Abstract
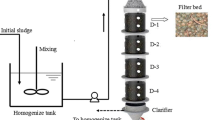
This paper presents a systematic study of a novel tower bio-vermifilter system for rural wastewater treatment at three scales: bench-scale, pilot-scale, and engineering applications. First, three types of bioreactors were tested in the bench-scale experiments: earthworm bioreactor, soil filter, and one-stage bio-vermifilter. Experiments with the earthworm bioreactor and soil filter determined the optimum earthworm density and soil layer depth to be 12.5 g/L and 40 cm, respectively. The one-stage bio-vermifilter’s poor performance in removing nitrogen and phosphorous led to several improvements in the design of the pilot tower bio-vermifilter system including the addition of one anaerobic biofilter for pretreatment, the use of two stages of bio-vermifilters, and the replacement of gravel with ceramsite in the media. Second, a pilot tower bio-vermifilter system built in Yixing City of Jiangsu province showed a good performance in the removal of chemical oxygen demand, ammonium nitrogen, and phosphorous. However, the system’s removal of total nitrogen showed considerable fluctuations, possibly due to the low ratio of carbon to nitrogen in its stage two bio-vermifilter. Finally, four operating tower bio-vermifilter systems in three basins of China were evaluated and compared with two other rural sewage treatment technologies in terms of economic costs and pollutant removal performance. Comparison results show that the tower bio-vermifilter system is a versatile system that can work effectively under a variety of natural and socioeconomic conditions at a reasonable cost.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias CA, Del Bubba M, Brix H (2001) Phosphorus removal by sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds. Water Res 35(5):1159–1168
Canti MG (2003) Earthworm activity and archaeological stratigraphy: a review of products and processes. J Archaeol Sci 30(2):135–148
Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (CMEP) (2011) The State of Environment in China, March 13. http://jcs.mep.gov.cn/hjzl/zkgb/ (in Chinese)
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323(5917):1014–1015
Del Bubba M, Arias CA, Brix H (2003) Phosphorus adsorption maximum of sands for use as media in subsurface flow constructed reed beds as measured by the Langmuir isotherm. Water Res 37(14):3390–3400
Duan H, Ma R, Xu X, Kong F, Zhang S, Kong W, Hao J, Shang L (2009) Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3522–3528
Fang CX, Zheng Z, Luo XZ, Guo FH (2010) Effect of hydraulic load on domestic wastewater treatment and removal mechanism of phosphorus in earthworm ecofilter. Fresen Environ Bull 19(6):1099–1108
Fang CX, Guo FH, Luo XZ, Chen GY, Zheng Z (2011) Performance of a three-stage tower earthworm ecofilter for simultaneous removal of carbon and nutrients from domestic wastewater. Fresen Environ Bull 20(1A):235–243
Guo L (2007) Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317(5842):1166
Hao Q, Zhang P (2010) Cost effectiveness analysis of rural domestic sewage treatment projects: a case study in Shanghai and southern Jiangsu province. China Popul Resour Environ 20(1):108–111 (in Chinese)
Hao Q, Guo S, Zhang P (2010) The popularization analysis of rural domestic sewage land treatment projects—a case study in Shanghai and southern Jiangsu area. Environ Sci Manage 35(5):80–82,109 (in Chinese)
Li S, Li H, Liang XQ, Chen YX, Wang SX, Wang FE (2009) Phosphorus removal of rural wastewater by the paddy-rice-wetland system in Tai Lake Basin. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):301–308
Liang H, Gao M, Liu J, Wei Y, Guo X (2010a) A novel integrated step-feed biofilm process for the treatment of decentralized domestic wastewater in rural areas of China. J Environ Sci 22(3):321–327
Liang H, Liu J, Wei Y, Guo X (2010b) Evaluation of phosphorus removal from wastewater by soils in rural areas in China. J Environ Sci 22(1):15–22
Ma JT (2012) 2012 International statistical year book. China Statistics Press, Beijing, pp. 116 (in Chinese)
Misiti TM, Hajaya MG, Pavlostathis SG (2011) Nitrate reduction in a simulated free-water surface wetland system. Water Res 45(17):5587–5598
Otten TG, Xu H, Qin B, Zhu G, Paerl HW (2012) Spatiotemporal patterns and ecophysiology of toxigenic Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: implications for water quality management. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3480–3488
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2008) Blooms like it hot. Science 320(5872):57–58
Paoletti MG (1999) The role of earthworms for assessment of sustainability and as bioindicators. Agr Ecosyst Environ 74(1–3):137–155
Seo DC, Cho JS, Lee HJ, Heo JS (2005) Phosphorus retention capacity of filter media for estimating the longevity of constructed wetland. Water Res 39(11):2445–2457
Sinha RK, Bharambe G, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low-cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28(4):409–420
Verbyla ME, Oakley S, Mihelcic J (2013) Wastewater infrastructure for small cities in an urbanizing world: integrating the protection of human health and the environment with resource recovery and food security. Environ Sci Technol (in Press)
Wang G, Wu L, Xu X, Jin Q, Li X (2010a) Influence of Eisenia foetida on biomass and urease activity in vertical constructed wetland. J Southeast Univ 40(5):1013–1018 (in Chinese)
Wang L, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2010b) The current pollution status and control technology of the Taihu Lake Basin, Jiangsu Province China. Int J Environ S 67(2):195–205
Wang C, Lu G, Peifang W, Wu H, Qi P, Liang Y (2011a) Assessment of environmental pollution of Taihu Lake by combining active biomonitoring and integrated biomarker response. Environ Sci Technol 45(8):3746–3752
Wang L, Guo F, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011b) Enhancement of rural domestic sewage treatment performance, and assessment of microbial community diversity and structure using tower vermifiltration. Bioresource Technol 102(20):9462–9470
Wang L, Zheng Z, Luo X, Zhang J (2011c) Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 195:245–253
Wang L, Luo XZ, Zhang Y, Chao J, Gao Y, Zhang JB, Zheng Z (2013) Community analysis of ammonia-oxidizing Betaproteobacteria at different seasons in microbial-earthworm ecofilters. Ecol Eng 51:1–9
Wei B, Sugiura N, Maekawa T (2001) Use of artificial neural network in the prediction of algal blooms. Water Res 35(8):2022–2028
Wu S, Austin D, Liu L, Dong R (2011) Performance of integrated household constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment in rural areas. Ecol Eng 37(6):948–954
Xin H, Stone R (2010) China amasses war chest to confront its environmental nightmares. Science 327(5972):1440–1441
Yang M, Yu J, Li Z, Guo Z, Burch M, Lin T (2008) Taihu Lake not to blame for Wuxi’s woes. Science 319(5860):158a
Yang X, Fang S, Lant CL, Luo X, Zheng Z (2012a) Overfertilization in the economically developed and ecologically critical Lake Tai Region China. Hum Eco 40(6):957–964
Yang X, Jiang G, Luo X, Zheng Z (2012b) Preliminary mapping of high-resolution rural population distribution based on imagery from Google Earth: a case study in the Lake Tai basin, eastern China. Appl Geogr 32(2):221–227
Zhang L, Liu W, You B, Bian B (2009) Characteristics of pollutant sources of Caoqiao River in Taihu Lake Basin. Res Environ Sci 10(22):1150–1155 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: 11ZR1402900), Fudan University 985 project (Grant Number: 2012SHKXQN009), Chinese Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: 41201191), and Chinese Ministry of Education New Faculty Fund (Grant Number: 20120071120034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, E., Wang, D., Yang, M. et al. Tower bio-vermifilter system for rural wastewater treatment: bench-scale, pilot-scale, and engineering applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 1053–1064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0479-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0479-6