Abstract
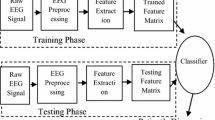
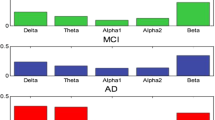
Alzheimer’s disease is an incurable neurological disorder that damages cognitive abilities, but early identification reduces the symptoms significantly. The absence of competent healthcare professionals has made automatic identification of Alzheimer’s disease more crucial since it lessens the amount of work for staff members and improves diagnostic outcomes. The major aim of this work is “to develop a computer diagnostic scheme that makes it possible to identify AD using the Electroencephalogram (EEG) signal”. Therefore, Dynamically Stabilized Recurrent Neural Network Optimized with Artificial Gorilla Troops espoused Alzheimer’s Disorder Detection using EEG signals (DSRNN-AGTO-ADD) is proposed in this paper. Here, Dynamic Context-Sensitive Filter (DCSF) is considered to eliminate the noise, and interference from the EEG signal. Then Adaptive and Concise Empirical Wavelet Transform (ACEWT) is utilized to separate the filtered signals from the frequency bands, and to feature extraction from the EEG signals. Signal’s characteristics, like logarithmic bandwidth power, standard deviation, variance, kurtosis, mean energy, mean square, norm are combined to ACEWT method to create feature vectors and enhance diagnostic performance. After that, the extracted features are fed to Dynamically Stabilized Recurrent Neural Network (DSRNN) for task classification. Weight parameter of DSRNN is enhanced using Artificial Gorilla Troops Optimization Algorithm (AGTOA). The proposed DSRNN-AGTOA-ADD algorithm is activated in MATLAB. The metrics including accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, precision, computation time, ROC are examined for AD diagnosis. The performance of the proposed DSRNN-AGTOA-ADD approach attains 12.98%, 5.98% and 23.45% high specificity; 29.98%, 23.32% and 19.76% lower computation Time and 29.29%, 8.365%, 8.551% and 7.915% higher ROC compared with the existing methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Janghel RR, Rathore YK. Deep convolution neural network based system for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Irbm. 2021;42(4):258–67.
Şeker M, Özbek Y, Yener G, Özerdem MS. Complexity of EEG dynamics for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using permutation entropy neuromarker. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;206: 106116.
Sidulova M, Nehme N, Park CH. Towards Explainable Image Analysis for Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Diagnosis. In 2021 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, (2021).
Tavakoli N, Karimi Z, AsadiJouzani S, Azizi N, Rezakhani S, Tobeiha A. Machine Learning-Based Brain Diseases Diagnosing in Electroencephalogram Signals, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s. In Prognostic Models in Healthcare: AI and Statistical Approaches (pp. 161–191). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, (2022).
Sharma R, Goel T, Tanveer M, Lin CT, Murugan R. Deep learning based diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, (2023).
Dixit S, Gaikwad A, Vyas V, Shindikar M, Kamble K. United Neurological study of disorders: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson's disease detection, Anxiety detection, and Stress detection using various Machine learning Algorithms. In 2022 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, (2022).
Arjaria SK, Rathore AS, Bisen D, Bhattacharyya S. Performances of Machine Learning Models for Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Annals of Data Science, pp.1–29, (2022).
Shajin FH, Salini P, Rajesh P, Nagoji Rao VK. Efficient framework for brain tumour classification using hierarchical deep learning neural network classifier. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng: Imaging Vis. 2023;11(3):750–7.
Fouladi S, Safaei AA, Arshad NI, Ebadi MJ, Ahmadian A. The use of artificial neural networks to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease from brain images. Multimed Tools Appl. 2022;81(26):37681–721.
Deepa N, Chokkalingam SP. Optimization of VGG16 utilizing the arithmetic optimization algorithm for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;74: 103455.
Ghoraani B, Boettcher LN, Hssayeni MD, Rosenfeld A, Tolea MI, Galvin JE. Detection of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using dual-task gait assessments and machine learning. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021;64: 102249.
Tu Y, Lin S, Qiao J, Zhuang Y, Zhang P. Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis via multimodal feature fusion. Comput Biol Med. 2022;148: 105901.
Dao Q, El-Yacoubi MA, Rigaud AS. Detection of alzheimer disease on online handwriting using 1D convolutional neural network. IEEE Access. 2022;11:2148–55.
English M, Kumar C, Ditterline BL, Drazin D, Dietz N. Machine Learning in Neuro-Oncology, Epilepsy, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Schizophrenia. Machine Learning in Clinical Neuroscience: Foundations and Applications, pp.349–361, (2022).
Seifallahi M, Mehraban AH, Galvin JE, Ghoraani B. Alzheimer’s disease detection using comprehensive analysis of Timed Up and Go test via Kinect V. 2 camera and machine learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 30, pp.1589–1600, (2022).
Sudharsan M, Thailambal G. Alzheimer’s disease prediction using machine learning techniques and principal component analysis (PCA). Materials Today: Proceedings (2021).
Liu J, Li M, Luo Y, Yang S, Li W, Bi Y. Alzheimer’s disease detection using depthwise separable convolutional neural networks. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;203: 106032.
NoorulJulaiha A, Priyatharshini R. A Study on Automatic Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Multimodalities. In Rising Threats in Expert Applications and Solutions: Proceedings of FICR-TEAS 2022 (pp. 631–642). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore (2022).
Alorf A, Khan MUG. Multi-label classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages from resting-state fMRI-based correlation connectivity data and deep learning. Comput Biol Med. 2022;151: 106240.
Kaplan E, Dogan S, Tuncer T, Baygin M, Altunisik E. Feed-forward LPQNet based automatic alzheimer’s disease detection model. Comput Biol Med. 2021;137: 104828.
Zhou Y, Lu Y, Pei Z. Intelligent diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on internet of things monitoring system and deep learning classification method. Microprocess Microsyst. 2021;83: 104007.
Helaly HA, Badawy M, Haikal AY. Deep learning approach for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Cogn Comput. 2022;14(5):1711–27.
Alvi AM, Siuly S, Wang H, Wang K, Whittaker F. A deep learning based framework for diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment. Knowl-Based Syst. 2022;248: 108815.
Petti U, Baker S, Korhonen A. A systematic literature review of automatic Alzheimer’s disease detection from speech and language. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(11):1784–97.
Alvi AM, Siuly S, De Cola MC, Wang H. Dram-net: A deep residual alzheimer's diseases and mild cognitive impairment detection network using eeg data. In International Conference on Health Information Science (pp. 42–53). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, (2022).
Alvi AM, Siuly S, Wang H. A long short-term memory based framework for early detection of mild cognitive impairment from EEG signals. IEEE Trans Emerg Topics Comput Intell. 2022;7(2):375–88.
Comput (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-023-04683-w
Ebrahimi A, Luo S. Disease neuroimaging initiative, FTAS: convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease detection on MRI images. J Med Imaging. 2021;8(2):024503–024503.
Alvi AM, Siuly S, Wang H. Developing a deep learning based approach for anomalies detection from EEG data. In International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering (pp. 591–602). Cham: Springer International Publishing. (2021).
Al-Shoukry S, Rassem TH, Makbol NM. Alzheimer’s diseases detection by using deep learning algorithms: a mini-review. IEEE Access. 2020;8:77131–41.
Dogan S, Baygin M, Tasci B, Loh HW, Barua PD, Tuncer T, Acharya UR. Primate brain pattern-based automated Alzheimer’s disease detection model using EEG signals. Cogn Neurodyn. 2023;17(3):647–59.
Alvi AM, Siuly S, Wang H. Challenges in electroencephalography data processing using machine learning approaches. In Australasian Database Conference (pp. 177–184). Cham: Springer International Publishing (2022).
Saab S Jr, Fu Y, Ray A, Hauser M. A dynamically stabilized recurrent neural network. Neural Process Lett. 2022;54(2):1195–209.
El-Dabah MA, Hassan MH, Kamel S, Zawbaa HM. Robust parameters tuning of different power system stabilizers using a quantum artificial gorilla troops optimizer. IEEE Access. 2022;10:82560–79.
Karthick R, Senthilselvi A, Meenalochini P, Senthil Pandi S. An optimal partitioning and floor planning for VLSI circuit design based on a hybrid bio-inspired whale optimization and adaptive bird swarm optimization (WO-ABSO) algorithm. J Circuits, Syst Comput. 2023;32(08):2350273.
Karthick R, Dawood MS, Meenalochini P. Analysis of vital signs using remote photoplethysmography (RPPG). J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2023;14(12):16729–39.
Meenalochini P, Karthick R, Sakthivel E. An Efficient Control Strategy for an Extended Switched Coupled Inductor Quasi-Z-Source Inverter for 3Φ Grid Connected System. J Circuits, SystComput (2023).
Jasper Gnana Chandran J, Karthick R, Rajagopal R, Meenalochini P. Dual-channel capsule generative adversarial network optimized with golden eagle optimization for pediatric bone age assessment from hand X-ray image. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell. 2023;37(02):2354001.
Zhang M, Liu J, Wang Y, Piao Y, Yao S, Ji W, Li J, Lu H, Luo Z. Dynamic context-sensitive filtering network for video salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 1553–1563),(2021).
Zhang K, Ma C, Xu Y, Chen P, Du J. Feature extraction method based on adaptive and concise empirical wavelet transform and its applications in bearing fault diagnosis. Measurement. 2021;172: 108976.
Loddo A, Buttau S, Di Ruberto C. Deep learning based pipelines for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis: a comparative study and a novel deep-ensemble method. Comput Biol Med. 2022;141: 105032.
Rad EM, Azarnoosh M, Ghoshuni M, Khalilzadeh MM. Diagnosis of mild Alzheimer’s disease by EEG and ERP signals using linear and nonlinear classifiers. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021;70: 103049.
Rodrigues PM, Bispo BC, Garrett C, Alves D, Teixeira JP, Freitas D. Lacsogram: a new EEG tool to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021;25(9):3384–95.
Safi MS, Safi SMM. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease from EEG signals using Hjorth parameters. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021;65: 102338.
AlSharabi K, Salamah YB, Abdurraqeeb AM, Aljalal M, Alturki FA. EEG signal processing for Alzheimer’s disorders using discrete wavelet transform and machine learning approaches. IEEE Access. 2022;10:89781–97.
Alvi AM, Siuly S, Wang H. Neurological abnormality detection from electroencephalography data: a review. Artif Intell Rev. 2022;55(3):2275–312.
Kibriya H, Masood M, Nawaz M, Nazir T. Multiclass classification of brain tumors using a novel CNN architecture. Multimed Tools Appl. 2022;81(21):29847–63.
Puri DV, Nalbalwar SL, Nandgaonkar AB, Gawande JP, Wagh A. Automatic detection of Alzheimer’s disease from EEG signals using low-complexity orthogonal wavelet filter banks. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023;81: 104439.
Rajagopal RK, Karthick R, Meenalochini P, Kalaichelvi T. Deep convolutional spiking neural network optimized with arithmetic optimization algorithm for lung disease detection using chest X-ray images. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023;79: 104197.
Karthick R, Senthilselvi A, Meenalochini P, Senthil Pandi S. Design and analysis of linear phase finite impulse response filter using water strider optimization algorithm in FPGA. Circuits, Syst Signal Process. 2022;41(9):5254–82.
Karthick R, Sundararajan M. SPIDER-based out-of-order execution scheme for Ht-MPSOC. Int J Adv Intell Paradig. 2021;19(1):28–41.
Karthick R, Meenalochini P. Implementation of data cache block (DCB) in shared processor using field-programmable gate array (FPGA). Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka. (2020);48(4).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. G. Sudha—(Corresponding Author)—Conceptualization Methodology, Original draft preparation. Dr. N. Saravanan – Supervision. Dr. M. Muthalakshmi –Supervision. Mrs. M. Birunda -Supervision.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sudha, G., Saravanan, N., Muthalakshmi, M. et al. Dynamically stabilized recurrent neural network optimized with Artificial Gorilla Troops espoused Alzheimer’s disorder detection using EEG signals. Health Inf Sci Syst 12, 25 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-024-00284-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-024-00284-9