Abstract
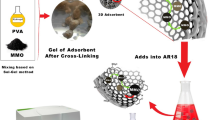
In this study, sago waste (SW) exhibited great potential in developing an efficient adsorbent in removing methylene blue (MB) from aqueous solution. Three types of adsorbents, namely, powdered SW, carboxymethyl sago pulp (CMSP) hydrogel beads and CMSP-immobilized SW hydrogel beads (CMSP-SW), were produced using SW as the precursor. The MB adsorption was investigated in a batch system to study the effects of experimental parameters of contact time, shaking speed (100–250 rpm), pH (4–10), dosage of SW (0.05–0.30 g) and initial MB concentration (50–250 mg/L). Among the adsorbents, CMSP hydrogel beads showed the lowest adsorption capacity; however, it showed capability in immobilizing SW to prevent the fungal infection and to ease the separation process. The combination of SW and CMSP has resulted in high adsorption capacity of CMSP-SW hydrogel beads for methylene blue, with Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity of 158 mg/g. Equilibrium adsorption data of CMSP-SW were observed to be fitted well into Langmuir isotherm model demonstrating adsorption process was limited to monolayer. On the other hand, the adsorption kinetics of MB onto CMSP-SW was found to be fitted well into pseudo-second order model, suggesting adsorption process was chemisorption. Based on the results obtained from the intraparticle diffusion model, CMSP-SW exhibited two-stage intraparticle diffusion. The reusability test using 50 mg/L of MB showed that the CMSP-SW could be reused up to three cycles with a total of 171 mg/g of MB being removed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida C, Debacher N, Downs A, Cottet L, Mello C (2009) Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay. J Colloid Interface Sci 332:46–53
Batzias F, Sidiras D, Schroeder E, Weber C (2009) Simulation of dye adsorption on hydrolyzed wheat straw in batch and fixed-bed systems. Chem Eng J 148:459–472
Belhouchat N, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Viseras C (2017) Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl Clay Sci 135:9–15
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment—a review. Chem Eng J 157:277–296
Bulut Y, Aydın H (2006) A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 194:259–267
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085
Chatterjee S, Chatterjee T, Lim SR, Woo, SH (2011) Adsorption of cationic dye, methylene blue, onto chitosan hydrogel beads generated by anionic surfactant gelation. J Environ Technol 32:1503–1514
Dahlan NA, Ng SL, Pushpamalar J (2017) Adsorption of methylene blue onto powdered activated carbon immobilized in a carboxymethyl sago pulp hydrogel. J Appl Polym Sci 134:44271
Doğan M, Alkan M, Onganer Y (2000) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto perlite. Water Air Soil Pollut 120:229–248
Doğan M, Alkan M, Demirbaş Ö, Özdemir Y, Özmetin C (2006) Adsorption kinetics of maxilon blue GRL onto sepiolite from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 124:89–101
Feng Y, Yang F, Wang Y, Ma L, Wu Y, Kerr PG, Yang L (2011) Basic dye adsorption onto an agro-based waste material–sesame hull (Sesamum indicum L.). Bioresour Technol 102:10280–10285
Feng Y et al (2012) Methylene blue adsorption onto swede rape straw (Brassica napus L.) modified by tartaric acid: equilibrium, kinetic and adsorption mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 125:138–144
Hebeish A, Higazy A, El-Shafei A, Sharaf S (2010) Synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and starch-based hybrids and their applications in flocculation and sizing. Carbohydr Polym 79:60–69
Ho Y-S (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689
Jung K-W, Choi BH, Hwang M-J, Jeong T-U, Ahn K-H (2016) Fabrication of granular activated carbons derived from spent coffee grounds by entrapment in calcium alginate beads for adsorption of acid orange 7 and methylene blue. Bioresour Technol 219:185–195
Karthika C, Vennilamani N, Pattabhi S, Sekar M (2010) Utilization of sago waste as an adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution: kinetic and isotherm studies. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2:1867–1879
Kavitha D, Namasivayam C (2007) Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour Technol 98:14–21
Khanday WA, Asif M, Hameed BH (2017) Cross-linked beads of activated oil palm ash zeolited/chitosan composite as a bio-adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue and acid blue 29 dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 95:895–902
Lai JC, Rahman WAWA, Toh WY (2013) Characterisation of sago pith waste and its composites. Ind Crops Prod 45:319–326
Liu QS, Zheng T, Wang P, Jiang JP, Li N (2010) Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers. Chem Eng J 157:348–356
Pathania D, Sharma S, Singh P (2013) Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arab J Chem 10:S1445–S1451
Pavan FA, Lima EC, Dias SL, Mazzocato AC (2008) Methylene blue biosorption from aqueous solutions by yellow passion fruit waste. J Hazard Mater 150:703–712
Peng Q, Liu M, Zheng J, Zhou C (2015) Adsorption of dyes in aqueous solutions by chitosan–halloysite nanotubes composite hydrogel beads. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 201:190–201
Pushpamalar V, Langford S, Ahmad M, Lim Y (2006) Optimization of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from sago waste. Carbohydr Polym 64:312–318
Sahraei R, Pour ZS, Ghaemy M (2017) Novel magnetic bio-sorbent hydrogel beads based on modified gum tragacanth/graphene oxide: removal of heavy metals and dyes from water. J Clean Prod 142:2973–2984
Salama A (2017) New sustainable hybrid material as adsorbent for dye removal from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 487:348–353
Sugama T, Pyatina T (2015) Effect of sodium carboxymethyl celluloses on water-catalyzed self-degradation of 200 °C-heated alkali-activated cement. Cem Concr Compos 55:281–289
Tan I, Ahmad A, Hameed B (2008) Adsorption of basic dye using activated carbon prepared from oil palm shell: batch and fixed bed studies. Desalination 225:13–28
Vadivelan V, Kumar KV (2005) Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J Colloid Interface Sci 286:90–100
Vučurović VM, Razmovski RN, Tekić MN (2012) Methylene blue (cationic dye) adsorption onto sugar beet pulp: equilibrium isotherm and kinetic studies. J Taiwan Chem Eng 43:108–111
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Zendehdel M, Barati A, Alikhani H, Hekmat A (2010) Removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater by adsorption onto semi-inpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of acrylamide and acrylic acid copolymer and polyvinyl alcohol. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 7:431–436
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from School of Science, Monash University Malaysia [Grant Number BCHH-SS-3-01-2012] and Universiti Sains Malaysia [Grant Number 304/PKIMIA/6313275] are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahlan, N.A., Lee, L., Pushpamalar, J. et al. Adsorption of methylene blue onto carboxymethyl sago pulp-immobilized sago waste hydrogel beads. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 2047–2058 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1789-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1789-5