Abstract
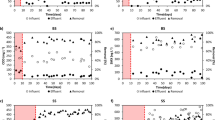
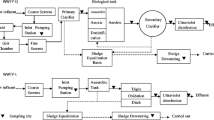
Antibiotic contamination of aqueous environment due to pharmaceutical sewage may lead to development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria strain. In this research, elimination of antibiotics from synthetic wastewater was investigated. For this purpose, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim were treated by a pilot scale of net-like rotating biological contactor with three compartments, 48 plastic discs with total volume of 78.75 L. This system was continuously operated for about one year at various organic loading rates with different antibiotic dosages. The obtained results indicated that by increasing hydraulic retention time, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal was gradually increased. The optimal hydraulic retention time for desired rate of COD removal was 36 h. In addition, the effect of hydraulic retention time, organic load rate and sulfamethoxazole concentration in the removal of sulfamethoxazole and organic matter was assessed. Moreover, the results demonstrated that with increasing in organic load rate, sulfamethoxazole elimination was enhanced. In the next step, simultaneous removal of both antibiotics for constant inlet COD concentration of 8000 mg/L at optimum hydraulic retention time was analysed. The results showed that trimethoprim removal efficiency was approximately 100%, even at high concentration of trimethoprim (50 mg/L). For observation of dominant microorganism, samples of the developed biofilm on rotating biological contactor discs were scanned by scanning electron microscopy. In the first compartment where biomass was exposed to highest concentration of antibiotics, fungus strains were the dominant organism. In the second and third compartment antibiotic-resistant bacteria were the dominant attached living organisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdessemed D, Nezzal G, Aim RB (1999) Treatment of wastewater by ultrafiltration. Desalination 126(1):1–5
Andrade LS, Rocha-Filho RC, Cass QB, Fatibello-Filho O (2009) Simultaneous differential pulse voltammetric determination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electroanalysis 21(13):1475–1480
Bitton G (2005) Wastewater microbiology. Wiley, New Jersey
Bouhabila EH, Aïm RB, Buisson H (1998) Microfiltration of activated sludge using submerged membrane with air bubbling (application to wastewater treatment). Desalination 118(1):315–322
Brown KD, Kulis J, Thomson B, Chapman TH, Mawhinney DB (2006) Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy effluent, municipal wastewater, and the Rio Grande in New Mexico. Sci Total Environ 366(2–3):772–783
Can MY, Kaya Y, Algur OF (2006) Response surface optimization of the removal of nickel from aqueous solution by cone biomass of Pinus sylvestris. Bioresour Technol 97(14):1761–1765
Castillo E, Vergara M, Moreno Y (2007) Landfill leachate treatment using a rotating biological contactor and an upward-flow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Waste Manage 27(5):720–726
Costley S, Wallis F (2001) Bioremediation of heavy metals in a synthetic wastewater using a rotating biological contactor. Water Res 35(15):3715–3723
Dantas RF, Contreras S, Sans C, Esplugas S (2008) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by means of ozonation. J Hazard Mater 150(3):790–794
Deegan A, Shaik B, Nolan K, Urell K, Oelgemöller M, Tobin J, Morrissey A (2011) Treatment options for wastewater effluents from pharmaceutical companies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(3):649–666
Drillia P, Dokianakis S, Fountoulakis M, Kornaros M, Stamatelatou K, Lyberatos G (2005) On the occasional biodegradation of pharmaceuticals in the activated sludge process: the example of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole. J Hazard Mater 122(3):259–265
Ebrahimi A, Najafpour GD, Mohammadi M, Hashemiyeh B (2010) Biological treatment of whey in an UASFF bioreactor following a three-stage RBC. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 16(2):175–182
Fukahori S, Fujiwara T (2014) Modeling of sulfonamide antibiotic removal by TiO2/high-silica zeolite HSZ-385 composite. J Hazard Mater 272:1–9
Gadipelly C, Pérez-González A, Yadav GD, Ortiz I, Ibáñez R, Rathod VK, Marathe KV (2014) Pharmaceutical industry wastewater: review of the technologies for water treatment and reuse. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(29):11571–11592
Gangcuangco LM, Alejandria M, Henson KE, Alfaraz L, Ata RM, Lopez M, Saniel M (2015) Prevalence and risk factors for trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole-resistant Escherichia coli among women with acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in a developing country. Int J Infec Dis 34:55–60
Godfrey E, Woessner WW, Benotti MJ (2007) Pharmaceuticals in on-site sewage effluent and ground water, Western Montana. Ground Water 45(3):263–271
González O, Sans C, Esplugas S (2007) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by photo-Fenton: toxicity, inhibition and biodegradability assessment of intermediates. J Hazard Mater 146(3):459–464
Hiras DN, Manariotis ID, Grigoropoulos SG (2004) Organic and nitrogen removal in a two-stage rotating biological contactor treating municipal wastewater. Bioresour Technol 93(1):91–98
Hoa PTP, Managaki S, Nakada N, Takada H, Shimizu A, Anh DH, Viet PH, Suzuki S (2011) Antibiotic contamination and occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquatic environments of northern Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 409(15):2894–2901
Jessick AM (2010) Detection, fate, and bioavailability of erythromycin in environmental matrices. Dissertation, Iowa State University
Khademi M, Najafpour G, Nia BN, Zinatizadeh A, Kalantary RR (2009) Biological treatment of antibiotic plant effluent in an UASFF bioreactor. World Appl Sci J 5:1–8
Kümmerer K (2001) Drugs in the environment: emission of drugs, diagnostic aids and disinfectants into wastewater by hospitals in relation to other sources—a review. Chemosphere 45(6):957–969
Middleton JH, Salierno JD (2013) Antibiotic resistance in triclosan tolerant fecal coliforms isolated from surface waters near wastewater treatment plant outflows (Morris County, NJ, USA). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:79–88
Müller E, Schüssler W, Horn H, Lemmer H (2013) Aerobic biodegradation of the sulfonamide antibiotic sulfamethoxazole by activated sludge applied as co-substrate and sole carbon and nitrogen source. Chemosphere 92(8):969–978
Najafpour GD (2015) Biochemical engineering and biotechnology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Najafpour G, Yieng HA, Younesi H, Zinatizadeh A (2005) Effect of organic loading on performance of rotating biological contactors using palm oil mill effluents. Process Biochem 40(8):2879–2884
Pruden A, Pei R, Storteboom H, Carlson KH (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 40(23):7445–7450
Renew JE, Huang C-H (2004) Simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolone, sulfonamide, and trimethoprim antibiotics in wastewater using tandem solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography–electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1042(1):113–121
Ryan CC, Tan DT, Arnold WA (2011) Direct and indirect photolysis of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in wastewater treatment plant effluent. Water Res 45(3):1280–1286
Sahinkaya E, Dilek FB (2006) Biodegradation of 4-CP and 2,4-DCP mixture in a rotating biological contactor (RBC). Biochem Eng J 31(2):141–147
Shon H, Phuntsho S, Chaudhary D, Vigneswaran S, Cho J (2013) Nanofiltration for water and wastewater treatment—a mini review. Drink Water Eng Sci 6(1):47–53
Siegrist H, Reithaar S, Koch G, Lais P (1998) Nitrogen loss in a nitrifying rotating contactor treating ammonium-rich wastewater without organic carbon. Water Sci Technol 38(8–9):241–248
Talalaj I (2015) Removal of organic and inorganic compounds from landfill leachate using reverse osmosis. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(9):2791–2800
Tan A, Xiao M, Cui X, Chen X, Chen Y, Fang D, Fu C, Giboni K, Giuliani F, Gon H (2016) Dark matter results from first 98.7 days of data from the PandaX-II experiment. Phys Rev Lett 117(12):121303
Thurman E, Hostetler K (1999) Analysis of tetracycline and sulfamethazine antibiotics in groundwater and animal-feedlot wastewater by highperformance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry using positive-ion electrospray. US Geological Survey, Lawrence
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35(17):3397–3406
Wei R, Ge F, Chen M, Wang R (2012) Occurrence of ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and florfenicol in animal wastewater and water resources. J Environ Qual 41(5):1481–1486
Won SY, Lee CH, Chang HS, Kim SO, Lee SH, Kim DS (2011) Monitoring of 14 sulfonamide antibiotic residues in marine products using HPLC-PDA and LC-MS/MS. Food Control 22(7):1101–1107
Yang SF, Lin CF, Lin AYC, Hong PKA (2011) Sorption and biodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics by activated sludge: experimental assessment using batch data obtained under aerobic conditions. Water Res 45(11):3389–3397
Acknowledgements
Authors are gratefully acknowledged Biotechnology Research Lab. Babol Noushirvani University of Technology (Babol, Iran) for the support and facilities provided to conduct present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Binbin Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azimi, N., Najafpour, G.D., Hassani, A.H. et al. Simultaneous sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim removal and biofilm growth characteristics in attached growth bioreactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 415–426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1390-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1390-3