Abstract
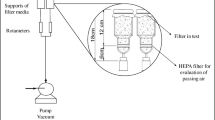
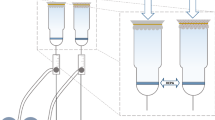
The aim of this study was to evaluate the adsorption of some hospital airborne microorganisms, e.g. Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcos pyogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida albicans by some inorganic nanoparticles. First, each microbial suspension (2 × 104 and 2 × 106 CFU/mL) was separately added to adsorbent columns (1 and 2 g), containing CaSO4, CaCO3, and FeSO4 nanoparticles. Then, the colony count reduction was measured for each adsorbent column. This study showed that all nanoparticles could adsorb all kinds of microorganisms. Importantly, the combination of CaSO4 and CaCO3 nanoparticles led to better adsorption property. Moreover, it was found that the adsorption was related to adsorbent weight and microbial density. The authors suggest that these adsorbent columns are good choice to remove hospital airborne microorganisms.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dancer SJ (2014) Controlling hospital-acquired infection: focus on the role of the environment and new technologies for decontamination. Clin Microbiol Rev 27:665–690
Daniel SCGK, Banu BN, Harshiny M, Nehru K, Ganesh PS, Kumaran S, Sivakumar M (2014) Ipomea carnea-based silver nanoparticle synthesis for antibacterial activity against selected human pathogens. J Exp Nanosci 9:197–209
Gomes F, Teixeira P, Oliveira R (2014) Mini-review: Staphylococcus epidermidis as the most frequent cause of nosocomial infections: old and new fighting strategies. Biofouling 30:131–141
Jung JH, Hwang GB, Lee JE, Bae GN (2011) Preparation of airborne Ag/CNT hybrid nanoparticles using an aerosol process and their application to antimicrobial air filtration. Langmuir 27:10256–10264
Karottki DG et al (2013) An indoor air filtration study in homes of elderly: cardiovascular and respiratory effects of exposure to particulate matter. Environ Health 12:10–1186
Kelly KN, Monson JRT (2012) Hospital-acquired infections. Surgery (Oxford) 30:640–644
Lobdell KW, Stamou S, Sanchez JA (2012) Hospital-acquired infections. Surg Clin N Am 92:65–77
Lukasik J, Scott TM, Andryshak D, Farrah SR (2000) Influence of salts on virus adsorption to microporous filters. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2914–2920
Ma K, Henderson B (2013) Ophthalmic air filtration practices in hospital and community settings and its role in modern day surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:811
Miaśkiewicz-Peska E, Łebkowska M (2011) Effect of antimicrobial air filter treatment on bacterial survival. Fibres Text East Europe 19:1
Pourakbari B, Rezaizadeh G, Mahmoudi S, Mamishi S (2015) Epidemiology of nosocomial infections in pediatric patients in an Iranian referral hospital. J Prev Med Hyg 53
Verdenelli M, Cecchini C, Orpianesi C, Dadea G, Cresci A (2003) Efficacy of antimicrobial filter treatments on microbial colonization of air panel filters. J Appl Microbiol 94:9–15
Wichmann J, Folke F, Torp-Pedersen C, Lippert F, Ketzel M, Ellermann T, Loft S (2013) Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and outdoor air pollution exposure in Copenhagen, Denmark. PLoS ONE 8:e53684
Acknowledgments
There is no acknowledgment to declare. This study was granted by Pajoohesh Lab, Yazd, Iran, Grant Number: 2015-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirjalili, M.R., Hekmatimoghaddam, S., Rezapour, I. et al. The surface adsorption of some hospital airborne microorganisms by nano-based columns. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 743–748 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0894-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0894-y