Abstract
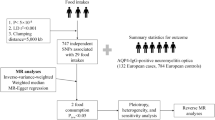
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) has unknown risk factors. The aim of this study was to identify the environmental risk factors for NMOSD. A case–control study was conducted in Tehran from 2015 to 2016 among 100 patients with NMOSD. Sex-matched healthy controls (n = 400) were selected through random digit dialing (RDD). Logistic regression was used to estimate unadjusted and adjusted ORs (odds ratio) at 95% confidence intervals (CI) via SPSS. Compared with the control population, in NMOSD patients, the adjusted OR for low dairy consumption per week was (OR = 18.09; 95% CI 6.91, 47.37), following low sea food intake (OR = 13.91; 95% CI 6.13, 31.57) and low fruit and vegetable consumption (OR = 6.23; 95% CI 3.07, 12.62). The lower heavy physical activity (OR: 16.11, 95% CI 7.03, 36.91) among patients had risen the risk of NMOSD. A past history of head trauma was considered a risk for NMOSD (OR: 8.39, 95% CI 4.97, 14.16). The association between NMOSD and intentional abortion only among females (OR: 7.42, 95% CI 2.81, 19.55) was detected. This study indicates significant associations between dietary habits, life style, history of head trauma and intentional abortion in female and the later diagnosis of NMOSD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etemadifar M, Dashti M, Vosoughi R, Abtahi SH, Ramagopalan SV, Nasr Z (2014) An epidemiological study of neuromyelitis optica in Isfahan. Multiple sclerosis. 20(14):1920–1922
Etemadifar M, Nasr Z, Khalili B, Taherioun M, Vosoughi R (2015) Epidemiology of neuromyelitis optica in the world: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Multiple sclerosis international. 2015:174720
Hedstrom AK, Olsson T, Alfredsson L (2015) The role of environment and lifestyle in determining the risk of multiple sclerosis. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 26:87–104
Abdollahpour I, Nedjat S, Sahraian MA, Mansournia MA, Otahal P, van der Mei I (2017) Waterpipe smoking associated with multiple sclerosis: a population-based incident case-control study. Mult Scler. 23(10):1328–1335
Eskandarieh S, Nedjat S, Abdollahpour I, Moghadasi AN, Azimi AR, Sahraian MA (2017) Comparing epidemiology and baseline characteristic of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica: a case-control study. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 12:39–43
Eskandarieh S, Heydarpour P, Minagar A, Pourmand S, Sahraian MA (2016) Multiple sclerosis epidemiology in East Asia, South East Asia and South Asia: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology. 46(3):209–221
Tan CT, Mao Z, Qiu W, Hu X, Wingerchuk DM, Weinshenker BG (2016) International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology. 86(5):491–492
Eskandarieh S, Nedjat S, Azimi AR, Moghadasi AN, Sahraian MA (2017) Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in Iran. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 18:209–212
Clagett B, Nathanson KL, Ciosek SL, McDermoth M, Vaughn DJ, Mitra N et al (2013) Comparison of address-based sampling and random-digit dialing methods for recruiting young men as controls in a case-control study of testicular cancer susceptibility. Am J Epidemiol 178(11):1638–1647
Ikeda N, Shibuya K, Hashimoto H (2011) Improving population health measurement in national household surveys: a simulation study of the sample design of the comprehensive survey of living conditions of the people on health and welfare in Japan. J Epidemiol. 21(5):385–390
Pugliatti M, Casetta I, Drulovic J, Granieri E, Holmoy T, Kampman MT et al (2012) A questionnaire for multinational case-control studies of environmental risk factors in multiple sclerosis (EnvIMS-Q). Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 195:43–50
Horton M, Rudick RA, Hara-Cleaver C, Marrie RA (2010) Validation of a self-report comorbidity questionnaire for multiple sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology. 35(2):83–90
Sahraian MA, Naghshineh H, Shati M, Jahromi SR, Rezaei N (2016) Persian adaptation of a questionnaire of environmental risk factors in multiple sclerosis (EnvIMS-Q). Mult Scler Relat Disord. 10:82–85
Morabia A (2014) Invited commentary: do-it-yourself modern epidemiology–at last! Am J Epidemiol 180(7):669–672
Andersen PK, Skrondal A (2015) A competing risks approach to “biologic” interaction. Lifetime Data Anal 21(2):300–314
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Lucchinetti CF, Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG (2007) The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 6(9):805–815
Cossburn M, Tackley G, Baker K, Ingram G, Burtonwood M, Malik G et al (2012) The prevalence of neuromyelitis optica in South East Wales. Eur J Neurol 19(4):655–659
Houzen H, Niino M, Hirotani M, Fukazawa T, Kikuchi S, Tanaka K et al (2012) Increased prevalence, incidence, and female predominance of multiple sclerosis in northern Japan. J Neurol Sci 323(1–2):117–122
Asgari N, Lillevang ST, Skejoe HP, Falah M, Stenager E, Kyvik KO (2011) A population-based study of neuromyelitis optica in Caucasians. Neurology. 76(18):1589–1595
Kashipazha D, Mohammadianinejad SE, Majdinasab N, Azizi M, Jafari M (2015) A descriptive study of prevalence, clinical features and other findings of neuromyelitis optica and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in Khuzestan Province. Iran. Iranian journal of neurology. 14(4):204–210
Shaygannejad V, Rezaie N, Paknahad Z, Ashtari F, Maghzi H (2016) The environmental risk factors in multiple sclerosis susceptibility: a case-control study. Adv Biomed Res. 5:98
Jahromi SR, Toghae M, Jahromi MJ, Aloosh M (2012) Dietary pattern and risk of multiple sclerosis. Iran J Neurol. 11(2):47–53
Bagur MJ, Murcia MA, Jimenez-Monreal AM, Tur JA, Bibiloni MM, Alonso GL et al (2017) Influence of diet in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Adv Nutr. 8(3):463–472
Koch-Henriksen N, Sorensen PS (2010) The changing demographic pattern of multiple sclerosis epidemiology. Lancet Neurol. 9(5):520–532
Belbasis L, Bellou V, Evangelou E, Ioannidis JP, Tzoulaki I (2015) Environmental risk factors and multiple sclerosis: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet Neurol. 14(3):263–273
Etemadi A, Khademi H, Kamangar F, Freedman ND, Abnet CC, Brennan P et al (2017) Hazards of cigarettes, smokeless tobacco and waterpipe in a Middle Eastern Population: a Cohort Study of 50,000 individuals from Iran. Tob Control. 26(6):674–682
Patil RR (2014) Urbanization as a determinant of health: a socioepidemiological perspective. Soc Work Public Health. 29(4):335–341
Wesnes K, Myhr KM, Riise T, Cortese M, Pugliatti M, Bostrom I et al (2017) Physical activity is associated with a decreased multiple sclerosis risk: the EnvIMS study. Mult Scler. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458517694088
Hart PH, Gorman S, Finlay-Jones JJ (2011) Modulation of the immune system by UV radiation: more than just the effects of vitamin D? Nat Rev Immunol 11(9):584–596
Abbasi M, Nabavi SM, Fereshtehnejad SM, Jou NZ, Ansari I, Shayegannejad V et al (2017) Multiple sclerosis and environmental risk factors: a case-control study in Iran. Neurol Sci. 38(11):1941–1951
Ramagopalan SV, Dyment DA, Guimond C, Yee IM, Ebers GC, Sadovnick AD (2010) No effect of parental age on risk of multiple sclerosis: a population-based study. Neuroepidemiology. 34(2):106–109
Degelman ML, Herman KM (2017) Smoking and multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis using the Bradford Hill criteria for causation. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 17:207–216
Funding
Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eskandarieh, S., Nedjat, S., Abdollahpour, I. et al. Environmental risk factors in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a case–control study. Acta Neurol Belg 118, 277–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0900-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0900-5