Abstract
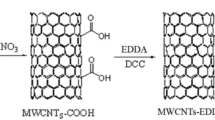
A nanosorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction was fabricated by functionalizing multiwalled carbon nanotubes with sulfosalicylic acid after oxidation and thiolation followed by decoration with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Incorporation of hydrophilic carboxylic and sulfonic acid groups introduces coordinating ability and accessibility for cadmium and lead, resulting in high sorption capacity of 217.39 and 454.54 mg g−1, respectively. Decoration by magnetic nanoparticles enhances its dispersibility and facilitates the separation of solid phase without tedious centrifugation or filtration processes, which is the exclusive objective of dispersive solid-phase extraction. The functionalized sorbent was characterized by FT-IR, SEM and TEM. The uniform and monolayer sorption behavior of the sorbent was proved by an evident fit of the equilibrium data to Langmuir isotherm model. The analytical method developed after optimizing the experimental variables such as solution pH, sorption time, amount of sorbent, desorption condition for preconcentration and separation enables the use of an economically viable less sensitive AAS for trace determination due to the improved detection limit of 0.13 and 1.21 µg L−1 for cadmium and lead, respectively. Commonly occurring concomitant ions in the real samples was not found to interfere in the trace determination of analyte. The good precision was assessed by the determined average day-to-day coefficient of variation of 3.02% for cadmium and 2.29% for lead. The accuracy and applicability of the present method for sequential cadmium and lead determination are substantiated by the analysis of Standard Reference Material and environmental water samples from electroplating industries, river water and tap water.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvand M, Shemirani F (2014) Preconcentration of trace cadmium ion using magnetic graphene nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent. Microchimica Acta 181(1–2):181–188
Al-Shalalfeh MM, Saleh TA, Al-Saadi AA (2016) Silver colloid and film substrates in surface-enhanced Raman scattering for 2-thiouracil detection. RSC Adv 6(79):75282–75292
Cheng X, Kan AT, Tomson MB (2005) Uptake and sequestration of Naphthalene and 1,2-Dichlorobenzene by C60. J Nanopart Res 7(4–5):555–567
Chen L, Wang T, Tong J (2011) Application of derivatized magnetic materials to the separation and the preconcentration of pollutants in water samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30(7):1095–1108
Cui Y, Liu S, Hu Z-J, Liu X-H, Gao H-W (2011) Solid-phase extraction of lead(II) ions using multiwalled carbon nanotubes grafted with tris(2-aminoethyl)amine. Microchimica Acta 174(1–2):107–113
Danmaliki GI, Saleh TA (2017) Effects of bimetallic Fe−Ce nanoparticles on the desulfurization of thiophenes using activated carbon. Chem Eng J 307(1):914–927
Dastgheib SA, Rockstraw DA (2002) A model for the adsorption of single metal ion solutes in aqueous solution on to activated carbon produced from pecan shells. Carbon 40(11):1843–1852
Ding Z, Hu X, Wan Y, Wang S, Gao B (2016) Removal of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel from aqueous solutions by alkali-modified biochar: Batch and column tests. Journal of Ind Eng Chem 33:239–245
Drago RS (1965) Physical Methods in Inorganic Chemistry. Litton Education Publishing Inc, New York
Haruna K, Saleh TA, Hossain MK, Al-Saadi AA (2016) Hydroxylamine reduced silver colloid for naphthalene and phenanthrene detection using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Eng J 304:141–148
Islam A, Kumar S (2016) Glycidylmethacrylate based resin functionalized with graphene oxide for column preconcentration and trace determination of Cd(II) and Ni(II) in environmental and food samples. RSC Adv 6:77629–77635
Islam A, Laskar MA, Ahmad A (2010a) Characterization of a novel chelating resin of enhanced hydrophilicity and its analytical utility for preconcentration of trace metal ions. Talanta 81(4–5):1772–1780
Islam A, Laskar MA, Ahmad A (2010b) Characterization and application of 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol functionalized amberlite XAD-4 for preconcentration of trace metal ions in real matrices. J Chem Eng Data 55(12):5553–5561
Islam A, Ahmad A, Laskar MA (2012) Characterization of a chelating resin functionalized via azo spacer and its analytical applicability for the determination of trace metal ions in real matrices. J Appl Polym Sci 123(6):3448–3458
Islam A, Laskar MA, Ahmad A (2013a) Preconcentration of metal ions through chelation on a synthesized resin containing O, O donor atoms for quantitative analysis of environmental and biological samples. Environ Monit Assess 185(3):2691–2704
Islam A, Ahmad H, Zaidi N, Yadav S (2013b) Selective separation of aluminum from biological and environmental samples using glyoxalbis(2-hydroxyanil) functionalized amberlite XAD-16 resin: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(14):5213–5220
Islam A, Zaidi N, Ahmad H, Yadav S (2014a) Synthesis, characterization, and systematic studies of a novel aluminum selective chelating resin. Environ Monit Assess 186(9):5843–5853
Islam A, Ahmad H, Zaidi N, Kumar S (2014b) Graphene oxide sheets immobilized polystyrene for column preconcentration and sensitive determination of lead by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6(15):13257–13265
Islam A, Zaidi N, Ahmad H, Kumar S (2015a) Efficacy of dihydroxy-mercaptopyrimidine functionalized polymeric resin for the trace determination of Cd by SPE coupled flame atomic absorption spectrometry. RSC Adv 5:46662–46671
Islam A, Zaidi N, Ahmad H, Kumar S (2015b) Amine-functionalized mesoporous polymer as potential sorbent for nickel preconcentration from electroplating wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(10):7716–7725
Islam A, Ahmad A, Laskar MA (2015c) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of trace metal ions in environmental and biological samples after preconcentration on a newly developed amberlite XAD-16 chelating resin containing p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid. J AOAC Int 98(1):165–175
Islam A, Ahmad H, Zaidi N, Kumar S (2016a) Graphene oxide decorated with triethylenetetramine-modified magnetite for separation of chromium species prior to their sequential speciation and determination via FAAS. Microchim Acta 183(1):289–296
Islam A, Ahmad H, Zaidi N, Kumar S (2016b) Copper selective self-sorting polymeric resin with mixed-mode functionality for column preconcentration and atomic absorption spectrometric determination. RSC Adv 6:5590–5598
Islam A, Kumar S, Zaidi N, Ahmad H (2016c) SPE coupled to AAS trace determination of Cd(II) and Zn(II) in food samples using amine functionalized GMA-MMA-EGDMA terpolymer: isotherm and kinetic studies. Food Chem 213:775–783
Kocot K, Zawisza B, Margu E, Queralt I, Hidalgo M, Sitko R (2013) Dispersive micro solid-phase extraction using multiwalled carbon nanotubes combined with portable total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for the determination of trace amounts of Pb and Cd in water samples. J Anal At Spectrom 28(5):736–742
Latorre CH, Mendez JA, Garcia JB, Martin SG, Pena-Crecente RM (2012) Carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction sorbents prior to atomic spectrometric determination of metal species: a review. Anal Chim Acta 749:16–35
Li J, He W, Yang L, Sun X, Hua Q (2007) Preparation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes grafted with synthetic poly(l-lysine) through surface-initiated ring-opening polymerization. Polymer 48(15):4352–4360
Li R, Chang X, Li Z, Zang Z, Hu Z, Li D, Tu Z (2011) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with 2-aminobenzothiazole modified for uniquely selective solid-phase extraction and determination of Pb(II) ion in water samples. Microchim Acta 172(3–4):269–276
Liang P, Liu Y, Guo L, Zeng J, Lu H (2004) Multiwalled carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the preconcentration of trace metal ions and their determination by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 19:1489–1492
Pena-Pereira F, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2010) Liquid-phase microextraction approaches combined with atomic detection: a critical review. Anal Chim Acta 669(1–2):1–16
Pyrzynska K (2010) Carbon nanostructures for separation, preconcentration and speciation of metal ions. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 29(7):718–727
Ramandi NF, Shemirani F (2015) Selective ionic liquid ferrofluid based dispersive-solid phase extraction for simultaneous preconcentration/separation of lead and cadmium in milk and biological samples. Talanta 131:404–411
Ramandi NF, Shemirani F, Farahani MD (2014) Dispersive solid phase extraction of lead(II) using a silica nanoparticle-based ionic liquid ferrofluid. Microchim Acta 181(15–16):1833–1841
Safarikova M, Safarik I (1999) Magnetic solid phase extraction. J Magn Magn Mater 194(1–3):108–112
Sahmetlioglu E, Yilmaz E, Aktas E, Soylak M (2014) Polypyrrole/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite for the solid phase extraction of lead(II) in water samples. Talanta 119:447–451
Saleh TA (2015) Mercury sorption by silica/carbon nanotubes and silica/activated carbon: a comparison study. J Water Supply Res Technol-AQUA 64(8):892–903
Saleh TA (2016) Nanocomposite of carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles and their use for adsorption of Pb(II): from surface properties to sorption mechanism. Desalin Water Treat 57(23):10730–10744
Saleh TA, Danmaliki GI (2016) Adsorptive desulfurization of dibenzothiophene from fuels by rubber tyres-derived carbons: kinetics and isotherms evaluation. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:9–19
Saleh TA, Sarı A, Tuzen M (2017a) Effective adsorption of antimony(III) from aqueous solutions by polyamide graphene composite as a novel adsorbent. Chem Eng J 307:230–238
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017b) Magnetic activated carbon loaded with tungsten oxide nanoparticles for aluminum removal from waters. J Environ Chem Eng 5(3):2853–2860
Saleh TA, Tuzen NM, Sarı A (2017c) Polyethylenimine modified activated carbon as novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of uranium from aqueous solution. Chem Eng Res Des 117:218–227
Savio M, Parodi B, Martinez LD, Smichowski P, Gil RA (2011) On-line solid phase extraction of Ni and Pb using carbon nanotubes and modified carbon nanotubes coupled to ETAAS. Talanta 85(1):245–251
Sigel A, Sigel H, Sigel RKO (2011) Metal Ions in Life Sciences. R Soc Chem, Cambridge
Sitko R, Gliwinska B, Zawisza B, Feist B (2013) Ultrasound-assisted solid-phase extraction using multiwalled carbon nanotubes for determination of cadmium by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 28(3):405–410
Smith G, Wermuth UD, Young DJ, White JM (2007) Polymeric structures in the metal complexes of 5-sulfosalicylic acid: the rubidium(I), caesium(I) and lead(II) analogues. Polyhedron 26(14):3645–3652
Taghizadeh M, Akbar A, Asgharinezhad Samkhaniany N, Tadjarodi A, Abbaszadeh A, Pooladi M (2014) Solid phase extraction of heavy metal ions based on a novel functionalized magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube composite with the aid of experimental design methodology. Microchim Acta 181(5–6):597–605
Vicentini FC, Silva TA, Pellatieri A, Janegitz BC, Fatibello-Filho O, Censi R (2014) Pb(II) determination in natural water using a carbon nanotubes paste electrode modified with crosslinked chitosan. Microchem J 116:191–196
Watson JS (1999) Separation methods for waste and environmental applications. Marcel Dekker, New York
U.S. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry Website. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/
Zawisza B, Skorek R, Stankiewicz G, Sitko R (2012) Carbon nanotubes as a solid sorbent for the preconcentration of Cr, Mn, Fe Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and Pb prior to wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Talanta 99:918–923
Zhang J, Zou H, Qing Q, Yang Y, Li Q, Liu Z, Guo X, Du X (2003) Effect of chemical oxidation on the structure of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 107(16):3712–3718
Zheng H, Jia B, Zhu Z, Tang Z, Hu S (2014) Determination of trace amounts of Pb, Cd, Ni and Co by wavelength-dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometry after preconcentration with dithizone functionalized graphene. Anal Methods 6(21):8569–8576
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to the University Grant Commission India for providing research fellowship to Noushi Zaidi (UGC-SRF D-658/MA) and Hilal Ahmad (UGC-BSR D-752/MR). The authors acknowledge the support provided by UGC-SAP program and DST (FIST & PURSE), New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, A., Zaidi, N., Ahmad, H. et al. Functionalized carbon nanotubes for dispersive solid-phase extraction and atomic absorption spectroscopic determination of toxic metals ions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 707–718 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1700-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1700-4