Abstract
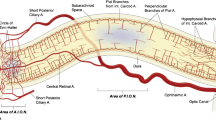
Ischemic optic neuropathies (IONs) are among the most prevalent diseases causing visual impairment in middle-aged and elderly people. While arteritic ION is an ocular emergency and requires early diagnosis and immediate treatment with systemic high-dose corticosteroids to prevent further visual loss, treatment options for non-arteritic ION remain limited. We describe the case of a woman with unilateral right-sided non-arteritic posterior ischemic optic neuropathy. The diagnosis was made on clinical and radiographic grounds. Diffusion-weighted sequences and apparent diffusion coefficient maps revealed markedly restricted diffusion in the right optic nerve. It was very helpful to precise the posterior topography of the optic nerve lesion. Furthermore, we reported the diffusion tensor tractography study which appears to be an objective tool to assess the incomplete visual recovery. These MRI techniques including tensor tractography remain to be evaluated in large cohort of ION patients’ particularly in future therapeutic trials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayreh SS (2009) Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res 28:34–62
Verma A, Jain KK, Mohan S, Phadke RV (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in posterior ischemic optic neuropathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1839–1840
Klein JP, Cohen AB, Kimberly WT, Shah AS, Leiderman YI, Cestari DM, Dinkin MJ (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of bilateral simultaneous optic nerve infarctions. Arch Neurol 66:132–133
Al-Shafai LS, Mikulis DJ (2006) Diffusion MR imaging in a case of acute ischemic optic neuropathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:255–257
Chen JS, Mukherjee P, Dillon WP, Wintermark M (2006) Restricted diffusion in bilateral optic nerves and retinas as an indicator of venous ischemia caused by cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1815–1816
Mathur S, Karimi A, Mafee MF (2007) Acute optic nerve infarction demonstrated by diffusion-weighted imaging in a case of rhinocerebral mucormycosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:489–490
Purvin V, Kuzma B (2005) Intraorbital optic nerve signal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging sequences in perioperative hypotensive ischemic optic neuropathy. J Neuroophthalmol 25:202
Ko S-B, Lee K (2010) Acute optic-nerve infarction in carotid dissection. N Engl J Med 363:765
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cauquil, C., Souillard-Scemama, R., Labetoulle, M. et al. Diffusion MRI and tensor tractography in ischemic optic neuropathy. Acta Neurol Belg 112, 209–211 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-012-0013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-012-0013-5