Abstract
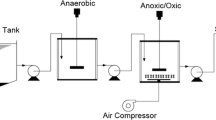
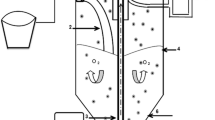
Septic tanks are very commonly used wastewater collection systems throughout the world, and especially in rural areas. In this study, the use of moving-bed biological reactors (MBBR) for the treatment of septic tank effluent (STE) was examined. The study was conducted in two phases. In Phase I, the performance of septic tanks from four projects working under different operational conditions and with different service lives was followed to determine the parameters that required further treatment. In Phase II, four specially designed continuous flow pilot-plant MBBRs and one laboratory-scale batch reactor were tested for their efficiency in treating STE. Experiments were carried out at various temperatures (8–25 °C) and with different hydraulic retention times (HRTs). MBBR effectively reduced STE’s nutrients and chemical oxygen demand by 90 and 85 %, respectively, over 180 days of operation. The average ammonia removal rate at 25 °C increased from 0.279 to 0.540 kg N/m3 when the reactor HRT changed from 5.7 to 13.3 h. Under these conditions, the ammonia removal kinetics were successfully correlated with a theta model with an average θ value of 1.054. The biofilm morphology showed a stable and global biomass coverage (>70 %) and a high percentage of live cells. A thinner biofilm was observed when the MBBR operated at high temperatures. The results of this study showed that MBBR is a promising technology for post-treatment of septic tank effluent.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi E, Gholami M, Farzadkia M, Nabizadeh R, Azari A (2015) Study of moving bed biofilm reactor in diethyl phthalate and diallyl phthalate removal from synthetic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 183:129–135
Almomani FA, Delatolla R, Ormeci B (2014) Field study of moving bed biofilm reactor technology for post-treatment of wastewater lagoon effluent at 1°C. Environ Technol 35(13):1596–1604
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation (APHA, AWWA, WEF) (eds) (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 19th edn. APHA, Washington, DC
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48(5):835–852
Blackburne R, Vadivelu VM, Yuan Z, Keller JR (2007) Kinetic characterisation of an enriched Nitrospira culture with comparison to Nitrobacter. Water Res 41(14):3033–3042
Chu W, Gao N, Deng Y, Templeton MR, Yin D (2011) Impacts of drinking water pretreatments on the formation of nitrogenous disinfection by-products. Bioresour Technol 102(24):11161–11166
Delatolla R, Tufenkji N, Comeau Y, Gadbois A, Lamarre D, Berk D (2010) Investigation of laboratory-scale and pilot-scale attached growth ammonia removal kinetics at cold temperature and low influent carbon. Water Qual Res J Can 45(4):427–436
Di Trapani D, Di Bella G, Mannina G, Torregrossa M, Viviani G (2015) Effect of C/N shock variation on the performances of a moving bed membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 189:250–257
Diak J, Ormeci B, Kennedy KJ (2012) Effect of enzymes on anaerobic digestion of primary sludge and septic tank performance. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35(9):1577–1589
Diak J, Ormeci B, Kennedy KJ (2013) Effect of micro-aeration on anaerobic digestion of primary sludge under septic tank conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36(4):417–424
Hao X, Heijnen JJ, Van Loosdrecht MCM (2002) Model-based evaluation of temperature and inflow variations on a partial nitrification—ANAMMOX biofilm process. Water Res 36(19):4839–4849
Hoang V, Delatolla R, Abujamel T, Mottawea W, Gadbois A, Laflamme E, Stintzi A (2014) Nitrifying moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) biofilm and biomass response to long term exposure to 1°C. Water Res 49:215–224
Houweling DW, Monette F, Millette L, Comeau Y (2007) Modelling nitrification of a lagoon effluent in moving-bed bioiflm reactors. Water Qual Res J Can 42(4):284–294
Jantrania AR, Gross MA (2006) Advanced onsite wastewater systems technologies. CRC Press, Boca Raton. ISBN 0-8493-3029-7
Karizmeh MS, Delatolla R, Narbaitz RM (2014) Investigation of settleability of biologically produced solids and biofilm morphology in moving bed bioreactors (MBBRs). Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37(9):1839–1848
Lazarova V, Bellahcen D, Manem J, Stahl DA, Rittmann BE (1999) Influence of operating conditions on population dynamics in nitrifying biofilms. Water Sci Technol 39(7):5–11
Li X-Y, Chu HP (2003) Membrane bioreactor for the drinking water treatment of polluted surface water supplies. Water Res 37(19):4781–4791
Lin Y-H (2008) Kinetics of nitrogen and carbon removal in a moving-fixed bed biofilm reactor. Appl Math Model 32(11):2360–2377
Liu H, Yang C, Pu W, Zhang J (2008) Removal of nitrogen from wastewater for reusing to boiler feed-water by an anaerobic/aerobic/membrane bioreactor. Chem Eng J 140(1–3):122–129
Luostarinen S, Luste S, Valentin L, Rintala J (2006) Nitrogen removal from on-site treated anaerobic effluents using intermittently aerated moving bed biofilm reactors at low temperatures. Water Res 40(8):1607–1615
Meuler S, Paris S, Hackner T (2008) Membrane bio-reactors for decentralized wastewater treatment and reuse. Water Sci Technol 58(2):285–294
Ødegaard H, Rusten B, Westrum T (1994) A new moving bed biofilm reactor-applications and results. Water Sci Technol 29:157–165
Oh JH, Park J, Ellis TG (2014) Septic wastewater treatment using recycled rubber particles as biofiltration media. Environ Technol 35(5):637–644
Persson F, Wik T, Sorensson F, Hermansson M (2002) Distribution and activity of ammonia oxidizing bacteria in a large full-scale trickling filter. Water Res 36(6):1439–1448
Richards S, Paterson E, Withers PJA, Stutter M (2016) Septic tank discharges as multi-pollutant hotspots in catchments. Science Total Environ-A 542:854–863
Rodgers M, Zhan X-M (2004) Biological nitrogen removal using a vertically moving biofilm system. Bioresour Technol 93(3):313–319
Rusten B, Siljudalen JG, Nordeidet B (1994) Upgrading to nitrogen removal with the KMT moving bed biofilm process. Water Sci Technol 29(12):185–195
Sabry T (2010) Evaluation of decentralized treatment of sewage employing Upflow Septic Tank/Baffled Reactor (USBR) in developing countries. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):500–505
Salvetti R, Azzellino A, Canziani R, Bonomo L (2006) Effects of temperature on tertiary nitrification in moving-bed biofilm reactors. Water Res 40(15):2981–2993
Schramm A, Larsen LH, Revsbech NP, Ramsing NB, Amann R, Schleifer KH (1996) Structure and function of a nitrifying biofilm as determined by in situ hybridization and the use of microelectrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(12):4641–4647
Van den Akker B, Holmes M, Pearce P, Cromar NJ, Fallowfield HJ (2011) Structure of nitrifying biofilms in a high-rate trickling filter designed for potable water pre-treatment. Water Res 45(11):3489–3498
Vayenas DV, Pavlou S, Lyberatos G (1997) Development of a dynamic model describing nitritification and nitratification in trickling filters. Water Res 31(5):1135–1147
Wilhelm SR, Schiff SL, Robertson WD (1996) Biogeochemical evolution of domestic waste water in septic systems: 2. Application of conceptual model in sandy aquifers. Ground Water 34(5):853–864
Yu X, Qi Z, Zhang X, Yu P, Liu B, Zhang L, Fu L (2007) Nitrogen loss and oxygen paradox in full-scale biofiltration for drinking water treatment. Water Res 41(7):1455–1464
Zamalloa C, Arends JBA, Boon N, Verstraete W (2013) Performance of a lab-scale bio-electrochemical assisted septic tank for the anaerobic treatment of black water. New Biotechnol 30(5):573–580
Zhang Y, Love N, Edwards M (2009) Nitrification in drinking water systems. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 39(3):153–208
Zhang S, Wang Y, He W, Wu M, Xing M, Yang J, Gao N, Yin D (2013) Responses of biofilm characteristics to variations in temperature and NH4 +-N loading in a moving-bed biofilm reactor treating micro-polluted raw water. Bioresour Technol 131:365–373
Zhang S, Wang Y, He W, Wu M, Xing M, Yang J, Gao N, Pan M (2014) Impacts of temperature and nitrifying community on nitrification kinetics in a moving-bed biofilm reactor treating polluted raw water. Chem Eng J 236:242–250
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Qatar University Internal Grant (QUUG-CENG-CHE-14\15-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almomani, F.A., Khraisheh, M.A.M. Treatment of septic tank effluent using moving-bed biological reactor: kinetic and biofilm morphology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 1917–1932 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1039-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1039-7