Abstract
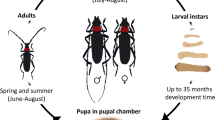
The mason bee Osmia excavata Alfken is an apple pollinating insect widely distributed in northern China, in order to effectively utilize the mason bee and improve the pollination rate of apples, there is a need to evaluate the pollination efficiency of the bees. This study evaluated the pollination efficiency of the mason bee on apple orchards in Jinan and Yantai, Shandong Province, China. The study compared natural pollination areas and pollination areas with different release densities of O. excavata in terms of the effects of bee density, timing of pollination, and distance effects on fruit set rate, fruit shape index, fruit shape skewness, fruit soluble solids content, and fruit firmness. The optimal release density of bees was 6000 cocoons per hectare, resulting in the highest fruit setting rate of apple lateral flowers. From 07:00 to 14:00 was the best time for bee pollination. The optimal distance of hives from apple trees for pollination by O. excavata was 60 m. Single fruit weight was significantly higher and fruit unsymmetrical rate, partial slope and hardness were all significantly lower at the release densities of 6000 or 12000 cocoons per hectare compared with 3000 cocoons per hectare or under natural pollination conditions. There was no significant difference in the content of soluble solids under different release densities. Thus, the radius of 60 m from the hive was the effective pollination range and 6000 cocoons per hectare of mason bees could ensure the fruit quality of apple.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confrm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Adamson NL, Roulston TH, Fell RD, Mullins DE (2012) From April to August-wild bees pollinating crops through the growing season in Virginia. USA Environ Entomol 41:813–821
Antonio F, Sagona S, Coppola F, Boni CB, Pinzauti M (2013) Effect of Ageing in the Mating Behaviour Sequence of Osmia cornuta Latr. (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Insects 14:1–11
Cao YB, Zhou XH, Ye BH, Li LL, Lu ZB, Xu H, Li WQ, Yu Y, Men XY (2017) Factors limiting Osmia excavata Alfken populations. Chin J Appl Entomol 54:652–659
Dong XY, Jin Z, Xi JY, Liu F (2012) Effects of different pollination methods on apple quality. Mod Agr Sci Technol 41(127):129
Fu BC, Yang JF (2014) Application of common pollination bees in facility agriculture. J Shanxi Agr Sci 42:925–928
Guo Y, Shen JS, Zhang YY, Shao YQ, Han XQ (2010) Study on the technology of pollination and increase for apple production by honeybee. Apic China 61:36–37
Holzschuh A, Dudenhoffer JH, Tscharntke T (2012) Landscapes with wild bee habitats enhance pollination, fruit set and yield of sweet cherry. Biol Conserv 153:101–107
Ji X, Guo SX, Sun X, Zhao RX, Liu YX, Dai HY, Zhan YG (2017) Flowering and pollination habit and fluorescence microexamination of pollen tube germination of ornamental aplle strains. Shandong Agr Sci 49(34–38):45
Liu C, Bu HD, Gu GJ, Cheng XM, Liu YJ, Wang GP (2014) Osmia excavata Alfken pollination and influence on fruit setting of cold area fruit trees. Forest By-Prod Spec China 29:8–10
Liu L, Li LL, Ouyang F, Li C, Yu Y, Qu CH, Qu ZL, Ye BH, Men XY (2019) Fruit-setting and yield increase for apple pollination by Osmia excavata Alfken and evaluation of economic value in Shandong Province. Apic China 70:65–68
Men XY, Li LL, Lu ZB, Ouyang F, Liu L, Xu H, Yu Y (2018) Biological characteristics and pollination service of mason bee. Chin J Appl Entomol 55:973–983
Nunes-Silva P, Witter S, da Rosa JM, Halinski R, Schlemmer LM, Arioli CJ, Ramos JD, Botton M, Blochtein B (2020) Diversity of floral visitors in apple orchards: influence on fruit characteristics depends on apple cultivar. Neotrop Entomol 49:511–524
Qiang XM (2019) Thoughts and suggestions on improving quality and efficiency of apple. Northwest Horticult 32:8–9
Shen JS, Ma WH, Wu WQ, Song HL, Zhang XF, Shao YQ (2016) Effect of colony put way on fruit setting rate of Malus pumila Mill. J Shanxi Agr Sci 44:962–964
Su R, Zhang XW, Dong K, Qin YH, Liang C (2014) Present research on apple pollination in China. Chin Agr Sci Bull 30:1–5
Torchio PF (1985) Field experiments with the pollinator species, Osmia lignaria propinqua Cresson, in apple orchards 5. (1979–1980), methods of introducing bees, nesting success, seed counts, fruit yields (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae). J Kansas Entomol Soc 58:448–464
Wang GP, Wang JZ (2017) Study and application of mason bee pollination technology for fruit trees. Northwest Horticult 30:14–16
Wang FH, Yang P (2008) The pollination of mason bees on several fruit trees in China and its application. Knowl Entomol 54:862–868
Wang GP, Zha YL, Ma M, Liu C, Wang JZ (2013) Studies on the biological characteristics and pollination effects of mason bee pollination in different apple producing areas. Chin Agr Sci Bull 29:171–176
Wang GP, Lin LH, Xue XM, Wang JZ, Tao JH (2018a) Research and application progress of Osmia pollnation techniques on apple in China. Deciduous Fruits 50:25–28
Wang LN, Yan Z, Ouyang F, Xiao YL, Qu CH, Ye BH, Men XY (2018b) Releasing Osmia excavata Alfken pheromones increases pollination activity and improves fruit set and quality. Chin J Appl Entomol 55:994–1000
Wang GP, Nei PX, Wang JZ (2019) Efficient light and simplified pollination technology for apple orchards. Northwest Horticult 32:17–19
Wei SG, Wang R (1990) Improving fruit setting rate and yield of apple trees by using Osmia cornifrons (Radoszkowski). China Fruits 32:31–32
Wei YP, Yuan F, Zhang YL (2000) Flower visiting habits and the essential number of Osmia excavata Alfken for economic apple production. J Northwest A F Univ 28:76–79
Wu CC, Li PB, Cao ML, Cao CR, Yang LL, Ren WB, Liu HM (2015) Behavioral characteristics of China and its application prospects in crop pollination. Chin Agr Sci Bull 31:40–44
Xiao YL, Tang WY, Liu CH, Yu K, Gong Y, Yang QM, Zhang YG, Qu CH, Wang LP, Guo D, Yu YL (2019) Analysis of the pollinating services provided by Osmia cornifrous (Rodoszkouski) and Apis mellifera ligustica Spin in apple and cherry orchards. Chin J Appl Entomol 56:1235–1242
Xu HL, Yang L, Kwon YJ (1995) Current status on the utilization of Osmia bees as pollinators of fruit trees in China (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). J Apic 10:111–116
Yan Z, Wang LN, Men XY, Xiao YL, Ge F, Ouyang F (2018) Effect of maintaining surrounding habitat near apple orchards on Osmia excavata (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Chin J Appl Entomol 55:1007–1015
Zhang CT, Sun WG (2012) Pollination and effect on fruit set by mason bee in apple orchard. J Hebei Forest Sci Technol 40(14–15):21
Zhao KC, Pang JF (1997) Artificial pollination technology of apple. J Hebei Forest Sci Technol 25:51–52
Zhao JY (2019) A Preliminary study on the diapause of the Osmia excavata Alfken and a survey of the status of population damage. Master dissertation, Yantai University, Yantai
Funding
This research was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020QC133), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, and Key R&D Program of Shandong Province (2019GSF107049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY and ZL conceived and designed the research. TZ, LN, MF, KY and LL conducted the experiments. YM and MS analyzed the data. ZL and MS wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Edited by Márcia M Maués
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Z., Feng, M., Nie, L. et al. Evaluation of the Pollination Efficiency of Apple Trees by Osmia excavata Alfken (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Neotrop Entomol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-023-01122-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-023-01122-5