Abstract
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada®) is a humanized monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis with active disease defined by clinical or imaging features. Alemtuzumab demonstrated superior efficacy over active comparator in both treatment naive patients and those with inadequate response to prior therapy. Alemtuzumab is associated with a consistent and manageable safety and tolerability profile. Treatment with alemtuzumab for multiple sclerosis increases the risk for autoimmune adverse events including immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Complete blood counts with differential should be obtained prior to initiation of treatment and at monthly intervals thereafter for 48 months after the last infusion. After this period of time, testing should be performed based on clinical findings suggestive of ITP. If ITP onset is confirmed, appropriate medical intervention should be promptly initiated, including immediate referral to a specialist. This paper presents the consensus of Belgian multiple sclerosis specialists and hematologists to guide the treating physician with practical recommendations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada®) is a humanized monoclonal antibody approved in more than 60 countries. Within the European Union, alemtuzumab is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) with active disease defined by clinical or imaging features. Lemtrada® is not recommended for patients with inactive disease or those stable on current therapy. Alemtuzumab demonstrated superior efficacy over active comparator in both treatment naive patients and those with inadequate response to prior therapy. Alemtuzumab is associated with a consistent and manageable safety and tolerability profile [1]. The most recent efficacy data over 6 years on clinical and MRI lesion activity as well as on brain volume loss suggest that alemtuzumab may provide a unique treatment approach for RRMS patients, offering durable efficacy in the absence of continuous treatment [2].
Treatment with alemtuzumab for multiple sclerosis (MS) increases the risk for autoimmune adverse events including immune thrombocytopenia (previously known as immune thrombocytopenic purpura) [3,4,5].
A first case of ITP after alemtuzumab occurred unexpectedly in the phase 2 study in MS and resulted in a fatal outcome [4]. A risk management plan (RMP) put in place ensured early detection of symptoms or signs of autoimmune disease, with the aim of minimizing the impact of alemtuzumab-associated autoimmune effects.
The European risk management plan includes complete blood counts with differential which should be obtained prior to initiation of treatment and at monthly intervals thereafter for 48 months after the last infusion. After this period of time, testing should be performed based on clinical findings suggestive of ITP. If ITP is suspected, a complete blood count should be obtained immediately. At the time of treatment with Alemtuzumab, the patient should be educated to remain vigilant for bleeding symptoms [6,7,8]. In the event of an abnormal platelet count the sequence of additional tests and the appropriate moment to refer the patient to a hematologist will be at the discretion of the treating physician. If ITP onset is confirmed, appropriate medical intervention should be promptly initiated, including immediate referral to a specialist. This paper presents the consensus of Belgian MS specialists and hematologists to guide the treating physician with practical recommendations.
Alemtuzumab and ITP
ITP after receiving alemtuzumab has been described as a specific form characterized by delayed onset, responsiveness to conventional ITP therapies, and prolonged remission [5].
Autoimmune adverse events were detected in MS patients treated with alemtuzumab in clinical trials [8]. The 6-year follow-up data of the CARE-MS studies were presented at ECTRIMS 2016 and showed the following frequencies: 39% of alemtuzumab treated subjects experienced an autoimmune thyroid disorder, 2.6% an immune thrombocytopenia and 0.2% (two cases) an autoimmune renal disease. The incidence of first occurrence of ITP by year is shown in Fig. 1 [9].
From all cases of thrombocytopenia detected in the phase 3 trials, 80% was by monthly blood monitoring and 20% by patients’ recognition of clinical symptoms [10].
In post-marketing use through February 2017, 13,000 patients have been treated worldwide with alemtuzumab for MS and the frequency for ITP has been estimated at 0.58% [11]. Post-marketing frequencies are not directly comparable to clinical trial incidences because of differences in ascertainment methodology and follow-up duration, and limitations of post-marketing reporting.
Recommendations for the follow up of platelet counts in patients treated with alemtuzumab
Before starting treatment with alemtuzumab
Complete blood count (CBC) with differential should be obtained prior to initiation of Alemtuzumab (treatment and pre-phase with steroids) [7].
There are no data available about initiation of alemtuzumab in patients with low platelet count.
Once treated with alemtuzumab: monitoring of platelet count
Complete blood count with differential should be obtained at monthly intervals thereafter for 48 months after the last infusion. After this period of time, testing should be performed based on clinical findings suggestive of ITP. If ITP is suspected a CBC should be obtained immediately [7].
Bleeding risk and platelet count
It’s also important to realize that there is no linear relationship between platelet count and bleeding symptoms. However, severe bleeding usually occurs with a platelet count below 10,000/μl Fig. 2 [12, 13].
If ITP onset is confirmed, appropriate medical intervention should be promptly initiated, including immediate referral to a specialist. The following consensus goes beyond alemtuzumab’s SmPC and aims to guide treating physicians on the necessary actions in case of an abnormal platelet count and before ITP is confirmed. Reference is made to the guidelines elaborated by the Belgian Hematological Society (BHS) for treating primary ITP in adults [14].
Education of the patients
It is imperative to educate the patient to be vigilant for any clinical sign suggestive of bleeding between the monthly CBC checks. In case of such a sign, the CBC must be obtained immediately.
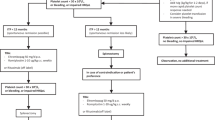
These suggestive clinical findings are described as follows: the observation of small scattered red, pink, or purple spots on the skin (petechiae); easy bruising; bleeding from a cut that is harder to stop; heavier, longer or more frequent menstrual periods than normal; bleeding between menstrual periods; bleeding from the gums or nose that is new or takes longer than usual to stop; or coughing up blood. Any of these should prompt further action including immediate referral to a specialist [7] (Fig. 3).
Values for referral and diagnostic work-up
Figure 3 describes which action to undertake depending on the platelet count received after every CBC check.
-
When the platelet count is at least 150,000/μl, continue the monthly blood platelet count and bleeding symptoms surveillance.
-
Any steep decrease of 50% or more from previous value but still above 100,000/μl must prompt an immediate recheck of the CBC to exclude pseudothrombocytopenia (platelet aggregates). Contact the hematologist when this steep decrease is confirmed.
-
Pseudothrombocytopenia (platelet aggregates) has to be excluded by checking the platelets on EDTA, heparin, or citrate anticoagulated blood. A peripheral blood smear must exclude platelet clumping or aggregation.
-
-
When the count is below 100,000/μl and still above 50,000/μl and with no bleeding symptoms, check the platelet count via a new CBC within 72 h to exclude pseudothrombocytopenia. If thrombocytopenia is confirmed, contact the hematologist to discuss referral.
-
With a value between 30,0000 and 50,000/μl and no bleeding symptoms, recheck the CBC within 48–72 h to exclude pseudothrombocytopenia and contact the hematologist after the results have been confirmed.
-
Below 30,000/μl, recheck the CBC and contact the hematologist immediately.
-
When bleeding symptoms are present, contact the hematologist immediately for urgent referral or send the patient to the emergency unit.
Further diagnostic work up and values for treatment of ITP
The further diagnostic work up for a suspected ITP has been well described in the publication of the practice guidelines by the BHS [14]. These guidelines also set clear values for the initiation of treatment (Fig. 4) and the therapeutic options.
Active bleeding or platelet count below 10.000/μl make treatment mandatory. When there’s no or mild bleeding and the platelet count is between 10 and 30,000/μl, then treatment is a potential option after evaluation of patient characteristics.
When there is no bleeding and platelet count is above 30,000/μl then there is no need for treatment unless special circumstances are present (e.g., invasive procedure).
The decision to hospitalize a patient with ITP will be made by the hematologist primarily based on the hemorrhage situation (patients with signs of mucosal or deep bleeding are frequently admitted) and on factors influencing the bleeding risk (age, comorbidities, need for treatment with anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents, etc.) [14].
Conclusion
The use of alemtuzumab has been associated with the development of ITP in 2, 6% of patients in clinical trials in MS. A lower frequency was reported in the post-marketing setting. Through the RMP, patients can be diagnosed early, and treated if needed, allowing for favorable outcomes. This important goal can be reached through a good education of the patient, a careful watch on the monthly lab tests and a close collaboration between the neurologist and the hematologist. The latter could be facilitated through the establishment of a reference network prior to initiation of alemtuzumab treatment. In this report, based on a consensus meeting with Belgian hematologists and neurologists, we have described different scenarios of platelet count abnormalities that can be encountered and the appropriate actions to take for every scenario.
Change history
03 March 2018
The article Management of immune thrombocytopenia in multiple sclerosis patients treated with alemtuzumab: a Belgian consensus, written by Lambert et al., was originally published electronically on the publisher’s internet portal on 27 January 2018 without open access.
References
Berger T, Elovaara I, Fredrikson S, McGuigan C et al (2017) Alemtuzumab use in clinical practice: recommendations from European multiple sclerosis experts. CNS Drugs 31:33–50
Ziemssen T, Thomas K (2017) Alemtuzumab in the long-term treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: an update on the clinical trial evidence and data from the real world. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 10(10):343–359
Cossburn M, Pace A, Jones J, Ali R, Ingram G, Baker G et al (2011) Autoimmune disease after alemtuzumab treatment for multiple sclerosis in a multicenter cohort. Neurology 77(6):573–579
Coles A, Compston D, Selmaj K et al (2008) CAMMS223 Trial Investigators. Alemtuzumab versu interferon beta-1a in early multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 359(17):1786–1801
Cuker A, Coles AJ, Sullivan H, Fox E, Goldberg M, Oyuela P, Purvis A, Beardsley DS, Margolin D (2011) A distinctive form of immune thrombocytopenia in a phase 2 study of alemtuzumab for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Blood 118(4):6299–6305
Willis MD et al (2015) Alemtuzumab for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:525–534
EMA (2016) Lemtrada: EPAR product information. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medicines/003718/human_med_001678.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058001d124. Accessed 10 Oct 2016
Havrdova E, Horakova D, Kovarova I (2015) Alemtuzumab in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: key clinical trial results and considerations for use. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 8(1):31–45
Dayan C, Cuker A, LaGanke C, Fernández O, Hupperts R, Sharrack B, Singer B, Vermersch P, Margolin D, Twyman C (2016) Autoimmunity in patients treated with alemtuzumab for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: 6-year follow-up of the CARE-MS studies. In: ECTRIMS, London, p 20
Cuker A, Arnold D, Cohen J, Coles A, Fox E, Hartung H, Havrdova E, et al. (2015) Detection and management of immune thrombocytopenia in alemtuzumab-treated patients in the multiple sclerosis clinical development program. In: ECTRIMS, Barcelona, p 590
Selmaj K, Habek M, Bass A, Brassat D, Brinar V, Coles A, Vladic A, Wray S, Margolin D, Thangavelu K, et al. (2017) Efficacy and safety of alemtuzumabin patients with RRMSIs durable over 10 years: follow-up From the CAMMS223 study. In: 69th Annual Meeting of the American academy of neurology (AAN), Boston, pp 5–338
Neylon A, Saunders P, Howard M, Proctor S, Taylor P, Northern Region Haematology Group (2003) Clinically significant newly presenting autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults: a prospective study of a population-based cohort of 245 patients. Br J Haematol 122(6):966–974
Lacey J, Penner J (1977) Management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in the adult. Semin Thromb Hemost 3(3):160–174
Janssens A, Lambert C, Bries G, Bosly A, Selleslag D, Beguin Y (2013) Primary immune thrombocytopenia in adults. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment anno 2013 proposed by the Belgian Hematological Societyf. Belg J Hematol 4(1):11–20
Disclosures
Editorial support was provided by Thomas Savoye, MD, Blue Jibe Medical Affairs, Herent, Belgium. This article was reviewed by Darren P. Baker, PhD, Claudio Rodriguez, MD, Steve Cavalier, MD Isabel Firmino, MD and Chantal Maertens, PharmD, PhD, of Sanofi as a courtesy, with no obligation on the authors’ part to revise the manuscript. Funding for this editorial support was provided by Sanofi. AL participated as an MS specialist prior to his employment by Sanofi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of article informed consent is not necessary.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised due to a retrospective Open Access order.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0899-7.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, C., Dubois, B., Dive, D. et al. Management of immune thrombocytopenia in multiple sclerosis patients treated with alemtuzumab: a Belgian consensus. Acta Neurol Belg 118, 7–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0882-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0882-3