calcium ions dynamics in striated muscle. PNAS 109:14158–14163. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211314109
Heath RJ, Rubin JR, Holland DR, Zhang E, Snow ME, Rock CO (1999) Mechanism of triclosan inhibition of bacterial fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem 274:11110–11114. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.16.11110
Heath RJ, Su N, Murphy CK, Rock CO (2000) The enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductases FabI and FabL from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 275:40128–40133. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M005611200
Holt JG, Kreig NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Hovander L, Malmberg T, Athanasiadou M, Athanassiadis I, Rahm S, Bergman A, Wehler EK (2002) Identification of hydroxylated PCB metabolites and other phenolic halogenated pollutants in human blood plasma. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010298
Hundt K, Martin D, Hammer E, Jonas U, Kindermann MK, Schauer F (2000) Transformation of triclosan by Trametes versicolor and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4157–4160. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.9.4157-4160.2000
James MO, Li W, Summerlot DP, Rowland-Faux L, Wood CE (2010) Triclosan is a potent inhibitor of estradiol and estrone sulfonation in sheep placenta. Environ Int 36:942–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.02.004
Lakshmi MVVC, Sridevi V, Neharika E, Beena CH, Rao MN, Swamy AVN (2009) Effect of temperature and carbon source on phenol degradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NCIM 2074) and Pseudomonas desmolyticum (NCIM 2028) and their comparison. Int J Chem Sci 7:2591–2601
Lee DG, Zhao F, Rezenom YH, Russell DH, Chu KH (2012) Biodegradation of triclosan by a wastewater microorganism. Water Res 46:4226–4234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.05.025
Mathew J, Joy NS, Kuppuswamy S (2017) A review on “Triclosan a controversial antibacterial”. Int J Pharm Pharm Res 8:200–216
McMurry LM, Oethinger M, Levy SB (1998) Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394:531–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/28970
Meade MJ, Waddell RL, Callahan TM (2001) Soil bacteria Pseudomonas putida and Alcaligenes xylosoxidans subsp. denitrificans inactivate triclosan in liquid and solid substrates. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:45–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10860.x
Miller TR, Heidler J, Chillrud SN, Delaquil A, Ritchie JC, Mihalic JN, Bopp R, Halden RU (2008) Fate of triclosan and evidence for reductive dechlorination of triclocarban in estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 42:4570–4576. https://doi.org/10.1021/es702882g
Mulla SI, Wang H, Sun Q, Hu Anyi YuCP (2016) Characterization of triclosan metabolism in Sphingomonas sp. strain YL-JM2C. Sci Rep 6:21965. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21965
Olaniyan LWB, Mkwetshana N, Okoh AI (2016) Triclosan in water, implications for human and environmental health. SpringerPlus 5:1639–1656. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3287-x
Orhan M (2012) Determination and characterization of triclosan on polyethylene terephthalate fibers. J Text Eng 19:27–30. https://doi.org/10.7216/130075992012198506
Schweizer HP (2001) Triclosan: a widely used biocide and its link to antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Lett 202:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10772.x
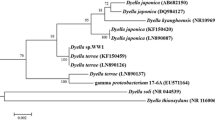
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tastan BE, Donmez G (2014) Biodegradation of pesticide triclosan by A. versicolor in simulated wastewater and semi-synthetic media. Pest Biochem Physiol 118:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.11.002
Tastan BE, Ozdemir C, Tekinay T (2016) Effects of different culture media on biodegradation of triclosan by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa and Penicillium sp. Water Sci Technol 74:473–481. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.221
Toyama T, Momotani N, Ogata Y, Miyamori Y, Inoue D, Sei K, Mori K, Kikuchi S, Ike M (2010) Isolation and characterization of 4-tert-butylphenol-utilizing Sphingobium fuliginis strains from Phragmites australis rhizosphere sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6733–6740. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00258-10
Trivedi MK, Branton A, Trivedi D, Nayak G, Singh R, Jana S (2015) Studies on physicochemical properties of biofield treated 2,4-dichlorophenol. Am J Environ Protect 4:292–299. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajep.20150406.15
Wilson BA, Salyers AA (2003) Is the evolution of bacterial pathogens an out-of-body experience? Trends Microbiol 11:347–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(03)00179-3
Zhao F (2006) Biodegradation of triclosan by a triclosan-degrading isolate and an ammonia oxidizing bacterium. Dissertation, Texas A&M University. http://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/5966
Acknowledgements
The authors are extremely thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (Scheme No. 24(0340)/16/EMR-II) for providing financial assistance for the research work. We would also like to acknowledge Department of Bio-Engineering and Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF) at Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, for providing us with the infrastructure to conduct our research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, R., Ghosh Sachan, S. Bioconversion of toxic micropollutant triclosan to 2,4-dichlorophenol using a wastewater isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa KS2002. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 7663–7672 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2129-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2129-5