Abstract
Introduction
To evaluate the ultrasound findings of the median nerve in patients with clinical assigned carpal tunnel syndrome but normal nerve conduction studies.
Methods
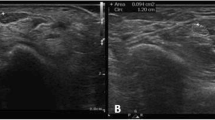
This prospective, cross-sectional study involved 41 patients (51 hands) with clinically assigned CTS and normal nerve conduction studies and 20 healthy controls (30 hands). Ultrasonography was performed in all participants, and cross-sectional area (CSA), hypoechogenicity, and mobility of the median nerve were evaluated. All patients were assessed with Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ).
Results
CSA of the median nerve in the wrist was significantly higher in the patient group when compared to the control group. Echogenicity and mobility were significantly decreased in the patient group. Ultrasound abnormalities were positively correlated with clinical features. A significant correlation was observed among sensory loss, provocative tests, body mass index, BCTQ, and high CSA.
Conclusion
US can help the clinicians with the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with clinical symptoms but negative nerve conduction study results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibrahim I, Khan WS, Goddard N, Smitham P (2012) Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of the recent literature. Open Orthop J 6:69
Bongers F, Schellevis F, Van Den Bosch W, Van Der Zee J (2007) Carpal tunnel syndrome in general practice (1987 and 2001): incidence and the role of occupational and non occupational factors. Br J Gen Pract 57:36–39
Yesildag A, Kutluhan S, Sengul N, Koyuncuoglu HR, Oyar O, Guler K et al (2004) The role of ultrasonographic measurements of the median nerve in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Radiol 59:910–915
Mousavi AA, Saied AR (2011) Comparison of sonography and electrodiagnostic tests in diagnosis and treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. World Appl Sci J 15:490–495
Claes F, Kasius KM, Meulstee J, Verhagen WI (2013) Comparing a new ultrasound approach with electrodiagnostic studies to confirm clinically defined carpal tunnel syndrome: a prospective, blinded study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 92:1005–1101
Taylor-Gjevre RM, Gjevre JA, Nair B (2010) Suspected carpal tunnel syndrome: do nerve conduction study results and symptoms match? Can Fam Phys 56:250–254
Grundberg AB (1983) Carpal tunnel decompression in site of normal electromyography. J Hand Surg 8:348–349
Werner RA, Andary M (2011) Electrodiagnostic evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 44:597–607
Fowler JR, Maltenfort MG, Ilyas AM (2013) Ultrasound as a first-line test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:932–937
Tai TW, Wu CY, Su FC, Chern TC, Jou IM (2012) Ultrasonography for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome: a meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Ultrasound Med Biol 38:1121–1128
De-la-Llave-Rincon AI, Laguarta-Val S, Arroyo-Morales M, Martinez-Perez A, Pareja JA, Fernandez-de-Las-Penas C (2012) Characterisation of pain in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome according to electromyographic severity criteria. Revista de neurologia 54:407–414
Cartwright MS, Hobson-Webb LD, Boon AJ, Alter KE, Hunt CH, Flores VH et al (2012) Evidence-based guideline: neuromuscular ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 46:287–293
Fowler JR, Gaughan JP, Ilyas AM (2011) The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: a meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1089–1094
Witt JC, Hentz JG, Stevens JC (2004) Carpal tunnel syndrome with normal nerve conduction studies. Muscle Nerve 29:515–522
Sezgin M, Incel NA, Serhan S, Camdeviren H, As I, Erdoğan C (2006) Assessment of symptom severity and functional status in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: reliability and functionality of the Turkish version of the Boston Questionnaire. Disabil Rehabil 30:28:1281–1285
Levıne DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, Katz JN (1993) A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 11:1585–1592
Campbell WW et al (1999) Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: summary statement. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, American Academy of Neurology. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80:357–359
Kimura J (2001) Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscle: principles and practice, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Van Doesburg MH, Henderson J, Yoshii Y, Mink Van der Molen AB, Cha SS, An KN et al (2012) Median nerve deformation in differential finger motions: ultrasonographic comparison of carpal tunnel syndrome patients and healthy controls. J Orthop Res 30:643–648
Cartwright MS, Walker FO, Blocker JN, Schulz MR, Arcury TA, Grzywacz JG et al (2013) Ultrasound for carpal tunnel syndrome screening in manual laborers. Muscle Nerve 48:127–131
Ellis H (2009) The carpal tunnel. Br J Hosp Med (Lond) 70:180–181
Beekman R, Visser LH (2003) Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: a critical review of the literature. Muscle Nerve 27:26–33
Iyer VG (1993) Understanding nerve conduction and electromyographic studies. Hand Clin 9:273–287
Burns TM (2001) Carpal tunnel sonography by the rheumatologist versus nerve conduction study by the neurologist. J Rheumatol 28:2560
Mills KR (1985) Orthodromic sensory action potentials from palmar stimulation in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:250–255
Strain RE, Olson WH (1975) Selective damage of large diameter peripheral nerve fi bers by compression: an application of Laplace’s law. Exp Neurol 47:68–80
George V, Smith AG (1996) Anatomic considerations of the peripheral nerve in compressive neuropathies of the upper extremity. Orthop Clin North Am 27:211–218
Lundborg G, Dahlin LB (1996) Anatomy, function, and pathophysiology of peripheral nerves and nerve compression. Hand Clin 12:185–193
Duncan I, Sullivan P, Lomas F (1999) Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:681–684
Merhar GL, Clark RA, Schneider HJ, Stern PJ (1986) High-resolution computed tomography of the wrist in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 15:549–552
Kwon BC, Jung KI, Baek GH (2008) Comparison of sonography and electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am 33:65–71
Visser LH, Smidt MH, Lee ML (2008) High-resolution sonography versus EMG in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:63–67
Hobson-Webb LD, Massey JM, Juel VC, Sanders DB (2008) The ultrasonographic wrist-to-forearm median nerve area ratio in carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol 119:1353–1357
Burg EW, Bathala L, Visser LH (2013) Difference in normal values of median nerve cross sectional area between Dutch and Indian subjects. Muscle Nerve 50:129–132
Hunderfund AN, Boon AJ, Mandrekar JN, Sorenson EJ (2011) Sonography in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 44:485–491
Lee D, van Holsbeeck MT, Janevski PK, Ganos DL, Ditmars DM, Darian VB (1999) Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Ultrasound vs electromyography. Radiol Clin N Am 37:85972
Mohammadi A, Afshar A, Etemadi A, Masoudi S, Baghizadeh A (2010) Diagnostic value of cross-sectional area of the median nerve in grading severity of carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Iran Med 13:51621
Klauser AS, Halpern EJ, De Zordo T, Feuchtner GM, Arora R, Gruber J et al (2009) Carpal tunnel syndrome assessment with US: value of additional cross-sectional area measurements of the median nerve in patients versus healthy volunteers. Radiology 250:171–177
Rahmani M, Esfe AG, Bozorg SM, Mazloumi M, Khalilzadeh O, Kahnouji H et al (2011) The ultrasonographic correlates of carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with normal electrodiagnostic tests. La radiologia medica 116:489–496
Al-Hashel JY, Rashad HM, Nouh MR, Amro HA, Khuraibet AJ, Shamov T et al (2015) Sonography in carpal tunnel syndrome with normal nerve conduction studies. Muscle nerve 51:592–597
Stuart RM, Koh ES, Breidahl WH (2004) Sonography of peripheral nerve pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:123–129
Mallouhi A, Pulzl P, Trieb T, Piza H, Bodner G (2006) Predictors of carpal tunnel syndrome: accuracy of grayscale and color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1240–1245
Lam N, Thurston A (1998) Association of obesity, gender, age and occupation with carpal tunnel syndrome. Aust N Z J Surg 68:190–193
Padua L, Pazzaglia C, Caliandro P, Granata G, Foschini M, Briani C et al (2008) Carpal tunnel syndrome: ultrasound, neurophysiology, clinical, and patient-oriented assessment. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2064–2069
Han HY, Kim HM, Park SY, Kim MW, Kim JM Jang DH (2016) Clinical findings of asymptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with diabetes mellitus. Annals of rehabilitation medicine 40.3 1:489–495
Yucel H (2015) Factors affecting symptoms and functionality of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: a retrospective study. J Phys Ther Sci 27:1097–1101. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.27.1097 (Epub 2015 Apr 30)
Acknowledgements
This study did not receive any specific funding or grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aktürk, S., Büyükavcı, R. & Ersoy, Y. Median nerve ultrasound in carpal tunnel syndrome with normal electrodiagnostic tests. Acta Neurol Belg 120, 43–47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0963-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0963-3