Abstract
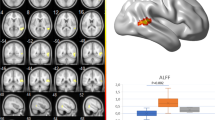
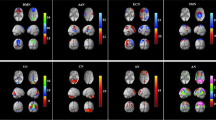
To evaluate the spontaneous neuronal activities and the changes of brain functional network in patients with vestibular migraine (VM). Three groups including18 patients with VM, 21 patients with migraine without aura (MWoA) and 21 healthy controls (HCs) underwent the scanning of the resting-state fMRI. Covariance analysis and bonferroni multiple comparisons were used to obtain brain regions with significant differences in amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) values. Furthermore, the brain regions with the most significant differences of ALFF values were recognized as a region of interest (ROI) and functional connectivity (FC) analysis was performed in these regions. (1) ALFF: Compared with HCs, patients with VM showed significantly lower ALFF in the right putamen (P < 0.05), and significantly higher ALFF in the right lingual gyrus (P < 0.05). In addition, compared with MWoA patients, patients with VM showed significantly higher ALFF in the right lingual gyrus (P < 0.05). (2) Compared with HCs, VM patients showed significantly higher FC among the cerebellum, the left dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus and the right putamen (P < 0.05) but significantly lower FC among the left median cingulate, paracingulate gyri and the right putamen (P < 0.05). Compared with MWoA patients, VM patients showed significantly higher FC between the cerebellum and the right putamen (P < 0.05) but significantly lower FC among the left median cingulate, paracingulate gyri and the right putamen (P < 0.05). There are functional abnormalities in nociceptive, vestibular and visual cortex regions in patients with VM during the interictal period.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Obermann M (2017) Vestibular migraine. Front Neurol 8:213
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (2018) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rD edition. Cephalalgia 38:1–211
Messina R, Rocca MA, Colombo B (2017) Structural brain abnormalities in patients with vestibular migraine. J Neurol 264(2):295–303
Obermann M, Wurthmann S, Steinberg BS, Theysohn N, Diener HC, Naegel S (2014) Central vestibular system modulation in vestibular migraine. Cephalalgia 34:1053–1061
Russo A, Marcelli V, Esposito F, Corvino V, Marcuccio L, Giannone A, Conforti R, Marciano E, Tedeschi G, Tessitore A (2014) Abnormal thalamic function in patients with vestibular migraine. Neurology 82:2120–2126
Teggi R, Colombo B, Rocca MA (2016) A review of recent literature on functional MRI and personal experience in two cases of definite vestibular migraine. Neurol Sci 37:1399–1402
Fox MD, Raichle ME (2007) Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:700–711
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29:83–91
Yuan K, Qin W, Dong M, Liu J, Liu P, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wang W, Wang Y, Li Q (2010) Combining spatial and temporal information to explore restingstate networks changes in abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 475:20–24
Yuan K, Qin W, Dong M, Liu J, Sun J, Liu P, Zhang Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhao L, Deneen KM, Liu Y, Gold MS, Tian J (2010) Gray matter deficits and resting-state abnormalities in abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 482:101–105
Yuan K, Qin W, Liu JX, Guo QA, Dong MH, Sun JB, Zhang Y, Liu P, Wang W, Wang YR, Li QA, Yang WC, Deneen KM, Gold MS, Liu YJ, Tian J (2010) Altered small-world brain functional networks and duration of heroin use in male abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 477:37–42
Greicius MD, Srivastava G, Reiss AL, Menon V (2004) Default-mode network activity distinguishes Alzheimer’s disease from healthy aging: evidence from functional MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:4637–4642
Lui S, Deng W, Huang XQ, Jiang LJ, Ma XH, Chen HF, Zhang TJ, Li XL, Li DM, Zou L, Tang HH, Zhou XHJ, Mechelli A, Collier DA, Sweeney JA, Li T, Gong QY (2009) Association of cerebral deficits with clinical symptoms in antipsychotic-naive first-episode schizophrenia: an optimized voxel-based morphometry and resting state functional connectivity study. Am Psychiatric Assoc 166:196–205
Wang S, Wang H, Zhao D, Liu X, Yan W, Wang M, Zhao R (2019) Grey matter changes in patients with vestibular migraine. Clin Radiol 74:898.e1-898.e5
Hoptman MJ, Zuo XN, Butler PD, Javitt DC, D’Angelo D, Mauro CJ, Milham MP (2010) Amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in schizophrenia: a resting state fMRI study. Schizophr Res 117:13–20
Xue T, Yuan K, Cheng P, Zhao L, Zhao L, Yu D, Dong T, Karen M, Gong Q, Qin W, Tian J (2013) Alterations of regional spontaneous neuronal activity and corresponding brain circuit changes during resting state in migraine without aura. NMR Biomed 26:1051–1058
Beckmann CF, DeLuca M, Devlin JT, Smith SM (2005) Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:1001–1013
Mantini D, Perrucci MG, Del Gratta C, Romani GL, Corbetta M (2007) Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:13170–13175
Shin JH, Kim YK, Kim HJ (2014) Altered brain metabolism in vestibular migraine: comparison of interictal and ictal findings. Cephalalgia 34:58–67
Wang J, Lewis RF (2016) Contribution of intravestibular sensory conflict to motion sickness and dizziness in migraine disorders. J Neurophysiol 116:1586–1591
Radtke A, Brevern M, Neuhauser H, Hottenrott T, Lempert T (2012) Vestibular migraine: Long-term follow-up of clinical symptoms and vestibulo-cochlear findings. Neurology 79:1607–1614
BronsteinLempertt MT (2007) Dizziness: a practical approach to diagnosis and management, vol 93. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 149–150
Choi JY, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Glasauer S, Kim JS (2015) Central paroxysmal positional nystagmus: Characteristics and possible mechanisms. Neurology 84:2238–2246
Jeong SH, Oh SY, Kim HJ, Koo JW, Kim JS (2010) Vestibular dysfunction in migraine: effects of associated vertigo and motion sickness. J Neurol 257:905–912
Akdal G, Baykan B, Karli N (2015) Population-based study of vestibular symptoms in migraineurs. Acta Otolaryngol 135:435
Yu D, Yuan K, Zhao L, Zhao L, Dong M, Liu P, Wang G, Liu J, Sun J, Zhou G, Deneena K, Liang F, Qin W, Tian J (2011) Regional homogeneity abnormalities in patients with interictal migraine without aura: a resting-state study. NMR Biomed 25:806–812
Klingner CM, Volk GF, Flatz C, Brodoehl S, Dieterich M, Witte OW, Guntinas-Lichius O (2013) Components of vestibular cortical function. Behav Brain Res 236:194–199
Bluhm RL, Miller J, Lanius RA, Osuch EA, Boksman K, Neufeld R, Theberge J, Schaefer B, Williamson P (2007) Spontaneous low-frequency fluctuations in the BOLD signal in schizophrenic patients: anomalies in the default network. Schizophr Bull 33:1004–1012
Liu H, Liu Z, Liang M, Hao Y, Tan L, Kuang F, Yi Y, Xu L, Jiang T (2006) Decreased regional homogeneity in schizophrenia: a resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuro Report 17:19–22
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Qingdao People’s Livelihood Science and Technology Project [17-3-3-18-nsh] for the financial support provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: HPW and SQW. Data acquisition: HPW, SQW, XJL, WJY, MHW and RLZ. Data analysis and interpretation: HPW, SQW, XJL, WJY, MHW and RLZ. Drafting of the manuscript: SQW. Revision of the manuscript: SQW, WJY and HPW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University. All of the procedures were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and relevant policies in China.
Informed consent
We have obtained written informed consent from all study participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, H., Liu, X. et al. A resting-state functional MRI study in patients with vestibular migraine during interictal period. Acta Neurol Belg 123, 99–105 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-021-01639-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-021-01639-9