Abstract
Objective
Whether alpha-synuclein in peripheral body fluids can be used for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) remains in controversy. This study evaluates diagnostic potential of alpha-synuclein for PD in various peripheral body fluids using a meta-analysis approach.
Methods
Studies published before October 2022 were searched in Web of Science and PubMed databases. The results were computed using the STATA 12.0 statistical software.
Results
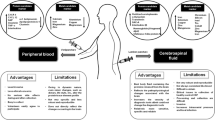
In plasma, PD patients exhibited elevated alpha-synuclein levels relative to healthy controls (HCs) [standard mean difference (SMD) = 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.42 to 1.15] with a sensitivity of 0.79 (95% CI: 0.64–0.89) and a specificity of 0.95 (95% CI: 0.90–0.98). Higher plasma alpha-synuclein levels were correlated with longer disease durations, higher Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale motor scores, and higher Hoehn and Yahr stages in PD patients. Plasma neural-derived exosomal alpha-synuclein levels (SMD = 1.82, 95% CI = 0.30 to 3.35), ratio of plasma neural-derived exosomal alpha-synuclein to total alpha-synuclein (SMD = 1.26, 95% CI = 0.19 to 2.33), and erythrocytic alpha-synuclein levels were also increased in PD patients (SMD = 6.57, 95% CI = 3.55 to 9.58). In serum, there was no significant difference in alpha-synuclein levels between PD patients and HCs (SMD = 0.54, 95% CI = − 0.27 to 1.34). In saliva, reduced alpha-synuclein levels were observed in PD patients (SMD = − 0.85, 95% CI = − 1.67 to − 0.04).
Conclusions
Alpha-synuclein levels in plasma, plasma neural-derived exosome, erythrocyte, and saliva may serve as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of PD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports our study are shown in the article and supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Akhtar RS, Licata JP, Luk KC, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee MY (2018) Measurements of auto-antibodies to α-synuclein in the serum and cerebral spinal fluids of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem
Albillos SM, Montero O, Calvo S, Solano B, Cubo E (2021) Can plasma α-synuclein help us to differentiate Parkinson’s disease from essential tremor? Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov 11
Barasa B, Slijper M (2014) Challenges for red blood cell biomarker discovery through proteomics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1844:1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.10.002
Barbour R, Kling K, Anderson JP, Banducci K, Cole T, Diep L, Fox M, Goldstein JM, Soriano F, Seubert P et al (2008) Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis 5:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1159/000112832
Bougea A, Stefanis L, Paraskevas GP, Emmanouilidou E, Vekrelis K, Kapaki E (2019) Plasma alpha-synuclein levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 40:929–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03738-1
Campo F, Carletti R, Fusconi M, Pellicano C, Pontieri FE, Di Gioia CR, de Vincentiis M (2019) Alpha-synuclein in salivary gland as biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Rev Neurosci 30:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2018-0064
Cao Z, Wu Y, Liu G, Jiang Y, Wang X, Wang Z, Feng T (2020) Differential diagnosis of multiple system atrophy-parkinsonism and parkinson’s disease using α-synuclein and external anal sphincter electromyography. Front Neurol 11:1043. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.01043
Caranci G, Piscopo P, Rivabene R, Traficante A, Riozzi B, Castellano AE, Ruggieri S, Vanacore N, Confaloni A (2013) Gender differences in Parkinson’s disease: focus on plasma α-synuclein. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 120:1209–1215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-0972-6
Cerri S, Ghezzi C, Sampieri M, Siani F, Avenali M, Dornini G, Zangaglia R, Minafra B, Blandini F (2018) The exosomal/total α-synuclein ratio in plasma is associated with glucocerebrosidase activity and correlates with measures of disease severity in PD patients. Front Cell Neurosci 12:125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00125
Cersosimo MG, Benarroch EE (2012) Pathological correlates of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 46:559–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.10.014
Chan DKY, Braidy N, Chen RF, Xu YH, Bentley S, Lubomski M, Davis RL, Chen J, Sue CM, Mellick GD (2022) Strong predictive algorithm of pathogenesis-based biomarkers improves Parkinson’s disease diagnosis. Mol Neurobiol 59:1476–1485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02604-6
Chang CW, Yang SY, Yang CC, Chang CW, Wu YR (2019) Plasma and serum alpha-synuclein as a biomarker of diagnosis in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 10:1388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.01388
Chang KH, Liu KC, Lai CS, Yang SY, Chen CM (2021) Assessing plasma levels of α-synuclein and neurofilament light chain by different blood preparation methods. Front Aging Neurosci 13:759182. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.759182
Chatterjee K, Roy A, Banerjee R, Choudhury S, Mondal B, Halder S, Basu P, Shubham S, Dey S, Kumar H (2020) Inflammasome and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional study. J Neuroimmunol 338:577089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577089
Chatterjee K, Roy A, Banerjee R, Choudhury S, Mondal B, Halder S, Basu P, Shubham S, Dey S, Kumar H (2020) Inflammasome and α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional study. J Neuroimmunol 338:577089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577089
Chen CH, Lee BC, Lin CH (2020) Integrated plasma and neuroimaging biomarkers associated with motor and cognition severity in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 10:77–88. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-191766
Chen NC, Chen HL, Li SH, Chang YH, Chen MH, Tsai NW, Yu CC, Yang SY, Lu CH, Lin WC (2020) Plasma levels of α-synuclein, Aβ-40 and T-tau as biomarkers to predict cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 12:112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00112
Devic I, Hwang H, Edgar JS, Izutsu K, Presland R, Pan C, Goodlett DR, Wang Y, Armaly J, Tumas V et al (2011) Salivary α-synuclein and DJ-1: potential biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Brain 134:e178. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr015
Dutta S, Hornung S, Kruayatidee A, Maina KN, del Rosario I, Paul KC, Wong DY, Duarte Folle A, Markovic D, Palma J-A et al (2021) alpha-Synuclein in blood exosomes immunoprecipitated using neuronal and oligodendroglial markers distinguishes Parkinson’s disease from multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol 142:495–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-021-02324-0
Eisele YS, Obermüller U, Heilbronner G, Baumann F, Kaeser SA, Wolburg H, Walker LC, Staufenbiel M, Heikenwalder M, Jucker M (2010) Peripherally applied Abeta-containing inoculates induce cerebral beta-amyloidosis. Science 330:980–982. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1194516
Emelyanov A, Andoskin P, Pchelina S (2017) Dataset of total, oligomeric alpha-synuclein and hemoglobin levels in plasma in Parkinson׳s disease. Data Brief 10:182–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2016.11.089
Emmanouilidou E, Melachroinou K, Roumeliotis T, Garbis SD, Ntzouni M, Margaritis LH, Stefanis L, Vekrellis K (2010) Cell-produced alpha-synuclein is secreted in a calcium-dependent manner by exosomes and impacts neuronal survival. J Neurosci 30:6838–6851. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5699-09.2010
Emmanouilidou E, Papagiannakis N, Kouloulia S, Galaziou A, Antonellou R, Papadimitriou D, Athanasiadou A, Bozi M, Koros C, Maniati M et al (2020) Peripheral alpha-synuclein levels in patients with genetic and non-genetic forms of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 73:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.03.014
Ferrer I (2001) Alpha-synucleinopathies. Neurologia 16:163–170
Foulds PG, Diggle P, Mitchell JD, Parker A, Hasegawa M, Masuda-Suzukake M, Mann DM, Allsop D (2013) A longitudinal study on α-synuclein in blood plasma as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 3:2540. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02540
Gupta V, Garg RK, Khattri S (2015) Serological analysis of alpha-synuclein and NF-kappaB in Parkinson’s disease patients. J Clin Diagn Res. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/12545.5978
Horvath I, Iashchishyn IA, Forsgren L, Morozova-Roche LA (2017) Immunochemical Detection of alpha-Synuclein Autoantibodies in Parkinson’s Disease: Correlation between Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels. ACS chemical neuroscience: acschemneuro.7b00063
Hu Y, Tang B, Guo J, Wu X, Sun Q, Shi C, Hu L, Wang C, Wang L, Tan L et al (2012) Variant in the 3’ region of SNCA associated with Parkinson’s disease and serum alpha-synuclein levels. J Neurol 259:497–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6209-4
Ishii R, Tokuda T, Tatebe H, Ohmichi T, Kasai T, Nakagawa M, Mizuno T, El-Agnaf OM (2015) Decrease in plasma levels of α-synuclein is evident in patients with Parkinson’s disease after elimination of heterophilic antibody interference. PLoS ONE 10:e0123162. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123162
Jiang C, Hopfner F, Katsikoudi A, Hein R, Catli C, Evetts S, Huang Y, Wang H, Ryder JW, Kuhlenbaeumer G et al (2020) Serum neuronal exosomes predict and differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91:720–729. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-322588
Kang W, Chen W, Yang Q, Zhang L, Zhang L, Wang X, Dong F, Zhao Y, Chen S, Quinn TJ et al (2016) Salivary total α-synuclein, oligomeric α-synuclein and SNCA variants in Parkinson’s disease patients. Sci Rep 6:28143. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28143
Kiely AP, Asi YT, Kara E, Limousin P, Ling H, Lewis P, Proukakis C, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Hardy J et al (2013) α-Synucleinopathy associated with G51D SNCA mutation: a link between Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy? Acta Neuropathol 125:753–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1096-7
Lee PH, Lee G, Park HJ, Bang OY, Joo IS, Huh K (2006) The plasma alpha-synuclein levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 113:1435–1439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0427-9
Li Q, Li Z, Han X, Shen X, Wang F, Bai L, Li Z, Zhang R, Wang Y, Zhu X (2022) A panel of plasma biomarkers for differential diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes. Front Neurosci 16:805953. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.805953
Lin L, Yang Wu, Chiu (2019) Plasma pS129-α-synuclein is a surrogate biofluid marker of motor severity and progression in Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Med 8:1601
Lin C-H, Liu H-C, Yang S-Y, Yang K-C, Wu C-C, Chiu M-J (2019) Plasma pS129-alpha-synuclein is a surrogate biofluid marker of motor severity and progression in Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101601
Lin CH, Yang SY, Horng HE, Yang CC, Chieh JJ, Chen HH, Liu BH, Chiu MJ (2018) Plasma biomarkers differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism syndromes. Front Aging Neurosci 10:123. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00123
Lin CH, Yang SY, Horng HE, Yang CC, Chieh JJ, Chen HH, Liu BH, Chiu MJ (2017) Plasma α-synuclein predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88:818–824. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2016-314857
Lin WC, Lu CH, Chiu PY, Yang SY (2020) Plasma total α-synuclein and neurofilament light chain: clinical validation for discriminating Parkinson’s disease from normal control. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 49:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510325
Luan M, Sun Y, Chen J, Jiang Y, Li F, Wei L, Sun W, Ma J, Song L, Liu J et al (2022) Diagnostic value of salivary real-time quaking-induced conversion in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28976
Malec-Litwinowicz M, Plewka A, Plewka D, Bogunia E, Morek M, Szczudlik A, Szubiga M, Rudzińska-Bar M (2018) The relation between plasma α-synuclein level and clinical symptoms or signs of Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Neurochir Pol 52:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pjnns.2017.11.009
Mollenhauer B, Locascio JJ, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Sixel-Döring F, Trenkwalder C, Schlossmacher MG (2011) α-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study. Lancet Neurol 10:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(11)70014-x
Moses LE, Shapiro D, Littenberg B (1993) Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary ROC curve: data-analytic approaches and some additional considerations. Stat Med 12:1293–1316
Ng ASL, Tan YJ, Lu Z, Ng EYL, Ng SYE, Chia NSY, Setiawan F, Xu Z, Tay KY, Prakash KM et al (2019) Plasma alpha-synuclein detected by single molecule array is increased in PD. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6:615–619. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.729
Niu M, Li Y, Li G, Zhou L, Luo N, Yao M, Kang W, Liu J (2020) A longitudinal study on α-synuclein in plasma neuronal exosomes as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease development and progression. Eur J Neurol 27:967–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14208
Ren J, Pan C, Wang Y, Xue C, Lin H, Xu J, Wang H, Zhang W, Xu P, Chen Y et al (2022) Plasma alpha-synuclein and phosphorylated tau 181 as a diagnostic biomarker panel for de novo Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15601
Reyes JF, Olsson TT, Lamberts JT, Devine MJ, Kunath T, Brundin P (2015) A cell culture model for monitoring α-synuclein cell-to-cell transfer. Neurobiol Dis 77:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.003
Sadanand A, Janardhanan A, Sankaradoss A, Vanisree AJ, Arulnambi T, Bhanu K (2017) Erythrocyte membrane in the evaluation of neurodegenerative disorders. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis 7:127–134. https://doi.org/10.2147/dnnd.s143989
Shalash A, Salama M, Makar M, Roushdy T, Elrassas HH, Mohamed W, El-Balkimy M, Abou Donia M (2017) Elevated serum α-synuclein autoantibodies in patients with Parkinson’s disease relative to Alzheimer’s disease and controls. Front Neurol 8:720. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00720
Shi M, Kovac A, Korff A, Cook TJ, Ginghina C, Bullock KM, Yang L, Stewart T, Zheng D, Aro P et al (2016) CNS tau efflux via exosomes is likely increased in Parkinson’s disease but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 12:1125–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.04.003
Shi M, Liu C, Cook TJ, Bullock KM, Zhao Y, Ginghina C, Li Y, Aro P, Dator R, He C et al (2014) Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 128:639–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1314-y
Si X, Tian J, Chen Y, Yan Y, Pu J, Zhang B (2019) Central nervous system-derived exosomal alpha-synuclein in serum may be a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 413:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.05.015
Singh AP, Bajaj T, Gupta D, Singh SB, Chakrawarty A, Goyal V, Dey AB, Dey S (2018) Serum mortalin correlated with α-synuclein as serum markers in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. Neuromolecular Med 20:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-017-8475-5
Stuendl A, Kraus T, Chatterjee M, Zapke B, Sadowski B, Moebius W, Hobert MA, Deuschle C, Brockmann K, Maetzler W et al (2021) alpha-Synuclein in plasma-derived extracellular vesicles is a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 36:2508–2518. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28639
Tian C, Liu G, Gao L, Soltys D, Pan C, Stewart T, Shi M, Xie Z, Liu N, Feng T et al (2019) Erythrocytic α-Synuclein as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 8:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-019-0155-y
Vivacqua G, Latorre A, Suppa A, Nardi M, Pietracupa S, Mancinelli R, Fabbrini G, Colosimo C, Gaudio E, Berardelli A (2016) Abnormal salivary total and oligomeric alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 11:e0151156. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151156
Vivacqua G, Suppa A, Mancinelli R, Belvisi D, Fabbrini A, Costanzo M, Formica A, Onori P, Fabbrini G, Berardelli A (2019) Salivary alpha-synuclein in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 63:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.02.014
Wang HL, Lu CS, Yeh TH, Shen YM, Chiu CC (2019) Combined assessment of serum alpha-synuclein and rab35 is a better biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurol 15:488
Wang J, Zheng B, Yang S, Hu M, Wang JH (2020) Differential circulating levels of naturally occurring antibody to α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia. Front Aging Neurosci 12:571437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.571437
Wang L, Wang G, Duan Y, Wang F, Lin S, Zhang F, Li H, Li A, Li H (2019) A comparative study of the diagnostic potential of plasma and erythrocytic α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 19:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1159/000506480
Wang X, Yu S, Li F, Feng T (2015) Detection of α-synuclein oligomers in red blood cells as a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 599:115–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.05.030
Wang XY, Kang WY, Yang Q, Zhang LY, Chen SD, Liu J (2014) Using gastrocnemius sEMG and plasma α-synuclein for the prediction of freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease patients. PLoS ONE 9:e89353. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089353
Youssef P, Kim WS, Halliday GM, Lewis SJG, Dzamko N (2021) Comparison of different platform immunoassays for the measurement of plasma alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease patients. J Parkinsons Dis 11:1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-212694
Yu Z, Liu G, Li Y, Arkin E, Zheng Y, Feng T (2022) Erythrocytic α-synuclein species for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis and the correlations with clinical characteristics. Front Aging Neurosci 14:827493. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.827493
Zhao A, Li Y, Niu M, Li G, Luo N, Zhou L, Kang W, Liu J (2020) SNCA hypomethylation in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder is a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 10:1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-201912
Zhao ZH, Chen ZT, Zhou RL, Zhang X, Ye QY, Wang YZ (2018) Increased DJ-1 and α-synuclein in plasma neural-derived exosomes as potential markers for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10:438. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00438
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81901108), the Talent Program of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (23YJRC21), and Beijing Henji Health Management and Development Foundation (No. HJKY2023002-015).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81901108), the Talent Program of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (23YJRC21), and Beijing Henji Health Management and Development Foundation (No. HJKY2023002-015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LG and HS designed, organized, and execute the project; LG and PZ designed, executed, and reviewed the statistical analysis. HS and LG wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
Our study was a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of published researches and was exempt from review and approval by the research ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, H., Zhang, P. & Gu, L. Alpha-synuclein in peripheral body fluid as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Belg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02452-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02452-2