Abstract
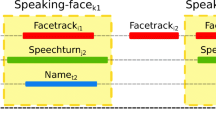
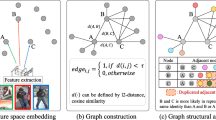
This work introduces a unified framework for mono-, cross- and multi-modal person recognition in multimedia data. Dubbed person instance graph models the person recognition task as a graph mining problem: i.e., finding the best mapping between person instance vertices and identity vertices. Practically, we describe how the approach can be applied to speaker identification in TV broadcast. Then, a solution to the above-mentioned mapping problem is proposed. It relies on integer linear programming to model the problem of clustering person instances based on their identity. We provide an in-depth theoretical definition of the optimization problem. Moreover, we improve two fundamental aspects of our previous related work: the problem constraints and the optimized objective function. Finally, a thorough experimental evaluation of the proposed framework is performed on a publicly available benchmark database. Depending on the graph configuration (i.e., the choice of its vertices and edges), we show that multiple tasks can be addressed interchangeably (e.g., speaker diarization, supervised or unsupervised speaker identification), significantly outperforming state-of-the-art mono-modal approaches.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barras C, Zhu X, Meignier S, Gauvain JL (2006) Multi-stage speaker diarization of broadcast news. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 14(5):1505–1512
Bäuml M, Tapaswi M, Stiefelhagen R (2013) Semi-supervised learning with constraints for person identification in multimedia data. In: International conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Bergstra J, Bengio Y (2012) Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13:281–305
Blondel VD, Guillaume JL, Lambiotte R, Lefebvre E (2008) Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat Mech Theory Exp 2008(10):P10008. doi:10.1088/1742-5468/2008/10/P10008
Bredin H, Chollet G (2007) Audio-visual speech synchrony measure: application to biometrics. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2007(1):070186. doi:10.1155/2007/70186
Bredin H, Poignant J (2013) Integer linear programming for speaker diarization and cross-modal identification in TV broadcast. In: Interspeech 2013, 14th annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Lyon
Canseco L, Lamel L, Gauvain JL (2005) A comparative study using manual and automatic transcriptions for diarization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE automatic speech recognition and understanding, workshop, pp 415–419
Chen SS, Gopalakrishnan P (1998) Speaker, environment and channel change detection and clustering via the Bayesian information criterion. In: DARPA broadcast news transcription and understanding workshop. Virginia
Cour T, Sapp B, Nagle A, Taskar B (2010) Talking pictures: temporal grouping and dialog-supervised person recognition. In: International conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Dimitrova N, Zhang HJ, Shahraray B, Sezan I, Huang T, Zakhor A (2002) Applications of video-content analysis and retrieval. IEEE Multimed 9(3):42–55
Dinarelli M, Rosset S (2011) Models cascade for tree-structured named entity detection. In: Proceedings of 5th international joint conference on natural language processing, Asian Federation of Natural Language processing, Chiang Mai, pp 1269–1278
Dupuy G, Rouvier M, Meignier S, Estève Y (2012) i-Vectors and ILP clustering adapted to cross-show speaker diarization. In: Interspeech 2012, 13th annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association
Estève Y, Meignier S, Deléglise, P, Mauclair J (2007) Extracting true speaker identities from transcriptions. In: Proceedings of interspeech, pp 2601–2604
Finkel JR, Manning CD (2008) Enforcing transitivity in coreference resolution. In: Annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (ACL HLT)
Fiscus JG, Garofolo, JS, Le, AN, Martin, AF, Pallett D, Przybocki MA, Sanders GA (2004) Results of the Fall 2004 STT and MDE evaluation. In: Fall 2004 rich transcription workshop (RT-04). Palisades
Gauvain JL, Lamel L, Adda G (1998) Partitioning and transcription of broadcast news data. In: Proceedings of international conference on spoken language processing (ICSLP 98), Sydney, pp 1335–1338
Gauvain JL, Lamel L, Adda G (2002) The limsi broadcast news transcription system. Speech Commun 37(1–2):89–109
Gauvain JL, Lee CH (1994) Maximum a posteriori estimation for multivariate gaussian mixture observations of markov chains. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 2(2):291–298
Giraudel A, Carré M, Mapelli V, Kahn J, Galibert O, Quintard L (2012) The REPERE corpus: a multimodal corpus for person recognition. In: International conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC)
Gravier G, Adda G, Paulson N, Carré M, Giraudel A, Galibert O (2012) The ETAPE corpus for the evaluation of speech-based TV content processing in the French language. In: International conference on language resources, evaluation and corpora, Turkey
Gurobi Optimization Inc (2012) Gurobi optimizer reference manual. http://www.gurobi.com. Accessed 5 May 2014
Hermansky H (1990) Perceptual linear predictive (PLP) analysis of speech. J Acoust Soc Am 87(4):1738–1752. doi:10.1121/1.399423
Jain AK, Murty MN, Flynn PJ (1999) Data clustering: a review. ACM Comput Surv 31(3):264–323
Jousse V, Petitrenaud S, Meignier S, Estève Y, Jacquin C (2009) Automatic named identification of speakers using diarization and ASR systems. In: ICASSP 2009, IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, Taïpei
Lawto J, Gauvain JL, Lamel L, Grefenstette G, Gravier G, Despres J, Guinaudeau C, Sebillot P (2011) A scalable video search engine based on audio content indexing and topic segmentation. In: Networked and electronic media (NEM) summit : implementing future media internet
Le VB, Barras C, Ferras M (2010) On the use of GSV-SVM for speaker diarization and tracking. In: Proceedings of Odyssey 2010—the speaker and language recognition workshop, Brno, pp 146–150
Long B, Zhang MZ, Yu PS, Tianbing X (2008) Clustering on complex graphs. In: Proceedings of the twenty-third AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Mauclair J, Meignier S, Estève Y (2006) Speaker diarization: about whom the speaker is talking? In: IEEE Odyssey
Mouysset S, Noailles J, Ruiz D, Guivarch R (2011) On a strategy for spectral clustering with parallel computation. High Perform Comput Comput Sci VECPAR 2010:408–420
Newman MEJ (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(23):8577–8582
Pan JY, Yang HJ, Faloutsos C (2004) MMSS: Multi-modal story-oriented video summarization. In: Proceedings of the fourth IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM)
Pan JY, Yang HJ, Faloutsos C, Duygulu P (2004) Automatic multimedia cross-modal correlation discovery. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGKDD conference
Pelecanos J, Sridharan S (2001) Feature warping for robust speaker verification. In: Proceedings of Odyssey 2001—the speaker recognition workshop, Crete, pp 213–218
Pelleg D, Moore AW (2000) X-means: extending K-means with efficient estimation of the number of clusters. Proceedings of the seventeenth international conference on machine learning, ICML ’00Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, pp 727–734
Poignant J, Besacier L, Le VB, Rosset S, Quénot G (2013) Unsupervised naming of speakers in broadcast TV: using written names, pronounced names or both? In: Interspeech 2013, 14th annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Lyon
Poignant J, Besacier L, Quénot G, Thollard F (2012) From text detection in videos to person identification. In: International conference on multimedia and expo (ICME)
Poignant J, Bredin H, Le VB, Besacier L, Barras C, Quénot G (2012) Unsupervised speaker identification using overlaid texts in TV broadcast. In: Interspeech 2012, 13th annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Portland
Reynolds DA, Quatieri TF, Dunn RB (2000) Speaker verification using adapted gaussian mixture models. Digit Signal Process 10(1–3):19–41
Smeulders A, Worring M, Santini S, Gupta A, Jain R (2000) Content-based image retrieval at the end of the early years. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(12):1349–1380
Smith R (2007) An overview of the tesseract OCR engine. In: Proceedings of the ninth international conference on document analysis and recognition, vol 02, ICDAR ’07IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 629–633
Tranter SE (2006) Who really spoke when? Finding speaker turns and identities in broadcast news audio. In: Proceedings of the ICASSP, pp 1013–1016
Wang Y, Liu Z, Huang JC (2000) Multimedia content analysis-using both audio and visual clues. IEEE Signal Process Mag 17(6):12–36
Acknowledgments
This work was partly realized as part of the Quaero Program and the QCompere project, respectively funded by OSEO (French State agency for innovation) and ANR (French national research agency). Thanks to Johann Poignant for providing the output of video OCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bredin, H., Roy, A., Le, VB. et al. Person instance graphs for mono-, cross- and multi-modal person recognition in multimedia data: application to speaker identification in TV broadcast. Int J Multimed Info Retr 3, 161–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-014-0055-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-014-0055-y