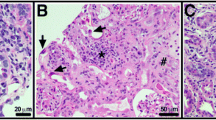
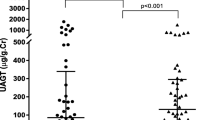
Abstract
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) is a rare syndrome in which idiopathic interstitial nephritis coexists with chronic recurrent uveitis. This syndrome often represents systemic disorders such as arthralgia, rash, prolonged fever, anaemia and ocular symptoms that require medication including glucocorticoid administration. Recently, novel urinary biomarkers, such as kidney injury molecule-1, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and liver-type fatty acid-binding protein, were shown to be associated with tubulointerstitial damage and were elevated in interstitial nephritis. We evaluated these urinary biomarkers in a case of TINU syndrome before and during treatment and found that their levels were elevated at onset and decreased during treatment, especially NGAL. We conclude that these urinary biomarkers are useful to evaluate and predict prognosis in interstitial nephritis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobrin RS, Vernier RL, Fish AL. Acute eosinophilic interstitial nephritis and renal failure with bone marrow-lymph node granulomas and anterior uveitits. A new syndrome. AmJ Med. 1975;59:325–33.
Vohra S, Eddy A, Levin AV, Taylor G, Laxer RM. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis in children and adolescents. Pediatr Nephrol. 1999;13:426–32.
Takemura T, Okada M, Hino S, et al. Course and outcome of Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Am J Kid Dis. 1999;34:1016–21.
Li C, Su T, Chu R, Li X. Yang L. Tubulointerstitial nephritis with uveitis in Chinese adults. Clin J Am Nephrol. 2014;9:21–8.
Nozaki Y, Kinoshita K, Yano T, et al. Estimation of kindey injury molecule-1(Kim-1) in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2014;23:769–77.
Sinnamon KT, Courtney AE, Harron C, O’Rourke DM, Mullan RN. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) syndrome: epidemiology, diagnosis and management. NDT Plus. 2008;1:112–6.
Legendre M, Devilliers H, Perad L, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics, treatment, and outcomes of tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome in adults: a national retrospective strobe-compliant study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e3964.
Mandeville JT, Levinson RD, Holland GN. The tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001;46:195–208.
Yu Wu L, Yang T, Su C, Wang G, Liu Xiao-mei, Li. Pathological significance of panel of urinary biomarkers in patients with drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis. Clin J AmSoc Nephrol. 2010;5:1954–59.
Mori K, Nakao K. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as the real-time indicator of active kidney damage. Kidney Int. 2007;71:967–70.
Cowland JB, Sorensen OE, Sehested M, Borregaard N. Neutrophil gelatinase- associated lipocalin is up-regulated in human epithelial cells by IL-1 beta, but not by TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 2003;171:6630–39.
Kuwabara T, Mori K, Mukoyama M, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels reflect damage to glomeruli, proximal tubules, and distal nephrons. Kidney Int. 2009;75:285–94.
Ichimura T, Joseph V, Boncentre, Veronique, Bailly, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1, a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4135–42.
van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly V, Bakker SJL, van Goor H, Stegeman CA. Tubular kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J Pathol. 2007;212:209–17.
Ichimura T, Asseldonk EJ, Humphreys BD, Gunaratnam L, Duffield JS, Bonventre JV. Kidney injury molecule-1 is a phosphatidylserine receptor that confers a phagocytic phenotype on epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:1657–68.
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Obama A, et al. Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein attenuates renal injury induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Pathol. 2006;169:1107–17.
Ferguson MA, Vaidya VS, Waikar SS, et al. Urinary liver-type fatty acid protein predicts adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2010;77:708–14.
Tanaka T, Doi K, Maeda-Mamiya R, et al. Urinary L-type fatty acid-binding protein can reflect renal tubulointerstitial injury. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:1203–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants including in this case report.
Ethical standards
All procedures followed have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, M. Measurement of urinary biomarkers in a case of tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome during glucocorticoid treatment. CEN Case Rep 7, 221–224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-018-0330-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-018-0330-5