Abstract
Background
Pure neuritic leprosy (PNL) is uncommon form of leprosy involving peripheral nerves. Some isolated case reports have shown imaging changes in the central nervous system (CNS) and also impairment in visual evoked potential (VEP), somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP) and brain stem auditory-evoked potentials (BAEPs) parameters in PNL, but there is lack of large study. This prospective observational study evaluates impairment in these central conduction studies among PNL patients.
Methods
We screened patients with leprosy presenting with features of neuropathy and/or thickened nerves. Patients with bacilli-positive nerve biopsies were included in the study and subjected to routine tests along with nerve conduction study (NCS), VEP, tibial SSEP and BAEPs. Parameters of these studies were analyzed based on data from previous studies.
Results
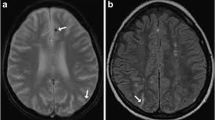
Of 76 patients screened for PNL 49 had positive findings in biopsy. Most of patients were male and mean age group was 46.35 ± 15.35 years. Mononeuritis multiplex was most common NCS pattern in 46.93% (23/49) patients. We found abnormal VEP in 13 out of 35 patients (37.14%). Similarly abnormal SSEP and BAEPs among 42.85% and 40% patients respectively.
Discussion
This study shows that in PNL significant number of patients have subclinical CNS involvement. Exact pathophysiology of CNS involvement is not known till now but study of VEP, SSEP and BAEPs parameter may help in early diagnosis of PNL.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Patient data is available with corresponding author and can be provided on request.
References
Verma S, Garg RK, Rizvi I, Malhotra HS, Kumar N, Jain A, Suvirya S, Parihar A, Verma R, Sharma PK, Pandey S, Uniyal R, Prakash S (2022) Central nervous system, spinal root ganglion and brachial plexus involvement in leprosy: a prospective study. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis 18(14):11795735221135476. https://doi.org/10.1177/11795735221135477.PMID:36277272;PMCID:PMC9583215
Shukla B, Verma R, Kumar V, Kumar M, Malhotra KP, Garg RK et al (2020) Pathological, ultrasonographic, and electrophysiological characterization of clinically diagnosed cases of pure neuritic leprosy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 25(2):191–203
Aung T, Kitajima S, Nomoto M, En J, Yonezawa S, Arikawa I, Goto M (2007) Mycobacterium leprae in neurons of the medulla oblongata and spinal cord in leprosy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(4):284–294. https://doi.org/10.1097/nen.0b013e31803d597e
Celik O, Yalcin S, Gok U, Yavrucuoglu E, Ozturk A, Akyol A (1997) Auditory brain stem evoked potentials in patients with leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis 65(2):166–169
Ulvi H, Yigiter R, Yoldas T, Erdem L, Müngen B (2003) Study of visual evoked potentials in the assessment of the central optic pathways in leprosy patients. Neurol Sci 24(5):346–350
Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis [Internet]. 1966;34(3):255—273. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/5950347
Hui M, Uppin MS, Challa S, Meena AK, Kaul S (2015) Pure neuritic leprosy: resolving diagnostic issues in acid fast bacilli (AFB)-negative nerve biopsies: a single centre experience from South India. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 18:292–297
Rao PN, Suneetha S (2016) Pure neuritic leprosy: current status and relevance. Ind J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.179086
Bilik L, Demir B, Cicek D. (2017) Leprosy Reactions. In: Ribòn W, (ed). Hansen’s Disease [Internet]. Rijeka: IntechOpen.https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.72481
Shahrokhi F, Chiappa KH, Young RR (1978) Pnntern shift visual evoked responses: two hundred patients with optic neuritis and/or multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 35(2):65–71. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1978.00500260003001
Misra UK, Kalita J. (2020) Visual evoked potential-anatomical basis of visual evoked Potential. Clinical Neurophysiology, 4th edn. Elsevier, New Delhi
Mauguière F, Allison T, Babiloni C, Buchner H, Eisen AA, Goodin DS, Jones SJ, Kakigi R, Matsuoka S, Nuwer M, Rossini PM, Shibasaki H (1999) Somatosensory evoked potentials. The International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 52:79–90
Chiappa KH, Gladstone KJ, Young RR (1979) Brain stem auditory evoked responses: studies of waveform variations in 50 normal human subjects. Arch Neurol 36(2):81–87. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1979.00500380051005
Kochar DK, Gupta DV, Sandeep C, Halwai M, Kumawat BL (1997) Study of brain stem auditory-evoked potentials (BAEPs) and visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis 65(2):157–165
Gupta BK, Kochar DK (1994) Study of nerve conduction velocity, somatosensory-evoked potential and late responses (H-reflex and F-wave) of posterior tibial nerve in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis 62(4):586–593
Polavarapu K, Preethish-Kumar V, Vengalil S, Nashi S, Lavania M, Bhattacharya K et al (2019) Brain and spinal cord lesions in leprosy: a magnetic resonance imaging-based study. Am J Trop Med Hyg 100(4):921–931
Bhoi SK, Naik S, Purkait S (2021) Pure neuritic leprosy with bilateral foot drop and central nervous involvement: a clinical, electrophysiological, and mr correlation. Neurol India 69(5):1349–1353
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr Dibyendu Deewan and Mr Swadhin Nayak for Neurophysiology and secretarial help.
Funding
Financial grant: R&D Biotechnology project, Science and Technology Department, Govt of Odisha (ST-BT-MISC-0020–2018-4002/ST, Dated 12.9.2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKB: concept, design, literature search, data acquisition, data analysis, manuscript preparation. YL: data acquisition, data analysis, literature search, manuscript preparation. MJ: data analysis, manuscript editing and review. SP: pathologic evaluation, manuscript editing, manuscript review. SN: radiologic evaluation, manuscript editing, manuscript review. PS: manuscript editing, manuscript review. GKS: biochemical analysis, manuscript review MK: data acquisition, data analysis, literature search. PB: data collection, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical clearance has been obtained from Institute Ethics committee, AIIMS Bhubaneswar (Ref: T/EMF/Neuro/19/21).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhoi, S.K., Lahre, Y., Jha, M. et al. From periphery to center, untold story of pure neuritic leprosy: an electrophysiological study. Acta Neurol Belg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-024-02503-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-024-02503-2