Abstract
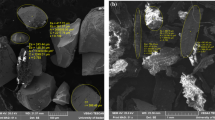
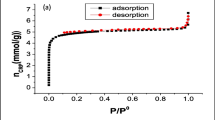
In the present study, the integration of magnetic dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction (MD-µSPE) with hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME) prior to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was developed to preconcentrate and determine trace amounts of chlorpyrifos pesticide. Azolla filiculoides fern biomass was loaded by magnetite nanoparticles to prepare magnetic adsorbent (azolla@Fe3O4). The structural characteristics of the produced magnetic nanocomposites (MNCs) were investigated by FESEM, TEM, VSM, FTIR, EDX, and XRD methods. In the proposed MD-µSPE/HF-LPME method, the adsorption/desorption variables in MD-µSPE step were optimized by Taguchi fractional factorial design. After chlorpyrifos adsorption in the optimized condition of MD-µSPE (Vsample = 50 mL, contact time = 15 min, solution pH = 3, adsorbent mass = 0.05 g, ionic strength = 0.01 mol L−1, and eluent type = ethanol), 2.0 mL of the desorbed ethanolic solution was added to 16 mL of 10% (w/v) NaCl aqueous solution for the next HF-LPME method and the final analysis was performed by GC/MS. The developed method showed a limit of detection of 0.05 μg L−1, a limit of quantification of 0.5 μg L−1, a dynamic linear range of 0.5–1000.0 μg L−1, preconcentration factors between 700 and 1050, and a repeatability (RSD%) of 6.9%. The suitability of the MD-µSPE/HF-LPME method was confirmed by measuring chlorpyrifos in real samples with relative recoveries in the range of 97.0–108.5%. The results showed good accuracy and precision of the developed MD-µSPE/HF-LPME method for the preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of chlorpyrifos in the aqueous samples.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this paper are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
E.A. Serna-Galvis, J. Porras, R.A. Torres-Palma, A critical review on the sonochemical degradation of organic pollutants in urine, seawater, and mineral water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 82, 105861 (2022)
M. Iaquinta, M. Stoller, C. Merli, Optimization of a nanofiltration membrane process for tomato industry wastewater effluent treatment. Desalination 245, 314–320 (2009)
S.K. Zahraei, A. Salemi, T.C. Schmidt, Sample preparation for determination of water taste and odor compounds: a review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 32, e00149 (2021)
C. Campanale, C. Massarelli, D. Losacco, D. Bisaccia, M. Triozzi, V.F. Uricchio, The monitoring of pesticides in water matrices and the analytical criticalities: a review. Trends Anal. Chem. 144, 116423 (2021)
F. Almomani, R. Bhosale, M. Khraisheh, A. Kumar, T. Almomani, Heavy metal ions removal from industrial wastewater using magnetic nanoparticles (MNP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144924 (2020)
H.M. Hamadeen, E.A. Elkhatib, M.E.I. Badawy, S.A.M. Abdelgaleil, Arab. J. Chem. 14, 102981 (2021)
K. Bano, S. Kaushal, P.P. Singh, A review on photocatalytic degradation of hazardous pesticides using heterojunctions. Polyhedron 209, 115465 (2021)
S. Noore, G. Ramesh, S.E. Vendan, V.D. Nagaraju, Persistence and diffusion behaviour of chlorpyrifos in five different species of vegetables: a comparative analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 217, 112208 (2021)
M. Nozari, Sh. Shariati, Poly(methacrylic acid) surface modified magnetite nanoparticles for dispersive solid-phase adsorption of chlorpyrifos pesticide from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 289, 163–179 (2023)
S.A. Asbchin, A.N. Omran, N. Jafari, Potential of Azolla filiculoides in the removal of Ni and Cu from wastewaters. African J. Biotechnol. 11(95), 16158–16164 (2012)
W. Raja, P. Rathaur, S.A. John, P.W. Ramteke, Azolla: an aquatic pteridophyte with great potential. Int. J. Res. Biol. Sci. 2(2), 68–72 (2012)
F. Shariati, S. Shariati, M.A.A. Moghaddam, Application of magnetite nanoparticles modified azolla as an adsorbent for removal of reactive yellow dye from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 212, 323–332 (2021)
N. Besharati, N. Alizadeh, S. Shariati, Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by azolla, fig leaves, eggshell and egg membrane modified with magnetite nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 225, 214–224 (2021)
C.F. Poole, New trends in solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 22(6), 362–373 (2003)
M.N. Oviedo, C.E. Luján, A.A. Lemos, M.B. Botella, M. Llaver, R.G. Wuilloud, An overview of preconcentration techniques combined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for trace element determination in biological studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 416, 2641–2656 (2024)
Z. Jafari, M. Ghani, Magnetic carbonized cellulose-MIL 101(Fe) composite as a sorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of selected organophosphorus pesticides combined with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection. Talanta Open. 7, 100212 (2023)
S. Shariati, N. Parto, E. Bozorgzadeh, P. Zanjanchi, S. Rahnama, Magnetic solid phase preconcentration of cadmium in water samples using sulfonic acid functionalized Kit-6 magnetite mesoporous nanocomposites followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 17, 3375–3382 (2020)
F.T. Rad, H. Kefayati, S. Shariati, Synthesis of propyl aminopyridine modified magnetite nanoparticles for cadmium (II) adsorption in aqueous solutions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33(2), e4732 (2019)
R. Kouchakinejad, S. Shariati, J. Abolhasani, E.G. Kalhor, M.T. Vardini, Core-shells of magnetite nanoparticles decorated by SBA-3-SO3H mesoporous silica for magnetic solid phase adsorption of paraquat herbicide from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 643, 128709 (2022)
A. Hoseinzadeh, H. Heidari, A.A. Matin, M. Soylak, Multi-response optimization of a deep eutectic solvent-based microextraction method for the simultaneous extraction of twenty organochlorine pesticides for monitoring in various water samples. Microchem. J. 194, 109226 (2023)
F. Darvishnejad, J.B. Raoof, M. Ghani, In-situ synthesis of nanocubic cobalt oxide @ graphene oxide nanocomposite reinforce d hollow fib er-solid phase microextraction for enrichment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from human urine prior to their quantification via high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1641, 461984 (2021)
A. Esrafili, Y. Yamini, S. Shariati, Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for extraction and determination of some antidepressant drugs in biological fluids. Anal. Chim. Acta 604(2), 127–133 (2007)
S. Shariati, Y. Yamini, A. Esrafili, Carrier mediated hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction combined with HPLC-UV for preconcentration and determination of some tetracycline antibiotics. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 877(4), 393–400 (2009)
M. Ganjikhah, S. Shariati, E. Bozorgzadeh, Preconcentration and spectrophotometric determination of trace amount of formaldehyde using hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction based on derivatization by Hantzsch reaction. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 14, 763–769 (2017)
M. Arvand, E. Bozorgzadeh, S. Shariati, Two-phase hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for preconcentration of pyrethroid pesticides residues in some fruits and vegetable juices prior to gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 31(2), 275–283 (2013)
M. Faraji, S. Shariati, Y. Yamini, M. Adeli, Preconcentration of trace amounts of lead in water samples with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide coated magnetite nanoparticles and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Arab. J. Chem. 9(2), S1540–S1546 (2016)
H. Sahebi, E. Konoz, A. Ezabadi, A. Niazi, S.H. Ahmadi, Simultaneous determination of five penicillins in milk using a new ionic liquid-modified magnetic nanoparticle based dispersive micro-solid phase extraction followed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 154, 104605 (2020)
J. Hong, X. Liu, X. Yang, Y. Wang, L. Zhao, Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by magnetic solid-phase extraction for determination of quinolones. Microchim. Acta 189(8), 1–10 (2022)
F. Monajemzadeh, A. Mohebbi, M.A. Farajzadeh, M. Nemati, M.R.A. Mogaddam, Dispersive solid phase extraction combined with in syringe deep eutectic solvent based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of some pesticides and their metabolite in egg samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 96, 103696 (2021)
N. Khodaee, A. Mehdinia, R. Esfandiarnejad, A. Jabbari, Ultra trace analysis of PAHs by designing simple injection of large amounts of analytes through the sample reconcentration on SPME fi ber after magnetic solid phase extraction. Talanta 147, 59–62 (2016)
X. Li, D. Zeng, Y. Liao, M. Tsunoda, Y. Zhang, X. Xie, R. Wang, L. Li, W. Hu, S. Deng, Y. Song, Magnetic nanoparticle-assisted in situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of pyrethroid pesticides in urine samples. Microchem. J. 159, 105350 (2020)
X. Gao, K. Xu, M. Chi, J. Li, L. Suo, L. Zhu, K. Chen, J. Mu, Determination of four parabens in cosmetics by high-performance liquid chromatography with magnetic solid-phase and ionic dispersive liquid–liquid extraction. Rev. Anal. Chem. 40(1), 161–172 (2021)
M. Darvishi, S. Shariati, F. Safa, A. Islamnezhad, Surface blocking of azolla modified copper electrode for trace determination of phthalic acid esters as the molecular barricades by differential pulse voltammetry: response surface modelling optimized biosensor. RSC Adv. 11, 32630–32646 (2021)
S. Toutounchi, S. Shariati, K. Mahanpoor, Application of magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon nanocomposite for the removal of ponceau 4R using factorial experimental design. SILICON 13, 1561–1573 (2021)
S. Rahnama, S. Shariati, F. Divsar, Selective aptamer conjugation to silver-coated magnetite nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction of trace amounts of Pb2+ ions. RSC Adv. 11, 4971–4982 (2021)
M. Eddaoudi, Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(40), 14117 (2005)
K.S.W. Sing, R.T. Williams, Physisorption hysteresis loops and the characterization of nanoporous materials. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 22(10), 773–782 (2004)
Z. Alothman, A review: fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Materials. 5(12), 2874–2902 (2012)
A. Esrafili, Y. Yamini, M. Ghambarian, S. Shariati, M. Moradi, Measurement of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from human plasma using hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction based on carrier mediated transport. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 35(3), 343–354 (2012)
M.R. Hadjmohammadi, M. Peyrovi, P. Biparva, Comparison of C18 silica and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as the adsorbents for the solid-phase extraction of Chlorpyrifos and Phosalone in water samples using HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 33(8), 1044–1051 (2010)
Z.O. Uygun, Y. Dilgin, A novel impedimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode for trace level determination of chlorpyrifos. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 188, 78–84 (2013)
J. Xiong, G. Zhou, Z. Guan, X. Tang, Q. He, L. Wu, Determination of chlorpyrifos and its main degradation product TCP in water samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 37(11), 1499–1512 (2014)
H. Mao, Z. Zuo, N. Yang, J.S. Huang, Y. Yan, A microfluidic colorimetric biosensor for chlorpyrifos determination based on peroxidase-like CuFe2O4/GQDs magnetic nanoparticles. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 14(1), 255–269 (2017)
B. Tajdar-oranj, L. Peivasteh-roudsari, V. Mahdavi, A.K. Behbahan, A.M. Khaneghah, Simultaneous multi-determination of pesticide residues in pistachio from Iran’s market: a probabilistic health risk assessment study. J. Food Compos. Anal. 103, 104085 (2021)
M. Rezaee, Application of polypyrrole/Fe3O4 composite for the extraction of chlorpyrifos using magnetic solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J. Anal. Chem. 76(12), 1422–1429 (2021)
R.A. Teixeira, L.A.F. Dinali, H.L. de Oliveira, A.T.M. da Silva, K. BastosBorges, Efficient and selective extraction of azamethiphos and chlorpyrifos residues from mineral water and grape samples using magnetic mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 361, 130116 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Rasht Branch, Islamic Azad University and Forensic Medicine Research Center—General Department of Legal Medicine of Guilan Province for their help.
Funding
There is no funding for supporting this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kouchakinejad, R., Shariati, S., Abolhasani, J. et al. Magnetic dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction integrated with hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction for preconcentration of trace amounts of chlorpyrifos pesticide in aqueous samples. J IRAN CHEM SOC (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-024-03028-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-024-03028-4