Abstract
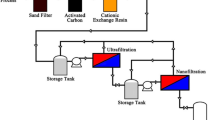
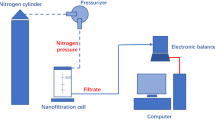
Nanofiltration of ternary mixtures of sodium chloride and aqueous solutions of Reactive Black-5 was studied in two different modules, namely, flat sheet and spiral wound over a wide range of operating conditions. Hydrophilized polyamide membrane with molecular weight cutoff of 150 was used for the experiments. Combined effect of dye and salt concentration, trans-membrane pressure drop, initial pH of feed solution on the permeate flux, and observed retention were investigated. Extent of color removal, chemical oxygen demand (COD), total dissolved solid (TDS), and conductivity were determined to assess performance of the membrane. The experimental results showed that both the permeate flux and observed retention decreased with increase in dye as well as salt concentration in the feed. Permeate fluxes were lower at higher pH values. Substantial removal of color was achieved in the nanofiltration experiments with a marked reduction in COD and TDS. The process allowed the production of permeate stream with great reutilization possibilities.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
(APHA) American Public Health Association (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste-water. In: Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD, (eds). Washington, D.C. ISBN 0-8755-3047-8
Al-Aseeri M, Bu-Ali Q, Haji S, Al-Bastaki N (2007) Removal of Acid Red and sodium chloride mixtures from aqueous solutions using nanofiltration. Desalination 206:407–413
Alcaina-Miranda MI, Barredo-Damas S, Bes-Pia A, Iborra-Clar MI, Iborra-Clar A, Mendoza-Roca JA (2009) Nanofiltration as a final step towards textile wastewater reclamation. Desalination 240:290–297
Allegre C, Moulin P, Maisseu M, Charbit F (2004) Savings and reuse of salts and water present in dye house effluents. Desalination 162:13–22
Avlonitis SA, Poulios I, Sotiriou D, Pappas M, Moutesidis K (2008) Simulated cotton dye effluents treatment and reuse by nanofiltration. Desalination 221:259–267
Braghetta A, DiGiano FA, Ball WP (1997) Nanofiltration of natural organic matter: pH and ionic strength effects. J Environ Eng ASCE 123:628
BTTG (1999). Report 5: waste minimization and best practice, British Textile Technology Group, http://www.e4s.org.uk/textilesonline/content/6library/fr_library.htm
Chakraborty S, Bag BC, Dasgupta S, De S, Basu JK (2003) Separation and fractionation of dye solution by nanofiltration. Sep Sci Technol 38:219–235
Erswell A, Brouckaert CJ, Buckley CA (1988) The reuse of reactive dye liquors using charged ultrafiltration membrane technology. Desalination 70:157–167
Forgacs E, Cserhati T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30:953–971
García-Molina V, Lyko S, Esplugas S, Wintgens Th, Melin Th (2006) Ultrafiltration of aqueous solutions containing organic polymers. Desalination 189:110–118
Goodman GA, Porter JJ (1980) Water quality requirements for reuse in textile dyeing processes. Am Dyest Rep 69:33–38
Hamlin JD, Phillips DAS, Whiting A (1999) UV-visible spectroscopic studies of the effects of common salt and urea upon reactive dye solutions. Dyes Pigm 41:137–142
He Y, Li GM, Wang H, Jiang Z-W, Zhao J-F, Su H-X, Huang Q-Y (2009) Experimental study on the rejection of salt and dye with cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 40:289–295
Jiraratananon R, Sungpet A, Luangsowan P (2000) Performance evaluation of nanofiltration membranes for treatment of effluents containing reactive dye and salt. Desalination 130:177–183
Koyuncu I, Topacik D (2002) Effect of organic ion on the separation of salts by nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 195:247–263
Koyuncu I, Topacik D, Yuksel E (2004) Reuse of reactive dyehouse wastewater by nanofiltration: process water quality and economical implications. Sep Purif Technol 36:77–85
Levenstein R, Hasson D, Semiat R (1996) Utilisation of the Donnan effect for improving electrolyte separation with nanofiltration membranes. J Mem Sci 116:77–92
Maheswari GP, Al-Ramadhan M, Al-Abdulhadi M (1995) Energy requirement of water production in dual-purpose plants. Desalination 101:133–140
Mo JH, Lee YH, Kim J, Jeong JY, Jegal J (2008) Treatment of dye aqueous solutions using nanofiltration polyamide composite membranes for the dye wastewater reuse. Dyes Pigm 76:429–434
Nataraj SK, Hosamani KM, Aminabhavi TM (2009) Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis thin film composite membrane module for the removal of dye and salts from the simulated mixtures. Desalination 249:12–17
Pastagia KM, Chakraborty S, DasGupta S, Basu JK, De S (2003) Prediction of permeate flux and concentration of two-component dye mixture in batch nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 218:195–210
Rai U, Guha BK, Kumar J (2000) Treatment of distillery waste water using membrane filtration for water reuse. In: Proceedings of Indian Chemical Engineering Congress, vol 2, WTR 17-20
Satyanarayana SV, Bhattacharya PK, De S (2000) Flux decline during ultrafiltration of kraft black liquor using different flow modules: a comparative study. Sep Purif Technol 20:155–167
Scholz W, Lucas M (2003) Techno-economic evaluation of membrane filtration for the recovery and re-use of tanning chemicals. Water Res 37:1859–1867
Uzal N, Yilmaz L, Yetis U (2010) Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for reuse of indigo dye rinsing waters. Sep Sci Tech 45:331–338
Van der Bruggen B, Daems B, Wilms D, Vandecasteele C (2001) Mechanisms of retention and flux decline for the nanofiltration of dye baths from textile industry. Sep Purif Technol 22–23:519–528
Yeung KW, Shang SM (1999) The influence of metal ions on the aggregation and hydrophobicity of dyes in solutions. J Soc Dyers Colour 115:228–232
Yu S, Liu M, Ma M, Qi M, Lü Z, Gao C (2010) Impacts of membrane properties on reactive dye removal from dye/salt mixtures by asymmetric cellulose acetate and composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 350:83–91
Zularisam AW, Ismail AF, Salim MR, Sakinah M, Ozaki H (2007) The effects of natural organic matter (NOM) fractions on fouling characteristics and flux recovery of ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 212:191–208
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. V. S. Patel, Sophisticated Instrumentation Centre for Applied Research and Testing (SICART), Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, and Dr. N. H. Khan of Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute (CSMCRI), Bhavnagar, for their valuable help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, T.M., Nath, K. Separation of ternary sodium chloride/Reactive Black-5 aqueous solutions using two different modules in a nanofiltration pilot plant. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 1237–1248 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0283-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0283-3