Abstract
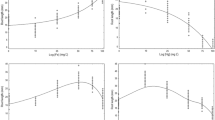
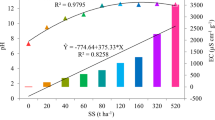
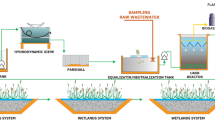
Sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) has increased in recent years in Spain and Europe in general. Agriculture seems a viable solution when seeking alternatives for its final disposal. Sewage sludge reuse can, however, pose risks given presence of heavy metals, pathogen microorganisms or toxic compounds, which must be controlled to minimize risks for human health and the environment. In the present study, the phytotoxicity of sewage sludge from the Alcázar de San Juan WWTP using two types of seeds (Lactuca sativa L. and Lepidium sativum L.) in bioassays was analyzed. The relative germination rates (RGP), relative radicle growth (RRG) and germination index were determined for both species. Hypocotyl length was measured in lettuce. Negative (distilled water) and positive (zinc sulfate) controls were prepared. Depending on the biological material and residue phytotoxicity dose, analyses can be modified given the different sensitivities of plants. Lepidium sativum L. was more sensitive to phytotoxic compounds than Lactuca sativa L. Hypocotyl measurements provide complementary toxicity information. A general agreement between authors and researchers to standardize this type of analysis would be useful to make criteria uniform.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguerre YS, Gavazzo GB (2012) Fitotoxicidad de papel reciclado. Ensayospreliminares. In: Proceedings of the ABTCP 2012 + VII CIADICYP.The 45th ABTCP international pulp and paper congress and VII Ibero American Congress on Pulp and Paper Research
Bettiol C, De Vettori S, Minervini G, Zuccon E, Marchetto D, Volpi AG, Argese E (2016) Assessment of phenolic herbicide toxicity and mode of action by different assays. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7398–7408
Celis J, Sandoval M, Zagal E, Briones M (2006) Effect of sewage sludge and salmon wastes applied to a Patagonian soil on lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.) germination. J. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 6(3):13–25
Cuevas MC, Espinosa G, Ilizaliturri CA, Mendoza A (2012) Métodos ecotoxicológicos para la evaluación de suelos contaminados con hidrocarburos.Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales Blvd. Adolfo Ruiz Cortines 4209. Col. Jardínes en la Montaña C.P. 14210. Delegación Tlalpan, México, D.FInstituto Nacional de Ecología (INE-Semarnat) Periférico Sur 5000. Col. Insurgentes Cuicuilco C.P. 04530. Delegación Coyoacán, México, D.F. www.ine.gob.mx, ISBN: 978-607-7908-62-3
D’Abrosca B, Fiorentino A, Izzo A, Cefarelli G, Pascarella MT, Uzzo P, Monaco P (2008) Phytotoxicity evaluation of five pharmaceutical pollutants detected in surface water on germination and growth of cultivated and spontaneous plants. J Environ Sci Health A 43:285–294
Gheorghe S, Vasile GG, Stoica C, Lazar MN, Lucaciu I, Banciu A (2013) Phytotoxicity tests applied on sewage sludge resulted from urban wastewater treatment plants. Rev Chim-Buchar 67(8):1469–1473
Jurado MM, Suarez-Estrella F, Vargas-García MC, Lopez MJ, Lopez-Gonzalez JA, Moreno J (2014) Evolution of enzymatic activities and carbon fractions throughout composting of plant waste. J Environ Manag 133:355–364
Kalai T, Khamassi K, Teixeira da Silva JA, Gouia H, Ben-Kaab LB (2014) Cadmium and copper stress affect seedling growth and enzymatic activities in germinating barley seeds. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60:765–783
Lencioni G, Imperiale D, Cavirani N, Marmiroli N, Marimiroli M (2016) Environmental application and phytotoxicity of anaerobic digestate from pig farming by in vitro and in vivo trials. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2549–2560
Mendes PM, Becker R, Corrêa LB, Bianchi I, Dai Prá MA, Lucia T Jr, Corrêa EK (2016) Phytotoxicity as an indicator of stability of broiler production residues. J Environ Manag 167:156–159
OECD (2006) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, updating guideline 208-terrestrial plants test: seedling emergence and seedling growth test. http://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/testing/oecdguidelinesforthetestingofchemicals.htm. Accessed 17 Sept 2017
Phoungthong K, Zhang H, Shao LM, He PJ (2016) Variation of the phytotoxicity of municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seed germination with leaching conditions. Chemosphere 146:547–554
Radetski CM, Ferrari B, Cotelle S, Masfaraud JF, Ferard JF (2004) Evaluation of the genotoxic, mutagenic and oxidant stress potentials of municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash leachates. Sci Total Environ 333:209–216
R.D. 1310/1990, de 29 de octubre, por el que se regula la utilización de los lodos de depuración en el sector agrario. BOE num 262, 1 November 1990
Rede D, Santos Lúcia HMLM, Ramos S, Oliva-Teles F, Antão C, Sousa SR, Delerue-Matos C (2016) Ecotoxicological impacta of twosoilremediatontreatments in Lactuca sativaseeds. Chemosphere 159:193–198
Sobrero MC, Ronco A (2004) Ensayo de toxicidad aguda con semillas de lechuga (Lactuca sativa L.). En: Castillo, G (ed) Ensayos Toxicológicos y Métodos de Evaluación de Calidad de Aguas, Ottawa, Canadá, pp 71–79
Tiquia SM (2000) Evaluating phytotoxicity of pig manure from the pig on litter system. In: Warman PR, Taylor BR (ed) Proceedings of the international composting symposium. CBA Press Inc. Truro, NS, pp 625–647
Tiquia SM (2010) Reduction of compost phytotoxicity during the process of decomposition. Chemosphere 79:506–512
Varnero MT, Rojas C, Orellana R (2007) Phytotoxicity indices of organic residues during composting. J Soil Sci Nutr 7(1):28–37
Zucconi F, Pera A, Forte M, De Bertoldi M (1981) Evaluating toxicity of immature compost. Biocycle 22:54–57
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the municipally owned company “Aguas de Alcázar” and the Alcázar de San Juan Town Hall for their financial support through Project: “Aptitud para uso agrícoladel agua y lodos procedentes de la depuradora de aguas residuales de Alcázar de San Juan.” We also thank Helen Warburton for reviewing the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with their research or preferential activities.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mañas, P., De las Heras, J. Phytotoxicity test applied to sewage sludge using Lactuca sativa L. and Lepidium sativum L. seeds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 273–280 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1386-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1386-z