Abstract
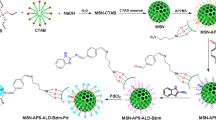
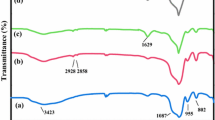
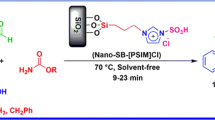
Tetrabutylammonium prolinate ionic liquid (TBAPIL) was prepared, and mesoporous silica nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized. Both of these were linked through propyltriethoxysilane to prepare a reusable catalyst TBAPIL@Si(CH2)3@silica NPs (TBAPILS). The formation of TBAPIL was checked through Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the structure of silica NPs and linking of TBPAIL on it. Transmission electron microscopy proved the flourishing development of silica NPs. Scanning electron microscopy graphs exposed the altering in morphology of silica NPs and TBAPILS. FT-IR analysis also confirmed the formation of TBAPILS catalyst. Moreover, the effectiveness of the TBAPILS was also checked for the synthesis of various derivatives of tetrahydrobenzoxanthenes-11-ones. The formation and structure of obtained compounds were confirmed by FT-IR, elemental analysis, 1HNMR and 13C NMR spectral analysis. The catalyst TBAPILS was found to be used successfully up to five cycles without significant loss of activity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Philippot, P. Serp, Concepts in nanocatalysis. Nanomater. Catal. First Ed. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527656875.ch1
S. Chaturvedi, P.N. Dave, N.K. Shah, Applications of nano-catalyst in new era. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 16, 307–325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.01.015
S.B.Singh, Tandon, P.K., Catalysis : A brief review on Nano-Catalyst Catalysis : A Brief Review on Nano-Catalyst. (2016)
H. Filian, A. Kohzadian, M. Mohammadi, A. Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A. Karami, Pd(0)-guanidine@MCM-41: a very effective catalyst for rapid production of bis (pyrazolyl)methanes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 34, 42–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5579
F. Feizpour, M. Jafarpour, A. Rezaeifard, Band gap modification of TiO2 nanoparticles by ascorbic acid-stabilized pd nanoparticles for photocatalytic suzuki-miyaura and ullmann coupling reactions. Catal. Letters. 149, 1595–1610 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02749-z
A. Agrwal, V. Kasana, [Fesipmim]Cl as highly efficient and reusable catalyst for solventless synthesis of dihydropyridine derivatives through Hantzsch reaction. J. Chem. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-020-01770-9
M. Nikoorazm, M. Khanmoradi, M. Mohammadi, Guanine-La complex supported onto SBA-15: a novel efficient heterogeneous mesoporous nanocatalyst for one-pot, multi-component Tandem Knoevenagel condensation–Michael addition–cyclization reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 34, 1–18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5504
M. Nikoorazm, M. Mohammadi, M. Khanmoradi, Zirconium@guanine@MCM-41 nanoparticles: an efficient heterogeneous mesoporous nanocatalyst for one-pot, multi-component tandem knoevenagel condensation–michael addition–cyclization reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5704
A. Ghorbani-Choghamarani, M. Mohammadi, R.H.E. Hudson, T. Tamoradi, Boehmite@tryptophan-Pd nanoparticles: a new catalyst for C–C bond formation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4977
I.I. Slowing, B.G. Trewyn, S. Giri, V.S.Y. Lin, Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and biosensing applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17, 1225–1236 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200601191
B. Karimi, D. Zareyee, A high loading sulfonic acid-functionalized ordered nanoporous silica as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for chemoselective deprotection of tert-butyldimethylsilyl ethers. Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 4661–4665 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.04.100
A.R. Karimi, Z. Alimohammadi, M. Mostafa Amini, Wells-Dawson heteropolyacid supported on silica: a highly efficient catalyst for synthesis of 2,4,5-trisubstituted and 1,2,4,5-tetrasubstituted imidazoles. Mol Divers. 14, 635–641 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-009-9197-x
R. Ratti, Ionic liquids: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Adv. Chem. 2014, 1–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/729842
T. Welton, Ionic liquids in catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 248, 2459–2477 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.04.015
J.P. Hallett, T. Welton, Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 111, 3508–3576 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1003248
N. Ferlin, M. Courty, A.N. Van Nhien, S. Gatard, M. Pour, B. Quilty, M. Ghavre, A. Haiß, K. Kümmerer, N. Gathergood, S. Bouquillon, Tetrabutylammonium prolinate-based ionic liquids: aA combined asymmetric catalysis, antimicrobial toxicity and biodegradation assessment. RSC Adv. 3, 26241–26251 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra43785j
U.C. Rajesh, D. Divya, D.S. Rawat, Functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4as an efficient quasi-homogeneous catalyst for multi-component reactions. RSC Adv. 40, 41323–41330 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra06803c
R. Fareghi-Alamdari, M.N. Niri, H. Hazarkhani, A novel hydrogen-bonded silica-supported acidic ionic liquid: An efficient, recyclable and selective heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of diesters. J. Chem. Sci. 130, 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1454-z
H.N. Hafez, M.I. Hegab, I.S. Ahmed-Farag, A.B.A. El-Gazzar, A facile regioselective synthesis of novel spiro-thioxanthene and spiro-xanthene-9′,2-[1,3,4]thiadiazole derivatives as potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 4538–4543 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.07.042
N. Hashim, M. Rahmani, M.A. Sukari, A.M. Ali, N.B. Alitheen, R. Go, H.B.M. Ismail, Two new xanthones from Artocarpus obtusus. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 12, 106–112 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020903450411
E. Vieira, J. Huwyler, S. Jolidon, F. Knoflach, V. Mutel, J. Wichmann, 9H-Xanthene-9-carboxylic acid [1,2,4]oxadiazol-3-yl- and (2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-amides as potent, orally available mGlu1 receptor enhancers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.05.135
F. Zelefack, D. Guilet, N. Fabre, C. Bayet, S. Chevalley, S. Ngouela, B.N. Lenta, A. Valentin, E. Tsamo, M.G. Dijoux-Franca, Cytotoxic and antiplasmodial xanthones from Pentadesma butyracea. J. Nat. Prod. 72, 954–957 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/np8005953
S.J. Tao, S.H. Guan, W. Wang, Z.Q. Lu, G.T. Chen, N. Sha, Q.X. Yue, X. Liu, D.A. Guo, Cytotoxic polyprenylated xanthones from the resin of Garcinia hanburyi. J. Nat. Prod. 72, 117–124 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/np800460b
S. Chatterjee, M. Iqbal, J.C. Kauer, J.P. Mallamo, S. Senadhi, S. Mallya, D. Bozyczko-Coyne, R. Siman, Xanthene derived potent nonpeptidic inhibitors of recombinant human calpain I. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 6, 1619–1622 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(96)00286-7
K. Kikuchi, K. Komatsu, T. Nagano, Zinc sensing for cellular application. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2004.02.007
A.M. El-Brashy, M. El-Sayed Metwally, F.A. El-Sepai, Spectrophotometric determination of some fluoroquinolone antibacterials by binary complex formation with xanthene dyes. Farmaco 59, 809–817 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.farmac.2004.07.001
A. Akbari, A. Hosseini-Nia, Biological evaluation and simple method for the synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthenes-11-one derivatives. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 21, S7–S11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2013.09.009
A. Kumar, S. Sharma, R.A. Maurya, J. Sarkar, Diversity oriented synthesis of benzoxanthene and benzochromene libraries via one-pot, three-component reactions and their anti-proliferative activity. J. Comb. Chem. 12, 20–24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/cc900143h
M.K. Schwaebe, T.J. Moran, J.P. Whitten, Total synthesis of psorospermin. Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 827–829 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2004.12.006
N. Singh, A.K. Shreshtha, M.S. Thakur, S. Patra, Xanthine scaffold: scope and potential in drug development. Heliyon. 4, e00829 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00829
P. Bedi, R. Gupta, T. Pramanik, Synthesis and biological properties of pharmaceutically important xanthones and benzoxanthone analogs: a brief review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 11, 12–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i2.22426
S.L. Niu, Z.L. Li, F. Ji, G.Y. Liu, N. Zhao, X.Q. Liu, Y.K. Jing, H.M. Hua, Xanthones from the stem bark of Garcinia bracteata with growth inhibitory effects against HL-60 cells. Phytochemistry 77, 280–286 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.01.010
J.M. Khurana, D. Magoo, K. Aggarwal, N. Aggarwal, R. Kumar, C. Srivastava, Synthesis of novel 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-thiones and evaluation of their biocidal effects. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 58, 470–477 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.10.025
J. Liu, Z. Diwu, W.Y. Leung, Synthesis and photophysical properties of new fluorinated benzo[c]xanthene dyes as intracellular pH indicators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 2903–2905 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(01)00595-9
R.J. Sarma, J.B. Baruah, One step synthesis of dibenzoxanthenes. Dye. Pigment. 64, 91–92 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.03.010
A. Banerjee, A.K. Mukherjee, Chemical aspects of santalin as a histological stain. Biotech. Histochem. 56, 83–85 (1981). https://doi.org/10.3109/10520298109067286
P. Srihari, S.S. Mandal, J.S.S. Reddy, R.S. Rao, J.S. Yadav, Synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthenes utilizing PMA-SiO2 as an efficient reusable catalyst. Chin. Chem. Lett. 19, 771–774 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2008.05.005
M.T. Maghsoodlou, S.M. Habibi-Khorassani, Z. Shahkarami, N. Maleki, M. Rostamizadeh, An efficient synthesis of 2,2′-arylmethylene bis(3-hydroxy-5,5-dimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1-one) and 1,8-dioxooctahydroxanthenes using ZnO and ZnO-acetyl chloride. Chin. Chem. Lett. 21, 686–689 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2010.02.005
X. Fan, X. Hu, X. Zhang, J. Wang, InCl3·4H2O-promoted green preparation of xanthenedione derivatives in ionic liquids. Can. J. Chem. 83, 16–20 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1139/v04-155
T.-S. Jin, J.-S. Zhang, J.-C. Xiao, A.-Q. Wang, T.-S. Li, Clean synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene derivatives catalyzed by p -dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid in aqueous media. Synlett (2004). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-820022
F. Rajabi, M. Abdollahi, E.S. Diarjani, M.G. Osmolowsky, O.M. Osmolovskaya, P. Gómez-López, A.R. Puente-Santiago, R. Luque, Solvent-free preparation of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthenes employing iron oxide nanomaterials. Materials 12, 2386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152386
Z. Karimi-Jaberi, S.Z. Abbasi, B. Pooladian, M. Jokar, Efficient, one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-ones and dibenzo[a, j]xanthenes using trichloroacetic acid as a solid heterogeneous catalyst under solvent-free conditions. E-Journal Chem. 8, 1895–1899 (2011)
M. Seyyedhamzeh, P. Mirzaei, A. Bazgir, Solvent-free synthesis of aryl-14H-dibenzo[a, j]xanthenes and 1,8-dioxo-octahydro-xanthenes using silica sulfuric acid as catalyst. Dye. Pigment. 76, 836–839 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.02.001
J. Li, W. Tang, L. Lu, W. Su, Strontium triflate catalyzed one-pot condensation of β-naphthol, aldehydes and cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 7117–7120 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.09.129
N.V. Shitole, S.B. Sapkal, B.B. Shingate, M.S. Shingare, A simple and green synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[α]-xanthen-11-one using peg-400 as efficient and recyclable reaction media. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 32, 35–36 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.1.35
B.B.F. Mirjalili, A. Bamoniri, N. Salehi, Synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthenes-11-one derivatives in water promoted by Bi(NO3)3·5H2O. Chemija 23, 118–123 (2012)
S.V. Goswami, P.B. Thorat, S.S. Dhone., S.R. Bhusrae, Phenylboronic acid-catalyzed synthesis of 99-dimethyl-12-phenyl-910- dihydro-8H-benzo[a] xanthen-11(12H)-one derivatives. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 3, 632–635 (2011).
X.J. Sun, J.F. Zhou, P.S. Zhao, Molecular iodine-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-one and diazabenzo[a]anthracene-9,11-dione derivatives under microwave irradiation. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 48, 1347–1350 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.742
J.M. Khurana, D. Magoo, p-TSA-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-ones in ionic liquid and neat conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 4777–4780 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.06.029
B. Das, P. Thirupathi, I. Mahender, V.S. Reddy, Y.K. Rao, Amberlyst-15: An efficient reusable heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthenes and 1,8-dioxo-decahydroacridines. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 247, 233–239 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.11.048
B. Das, P. Thirupathi, K.R. Reddy, B. Ravikanth, L. Nagarapu, An efficient synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthenes using heterogeneous catalysts. Catal. Commun. 8, 535–538 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2006.02.023
M. Litschauer, M.A. Neouze, Nanoparticles connected through an ionic liquid-like network. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 640–646 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/b713442h
M. Mahkam, F. Hosseinzadeh, M. Galehassadi, Preparation of ionic liquid functionalized silica nanoparticles for oral drug delivery. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 03, 391–395 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4236/jbnb.2012.33038
K. Fukumoto, M. Yoshizawa, H. Ohno, Room temperature ionic liquids from 20 natural amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2398–2399 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja043451i
A. Kumari, B. Kaur, R. Srivastava, R.S. Sangwan, Isolation and immobilization of alkaline protease on mesoporous silica and mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite materials for improved catalytic properties. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2, 108–114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.05.009
E.I. Jiménez, W.E.V. Narváez, T. Rocha-Rinza, M. Hernández-Rodríguez, Design and application of a bifunctional organocatalyst guided by electron density topological analyses. Catal. Sci. Technol. 7, 4470–4477 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cy00430c
G.C. Nandi, S. Samai, R. Kumar, M.S. Singh, An efficient one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-one and diazabenzo[a]anthracene-9,11-dione derivatives under solvent free condition. Tetrahedron 65, 7129–7134 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2009.06.024
V. Rama, K. Kanagaraj, K. Pitchumani, A multicomponent, solvent-free, one-pot synthesis of benzoxanthenones catalyzed by HY zeolite: Their anti-microbial and cell imaging studies. Tetrahedron Lett. 53, 1018–1024 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.10.143
Fatahpour, M., Hazeri, N., Maghsoodlou, M.T., Lashkari, M.: Lactic acid: a new application as an efficient catalyst for the green one-pot synthesis of 2-hydroxy-12-aryl-8,9, 10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11-one and 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-one Analogs. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 42, 533–538 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0064-1.
B. Maleki, M. Gholizadeh, Z. Sepehr, 1,3,5-Trichloro-2,4,6-triazinetrion: a versatile heterocycle for the one-pot synthesis of 14-aryl-or alkyl -14H-dibenzo[a, j]xanthene, 1,8-dioxooctahydroxanthene and 12-aryl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthene-11- one derivatives under solvent-free conditions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 32, 1697–1702 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.5.1697
S. Sudha, M.A. Pasha, Ultrasound assisted synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[c]xanthene-11-ones using CAN as catalyst. Ultrason Sonochem. 19, 994–998 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.02.002
J. Li, L. Lu, W. Su, A new strategy for the synthesis of benzoxanthenes catalyzed by proline triflate in water. Tetrahedron Lett. 51, 2434–2437 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.02.149
H. Wang, X. Ren, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Synthesis 12-aryl or 12-alkyl-8,9,10,12-tetrahydrobenzo[a]xanthen-11-one derivatives catalyzed by dodecatungstophosphoric acid. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 20, 1939–1943 (2009)
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar (Uttarakhand), India, for providing necessary research facility and KIET Group of Institutions for constant help and support during the research. We would also thank Manish Kumar, IIT Ropar, for providing NMR spectra and ISFAL, Moga, for providing IR spectra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrwal, A., Kumar, V. & Kasana, V. Preparation and application of highly efficient and reusable TBAPIL@Si(CH2)3@nano-silica-based nano-catalyst for preparation of benzoxanthene derivatives. J IRAN CHEM SOC 18, 2583–2595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02211-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02211-1