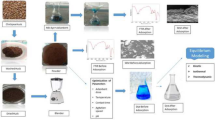
Abstract
The use of commercial adsorbents for the removal of dye from aqueous environment is expensive. Anthill could serve as alternative and cheap adsorbent in treating coloured effluents. However, this study focused on adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by anthill via batch mode process. The anthill was thermally activated at 900 °C for 2 h and then characterized using various techniques. The 2k factorial experimental design in Design Expert Software version 11 was employed for the optimization of adsorption process variables, which include initial dye concentration, contact time, adsorbent dosage and pH. Experimental data were evaluated using Langmuir and Freundlich models. The main effect analysis showed that adsorbent dosage contributes significantly to the adsorption of CR as much as 38.48%, while initial dye concentration contributes the least to the process as low as 0.00066%. The obtained data revealed that the maximum dye uptake was achieved under the optimized factor combination of adsorbent dosage of 0.5 g, contact time of 120 min, medium pH of 4 and initial CR concentration of 50 mg/L. Equilibrium adsorption isotherm and kinetic analyses revealed that Freundlich isotherm and pseudo-second-order model fitted well to the experimental data. The value of Freundlich exponent (n = 1.11) indicated that the adsorption process was favourable. The work showed that anthill material is a promising adsorbent for removing dyes from aqueous solution.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Trari M (2015) Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study on the removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto apricot stone. Process Saf Environ Prot 98:424–436
Akinwekomi AD, Omotoyinbo JA, Folorunso D (2012) Effect of high alumina cement on selected foundry properties of anthill clay. Leonardo Electron J Pract Technol 1:37–46
Alahiane S, Sennaoui A, Safr F, Qourzal S, Dinne M, Assabbane A (2017) A study of the photocatalytic degradation of the textile dye reactive yellow 17 in aqueous solution by TiO2-coated non-woven fibres in a batch photoreactor. J Mater Environ Sci 8(10):3556–3563
Arumugam A, Saravanam M (2015) Adsorption of Congo red dye from aqueous solution onto a low-cost natural orange peel and groundnut shell powder. Der Pharmacia Lettre 7(12):332–337
Aworn A, Thiravetyan P, Nakbanpote W (2008) Preparation and characteristics of agricultural waste activated carbon by physical activation having micro- and mesopores. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 82:279–285
Chiban M, Lehutu G, Sinan F, Carja G (2009) Arsenate removal by Withama frutescens plant from the south-western Morocco. Environ Eng Manag J 8:1377–1383
Fisli A, Krisnanandi YK, Gunlazuardi J (2017) Preparation and characterization of Fe2O3/SiO2/TiO2 composite for methylene blue removal in water. Int J Technol 1:76–84
Gupta OP (2008) Elements of fuels, furnaces, and refractories. Romesh Chander Khana Press, Jabalpur, pp 665–791
Hameed BH, Krishni RR, Sata SA (2009) A novel agricultural waste adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 162:305–311
Henne GA (2009) Anthill as a resource for ceramics. Published Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of fine art, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Ghana
Kamaraj R, Ganesan P, Vasudevans S (2013) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:683–692
Khaniabadi YO, Mohammadi MJ, Shegerd M, Sadeghi S, Saeedi S (2017) Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions by a low-cost adsorbent: activated carbon prepared from Aloe vera leaves shell. Environ Health Eng Manag J 4(1):29–35
Lakdioui T, Essamri A, El Harfi A (2017) Optimization study of ultrafiltration rate of a membrane based on polysulfone modified titanium dioxide on coloured water by indigo. J Mater Environ Sci 8(11):4052–4056
Leechart PW, Nakbanpote W, Thiravetyan P (2009) Application of waste wood-shaving bottom ash for adsorption of azo reactive dye. J Environ Manag 90:912–920
Lian L, Guo I, Guo C (2009) Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solutions onto Ca-bentonite. J Hazard Mater 16(1):126–131
Lim S, Lee AYW (2015) Kinetic study on removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by using soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(13):10144–10158
Mohamed Z, Abdelkarim A, Ziat K, Mohamed S (2016) Adsorption of Cu(II) onto natural clay. Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Mater Environ Sci 7(2):566–570
Mohapatra M, Khatum S, Anand S (2009) Adsorption behaviour of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) on NALCO plant sand. Indian J Chem Technol 16:291–300
Morsi MS, Al-Sarawy AA, Shehab Eldein WA (2011) Electrochemical degradation of some organic dyes by electrochemical oxidation on a Pb/PbO2 electrode. Desalination Water Treat 26:301–308
Raichur AM, Panvekar V (2002) Removal of As(V) by adsorption onto mixed rare earth oxides. Sep Sci Technol 37:1095–1108
Ran J, Wu L, He Y, Yang Z, Wang Y, Jiang C, Ge L, Bakangura E, Xu T (2017) Ion exchange membranes: new developments and application. J Membr Sci 522(15):267–291
Sahu R (2015) Removal of Congo red dye from water using orange peel as an adsorbent. B.Tech. Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India
Saleh SM, Maarof HI, Rahim SNSA, Nasuha N (2012) Adsorption of Congo red onto bottom ash. J Appl Sci 12(11):1181–1185
Sharma J, Janvega B (2008) A study on removal of Congo red dye from the effluents of textile industry using rice husk carbon activated by steam. Rasyan J Chem 1(4):936–942
Sharma V, Sumbali G (2013) An overview of the symbiotic interaction between ants, fungi and other living organisms in ant-hill soil. Int J Environ Sci 4(3):432–443
Vimonses V, Lei S, Jin B, Chow C, Saint C (2009) Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo red adsorption by clay materials. Chem Eng J 148(2–3):354–364
Wang L, Wang A (2007) Adsorption characteristics of Congo red onto the Chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite. J Hazard Mater 147(3):978–985
Yusuff AS, Olateju II, Ekanem SE (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by thermally treated quail eggshell. J Environ Sci Technol 10(5):246–257
Acknowledgments
We authors thank the head, Chemical and Petroleum Engineering Department, Afe Babalola University, Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria, for allowing us to make use of their research facilities. The authors also thank Mr. Paul Attah of the Department of Geology, University of Ibadan for the assistance he rendered in the adsorbent characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that no potential conflicts of interest exist.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Parveen Fatemeh Rupani.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusuff, A.S., Adesina, O.A. Characterization and adsorption behaviour of anthill for the removal of anionic dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 3419–3428 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1981-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1981-7