Abstract
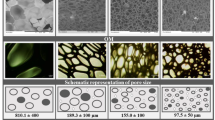
The development of durable and effective antibacterial materials has been a research hotspot. Here, we reported a new kind of long-lasting stable antibacterial material [Cu-metal–organic framework (MOF)-embedded polyethylene (PE)/ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), namely Cu-MOF-embedded PE/EVA] through extrusion foaming, and its structure was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The degree of agglomeration or cluster formation, thermal stability, and melting point temperature of different contents of Cu-MOF/PE/EVA foams were evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), respectively. The results indicated that with the increase of Cu-MOF content, the average size and swelling ratio for foams increased, instead, the density decreased. Besides, the surface gradually showed good hydrophobicity. Remarkably, the water absorption rate was nearly 8 times that of pure PE/EVA when the Cu-MOF content reached 3%. Since Cu-MOF is stably embedded in the foaming structure and well dispersed, it can release Cu2+ at a rate of about 37 ppb/day in foams containing 3% Cu-MOF, which not only maintains the antimicrobial capacity up to 99.2%, but also have no cytotoxicity. Finally, a promising new candidate for medical material with excellent, durable antibacterial ability was proposed.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Jahromi LP, Shahbazi M, Maleki A, Azadi A, Santos HA (2021) Chemically engineered immune cell-derived microrobots and biomimetic nanoparticles: emerging biodiagnostic and therapeutic tools. Adv Sci 8:2002499
Shima K, Coopmeiners J, Graspeuntner S, Dalhoff K, Rupp J (2016) Impact of micro-environmental changes on respiratory tract infections with intracellular bacteria. FEBS Lett 590:3887–3904
Yang J, Yang Y (2020) Metal-organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Small 16:1906846
Amiri S, Rahimi A (2019) Poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanofibers containing cinnamon essential oil nanocapsules: a promising technique for controlled release and high solubility. J Ind Text 48:1527–1544
Fasciani C, Silvero MJ, Anghel MA, Argüello GA, Becerra MC, Scaiano JC (2014) Aspartame-stabilized gold–silver bimetallic biocompatible nanostructures with plasmonic photothermal properties, antibacterial activity, and long-term stability. J Am Chem Soc 136:17394–17397
Pelaez M, Nolan NT, Pillai SC, Seery MK, Falaras P, Kontos AG, Dunlop PSM, Hamilton JWJ, Byrne JA, O’Shea K, Entezari MH, Dionysiou DD (2012) A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl Catal B Environ 125:331–349
Alig I, Pötschke P, Lellinger D, Lellinger D, Skipa T, Pegel S, Kasaliwal GR, Villmow T (2012) Establishment, morphology and properties of carbon nanotube networks in polymer melts. Polymer 53:4–28
Santo CE, Quaranta D, Grass G (2012) Antimicrobial metallic copper surfaces kill Staphylococcus haemolyticus via membrane damage. MicrobiologyOpen 1:46–52
Abbasi AR, Akhbari K, Morsali A (2012) Dense coating of surface mounted CuBTC metal-organic framework nanostructures on silk fibers, prepared by layer-by-layer method under ultrasound irradiation with antibacterial activity. Ultrason Sonochem 19:846–852
Chui SSY, Lo SMF, Charmant JPH, Orpen AG, Williams ID (1999) A chemically functionalizable nanoporous material [Cu3(TMA)2(HO)3]n. Science 283:1148–1150
Liang S, Wu XL, Xiong J, Zong MH, Lou WY (2020) Metal-organic frameworks as novel matrices for efficient enzyme immobilization: an update review. Coord Chem Rev 406:213149
Petit C, Burress J, Bandosz TJ (2011) The synthesis and characterization of copper-based metal–organic framework/graphite oxide composites. Carbon 49:563–572
Mombini S, Mohammadnejad J, Bakhshandeh B, Narmani A, Nourmohammadi J, Vahdat S, Zirak S (2019) Chitosan-PVA-CNT nanofibers as electrically conductive scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 140:278–287
Shafek R, Michael H, Zaky Sayed A, Ibrahim AG, Al-sayed A (2018) Phytochemical study, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Brassica rapa L. leaves extract and its silver nanoparticles. Egypt J Chem 61:237–247
Wu T, Xu W, Guo K, Xie H, Qu JP (2021) Efficient fabrication of lightweight polyethylene foam with robust and durable superhydrophobicity for self-cleaning and anti-icing applications. Chem Eng J 407:127100
Xu X, Lu G, Yang J, Liu X (2020) Mechanism and rheological properties of high-modulus asphalt. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:e8795429
Haque MM, Hasan M (2018) Influence of fiber surface treatment on physico-mechanical properties of betel nut and glass fiber reinforced hybrid polyethylene composites. Adv Mater Proc Technol 4:511–525
Roy S, Darabdhara J, Ahmaruzzaman M (2023) ZnO-based Cu metal-organic framework (MOF) nanocomposite for boosting and tuning the photocatalytic degradation performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:95673–95691
Kang F, Su Y, Huang X, Zhao ZL, Liu FQ (2023) Microstructure and bactericidal properties of Cu-MOF, Zr-MOF and Fe-MOF. J Cent South Univ 30:3237–3247
Peterson GW, Au K, Tovar TM, Epps THI (2019) Multivariate CuBTC metal-organic framework with enhanced selectivity, stability, compatibility, and processability. Chem Mater 31:8459–8465
Musuc AM, Badea-Doni M, Jecu L, Rusu A, Popa VT (2013) FTIR, XRD, and DSC analysis of the rosemary extract effect on polyethylene structure and biodegradability. J Therm Anal Calorim 114:169–177
Farias GMG, Agrawal P, Hanken RBL, De Araújo JP, De Oliveira ADB, De Mélo TJA (2021) Effect of EVA copolymer containing different VA content on the thermal and rheological properties of bio-based high-density polyethylene/ethylene vinyl acetate blends. J Therm Anal Calorim 146:2127–2139
Hao S, Liu Y (2022) Constructing and synthesizing optimal Cu-BTC and its application in low-temperature denitration. J Mater Sci 57:1689–1702
Wang S, Ye B, An C, Wang J, Li Q (2019) Synergistic effects between Cu metal-organic framework (Cu-MOF) and carbon nanomaterials for the catalyzation of the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP). J Mater Sci 54:4928–4941
Hung KC, Wu JH (2010) Mechanical and interfacial properties of plastic composite panels made from esterified bamboo particles. J Wood Sci 56:216–221
Yasim-Anuar TAT, Ariffin H, Norrrahim MNF, Hassan MA, Tsukegi T, Nishida H (2019) Sustainable one-pot process for the production of cellulose nanofiber and polyethylene/cellulose nanofiber composites. J Clean Prod 207:590–599
Abdul Hamid AR, Osman AF, Mustafa Z, Mandal S, Ananthakrishnan R (2020) Tensile, fatigue and thermomechanical properties of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) nanocomposites incorporating low and high loadings of pre-swelled organically modified montmorillonite. Polym Test 85:106426
Sahebian S, Zebarjad SM, Khaki JV, Sajjadi SA (2009) The effect of nano-sized calcium carbonate on thermodynamic parameters of HDPE. J Mater Proc Technol 209:1310–1317
Harkes G, Feijen J, Dankert J (1991) Adhesion of Escherichia coli on to a series of poly(methacrylates) differing in charge and hydrophobicity. Biomater 12:853–860
Vincent M, Duval RE, Hartemann P, Engels-Deutsch M (2018) Contact killing and antimicrobial properties of copper. J Appl Microbiol 124:1032–1046
Fallahnejad Z, Bakeri G, Fauzi Ismail A (2024) Internally functionalized MnO2 nanotubes in modification of thin-film nanocomposite membranes for water and wastewater treatment. Iran Polym J 33:493–509
Gupta RS, Mandal Samir, Malakar A, Rege S, Safikul Islam SK, Samanta K, Misra A, Bose S (2024) Graphene oxide offers precise molecular sieving, structural integrity, microplastic removal, and closed-loop circularity in water-remediating membranes through a covalent adaptable network. J Mater Chem A 12:321–334
Acknowledgement
This research was financially supported by the University Student Innovation Program (2021R434005) and the Lishui “Higher Education Research” Special Project (No. GJYJ202110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, X., Ye, Z., Liang, J. et al. Copper-based metal organic framework/polymer foams with long-lasting antibacterial effect. Iran Polym J (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-024-01314-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-024-01314-9