Abstract
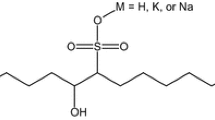
This paper describes an investigation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) and nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEO) and their metabolites in the vicinity of the Marseille sewage outfall (wastewater treatment plant with a capacity of 1.860 million inhabitant equivalents, Northwestern Mediterranean, southeast of France). This analytical survey describes their occurrence in the subsurface and sea surface layers and investigates their possible fates in this marine environment. The results indicated the presence of LAS in both layers and up to 3 km from the discharge point, whereas the concentration of sulfophenyl carboxylic acids, which are the main metabolites of LAS, was only significant near the sewer outfall and in the surface layer. The NPEO were present only in minor quantities, especially near the discharge point, and no other selected metabolites were detected. The fate of the surfactants in question was then assessed by two types of experiments according to their potential means of degradation under natural conditions. Biodegradation assays were conducted according to a protocol defined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (“Biodegradability in sea water, 835.3160”), with variations in the substrate input frequencies. Photodegradation experiments were carried out in a solar simulator reactor. These results demonstrated the low photodegradability and rapid primary biodegradation of LAS (with half-life times between 10.3 and 11.5 days) in the coastal area under study, although some LAS metabolites were more recalcitrant to biodegradation in this specific environment, which was also validated by linear alkylbenzene analysis in the two selected sediment stations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu V, Pico Y (2004) Determination of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates and their degradation products in soils by liquid chromatography-electrospray-ion trap multiple-stage mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:2878–2885
Bayona JM, Albaiges J, Solanas AM, Grifoll M (1986) Selective aerobic degradation of linear alkylbenzenes by pure microbial cultures. Chemosphere 15(5):595–598
Bellan G, Bourcier M, Salen-Picard C, Arnoux A, Casserley S (1999) Benthic ecosystem changes associated with wastewater treatment at marseille: implications for the protection and restoration of the Mediterranean coastal shelf ecosystems. Water Environ Res 71:483–493
Bester K, Theobald N, Schröder HF (2001) Nonylphenols, nonylphenol-ethoxylates, linear alkylbenzenesulfonates (LAS) and bis(4-chlorophenyl)-sulfone in the German Bight of the North Sea. Chemosphere 45(6–7):817–826
Boudenne JL, Coulomb B, Djellal L, Théraulaz F (2001) Determination of LAS in wastewater treatment plants: comparative study between conventional biodegradation testing and an alternative photo-oxidation method. Int J Environ Anal Chem 81(1):55–72
Castillo M, Riu J, Ventura F, Boleda R, Scheding R, Schröder HF, Nistor C, Emneus J, Eichhorn P, Knepper TP, Jonkers CCA, De Voogt P, Gonzalez-Mazo E, Leon VM, Barcelo D (2000) Inter-laboratory comparison of liquid chromatographic techniques and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of surfactants in wastewaters. J Chromatogr A 889:195–199
Di Corcia A, Samperi R, Marcomini A (1994) Aromatic surfactants and biodegradation intermediates in sewage by solid-phase extraction and LC. Environ Sci Technol 28:850–858
Diaz A, Ventura F, Galceran MT (2002) Simultaneous determination of estrogenic short ethoxy chain nonylphenols and their acidic metabolites in water by an in-sample derivatization/solid phase microextraction method. Anal Chem 74:3869–3876
Ding WH, Tzing SH (1998) Analysis of nonylphenol polyethoxylates and their degradation products in river water and sewage effluent by gas chromatography-ion trap (tandem) mass spectrometry with electron impact and chemical ionization. J Chromatogr A 824:79–86
Eganhouse RP, Sherblom PM (2001) Anthropogenic organic contaminants in the effluent of a combined sewer overflow: impact on Boston Harbor. Mar Environ Res 51(1):51–74
European Committee of Surfactants and their Organic Intermediates (CESIO), Statistics, 2008 (http://www.cefic.be/files/publications/cesio)
Fernandez J, Riu J, Garcia-Calvo E, Rodriguez A, Fernandez-Alba AR, Barcelo B (2004) Determination of photodegradation and ozonation by products of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates by liquid chromatography and ion chromatography under controlled laboratory experiments. Talanta 64(1):69–79
Gledhill W, Saeger VW, Treh ML (1991) An aquatic environmental safety assessment of linear alkylbenzene. Environ Toxicol Chem 10(2):169–178
Gonzalez S, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2004) Simultaneous extraction and fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates, coconut diethanol amides, nonylphenol ethoxylates and their degradation products in wastewater treatment plants, receiving coastal waters and sediments in the Catalonian area (NE Spain). J Chromatogr A 1052(1–2):111–120
Gonzalez-Mazo E, Honing M, Barcelo D, Gomez-Parra A (1997) Monitoring long-chain intermediate products item the degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in the marine environment by solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography/ionspray mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 31:504–510
Gustafsson O, Long CM, Macfarlane J, Gschwend PM (2001) Fate of Linear alkylbenzenes released to the coastal environment near Boston Harbor. Environ Sci Technol 35(10):2040–2048
Hampel M, Mreno-Garrido I, Sobrino C, Lubian LM, Blasco J (2001) Acute toxicity of LAS homologues in marine microalgae: esterase activity and inhibition growth as endpoints of toxicity. Ecotox Environ Saf 48(3):287–292
Houde F, DeBlois C, Berryman D (2002) Liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric determination of nonylphenol polyethoxylates and nonylphenol carboxylic acids in surface waters. J Chrom A 961:245–256
Jahnke A, Gandrass J, Ruck W (2004) Simultaneous determination of alkylphenol ethoxylates and their biotransformation products by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. J Chrom A 1035:115–122
Jobling S, Sheahan D, Osborne JA, Matthiessen P, Sumpter JP (1996) Inhibition of testicular growth in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to estrogenic alkylphenolic chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:194–202
Jonkers N, Laane R, de Voogt P (2005) Sources and fate of nonylphenol ethoxylates and their metabolites in the Dutch coastal zone of the North Sea. Mar Chem 96(1–2):115–135
Koh YK, Chiu TY, Boobis AR, Cartmell E, Pollard SJT, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2008) A sensitive and robust method for the determination of alkylphenol polyethoxylates and their carboxylic acids and their transformation in a trickling filter wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 73:551–556
Lara-Martin PA, Gomez-Parra A, Gonzalez-Mazo E (2008a) Reactivity and fate of synthetic surfactants in aquatic environments. Trends Anal Chem 27(8):684–695
Lara-Martin PA, Gomez-Parra A, Gonzalez-Mazo E (2008b) Sources, transport and reactivity of anionic and non-ionic surfactants in several aquatic ecosystems in SW Spain: a comparative study. Environ Pollut 156(1):36–45
Lara-Martin PA, Gomez-Parra A, Sanz JL, Gonzalez-Mazo E (2010) Anaerobic degradation pathway of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) in sulfate-reducing marine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 44:1670–1676
Leon SM, Gonzalez-Mazo E, Gomez-Parra A (2000) Extraction and isolation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates and their intermediate metabolites from various marine organisms. J Chromatogr A 889(1–2):99–104
Leon SM, Gomez-Parra A, Gonzalez-Mazo E (2004) Biodegradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates and their degradation intermediates in seawater. Environ Sci Technol 38(8):2359–2367
Marcomini A, Capri S, Giger W (1987) Determination of linear alkylbenzenesulphonates, alkylphenol polyethoxylates and nonylphenol in waste water by high-performance liquid chromatography after enrichment on octadecylsilica. J Chromatogr A 403:243–252
Marcomini A, Di Corcia A, Samperi R, Capri S (1993) Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates, nonylphenol polyethoxylates and their carboxylic biotransformation products. J Chromatogr A 644:59–61
Mungray AK, Kumar P (2009) Fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in the environment: a review. Int Biodeter Biodegrad 63:981–987
Munoz I, Gomez-Ramos MJ, Aguera A, Fernandez-Alba AR, Garcia-Reyes JF, Molina-Diaz A (2009) Chemical evaluation of contaminants in wastewater effluents and the environmental risk of reusing effluents in agriculture Trends. Anal Chem 28(6):676–694
Nunez L, Turiel E, Tadeo JL (2007) Determination of nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates in environmental solid samples by ultrasonic-assisted extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1146:157–163
Perales JA, Manzano MA, Sales D, Quiroga JM (2003) Biodisposition of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates and their associated sulphophenyl carboxylic acid metabolites in sea water. Int Biodeter Biodegr 51:187–194
Petrovic M, Diaz A, Ventura F, Barcelo D (2001) Simultaneous determination of halogenated derivatives of alkylphenol ethoxylates and their metabolites in sludges, river sediments and surface, drinking, and wastewaters by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 73:5886–5895
Prats D, Lopez C, Vallejo D, Varo P, Leon VM (2006) Effect of temperature on the biodegradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and alcohol ethoxylate. J Surf Deterg 9(1):69–75
Sarrazin L, Arnoux A, Rebouillon P (1997) High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of a linear alkylbenzenesulfonate an dits environmental biodegradation metabolites. J Chromatogr A 760:285–291
Suri M, Huld TA, Dunlop ED, Ossenbrink HA (2007) Potential of solar electricity generation in the European Union member states and candidate countries. Sol Energy 81:1295–1305
Swisher RD (1987) Surfactant biodegradation. Marcel Dekker, New York
Takada H, Ogura N (1992) Removal of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates (LAS) in the Tamagawa estuary. Mar Chem 37:257–263
Tan X, Yim SY, Uppu P, Kleinow KM (2010) Enhanced bioaccumulation of dietary contaminants in catfish with exposure to the waterborne surfactant linear alkylbenzene sulfonate. Aquat Toxicol 99(2):300–308
Trehy ML, Gledhill WE, Orth RG (1990) Determination of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates and dialkyltetralinsulfonates in water and sediment by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 62:2581–2589
Tubau I, Vasquez-Sune E, Carrera J, Gonzalez S, Petrovic M, Lopez de Alda MJ, Barcelo D (2010) Occurrence and fate of alkylphenol polyethoxylate degradation products and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactants in urban ground water: Barcelona case study. J Hydrol 383(1–2):102–110
US.EPA (1998) Fate, transport and transformation test guidelines. OPPTS 835. 3160: biodegradability in sea water. Washington, DC. http://fedbbs.access.gpo.gov/library/epa_835/835-3160.pdf, Jan 2013
Zgola-Grzeskowiak A, Grzeskowiak T, Rydlichowski R, Lukaszewski Z (2009) Determination of nonylphenol and short-chained nonylphenol ethoxylates in drain water from an agricultural area. Chemosphere 75:513–518
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Rhone-Mediterranean and Corsica Water Agency (Grant 2009-1316). This work was partially supported by ANR project MARSECO (ANR-CESA-018-06). We acknowledge Ms. Valentini-Poirier and Mr. Boissery for sparking our interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robert-Peillard, F., Syakti, A.D., Coulomb, B. et al. Occurrence and fate of selected surfactants in seawater at the outfall of the Marseille urban sewerage system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 1527–1538 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0577-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-014-0577-0