Abstract
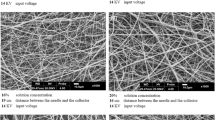
The production of nanofibers holds significant importance in both laboratory-based research and industrial applications. This study employed multiple spinnerets in the process of electrospinning to produce polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibers, which exhibited a desirable characteristic of being both thin and uniform. The spinning performance of multiple jet electrospinning was done. In addition, an examination was conducted to assess the impact of antistatic non-woven support materials on the fiber morphology of PVDF electrospun nanofibers. The morphology and β-phase (beta phase) of the electrospun nanofibers were analyzed using characterization techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The findings of the study indicate that the selection of antistatic non-woven support material had a notable impact on fiber morphology. Upon the utilization of various suitable substrate materials, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) contributed to the successful formation of well-structured and consistent nanofibers with a lesser diameter of 173 ± 38 nm, 92.8% β-fraction and a surface area of 12.99 m2/g. The laminating temperature and density of the fiber decreased the porosity and air permeability by 50%. The excellent flux recovery of 400 L/(m2 h) on the nanofibers laminated at 130 °C of pore size of 0.54 µm even after dried and stored for 48 h at room temperature. A finite-element analysis (FEA) was conducted on computer-aided design (CAD) fiber structure, and results showed that at low pressure of 0.01 N, a max of 130.29 MPa stress was generated on fibers.
Graphical abstract



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Kenry LCT (2017) Nanofiber technology: current status and emerging developments. Prog Polym Sci 70:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.03.002
Tlili I, Alkanhal TA (2019) Nanotechnology for water purification: electrospun nanofibrous membrane in water and wastewater treatment. J Water Reuse Desalin 9:232–248. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2019.057
Abdulhamid MA, Muzamil K (2023) Recent progress on electrospun nanofibrous polymer membranes for water and air purification: a review. Chemosphere 310:136886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136886
Liu Z, Zhao J, Zhou L, Xu Z, Xing J, Feng Q (2019) Recent progress of the needleless electrospinning for high throughput of nanofibers. Recent Pat Nanotechnol 13:164–170. https://doi.org/10.2174/1872210513666190426151150
Ali M, Li Y, He JH (2024) Double bubble electrospinning: patents and nanoscale interface. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.2174/0118722105259729231004040238
Liu HY, Yao YJ, Qian MY (2023) Interaction of multiple jets in bubble electrospinning. Therm Sci 27:1741–1746. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI211228083L
Yardimci AI, Kayhan M, Durmus A, Aksoy M, Tarhan O (2022) Synthesis and air permeability of electrospun PAN/PVDF nanofibrous membranes. Res Eng Struct Mater 8:223–231. https://doi.org/10.17515/resm2022.357na1027
Akbari N, Khorshidi S, Karkhaneh A (2022) Effect of piezoelectricity of nanocomposite electrospun scaffold on cell behavior in bone tissue engineering. Iran Polym J 31:919–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-022-01047-7
Rehan M, Nada AA, Khattab TA, Abdelwahed NA, Abou El-Kheir AA (2020) Development of multifunctional polyacrylonitrile/silver nanocomposite films: antimicrobial activity, catalytic activity, electrical conductivity, UV protection and SERS-active sensor. J Mater Res Technol 9:9380–9394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.079
Pardo Figuerez M, Chiva Flor A, Figueroa Lopez K, Prieto C, Lagaron JM (2021) Antimicrobial nanofiber based filters for high filtration efficiency respirators. Nanomaterials 11:900. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano
Kimmer D, Vincent I, Lovecka L, Kazda T, Giurg A, Skorvan O (2017) Some aspects of applying nanostructured materials in air filtration, water filtration and electrical engineering. AIP Conf Proc 1843:060001. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4983003
Avvari VD, Boggarapu V, Kimmer D, Rama Sreekanth PS (2023) Potential of polyurethane functionalized electrospun nanofiber membrane as self-cleaning water filter. Arab J Sci Eng 2023:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08230-9
Khatri M, Francis L, Hilal N (2023) Modified electrospun membranes using different nanomaterials for membrane distillation. Membranes 13:338. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030338
Szewczyk PK, Gradys A, Kim SK, Persano L, Marzec M, Kryshtal A, Busolo T, Toncelli A, Pisignano D, Bernasik A, Kar-Narayan S (2020) Enhanced piezoelectricity of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers for energy harvesting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:13575–13583. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c02578
Subrahmanya TM, Arshad AB, Lin PT, Widakdo J, Makari HK, Austria HF, Hu CC, Lai JY, Hung WS (2021) A review of recent progress in polymeric electrospun nanofiber membranes in addressing safe water global issues. RSC Adv 11:9638–9663. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00060h
Nueraji M, Toktarbay Z, Ardakkyzy A, Sridhar D, Algadi H, Xu BB, Althakafy JT, Alanazi AK, Abo-Dief HM, Adilov S, Guo Z (2023) Mechanically-robust electrospun nanocomposite fiber membranes for oil and water separation. Environ Res 220:115212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115212
Gade H, Nikam S, Chase GG, Reneker DH (2021) Effect of electrospinning conditions on β-phase and surface charge potential of PVDF fibers. Polymer 228:123902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123902
Zhang M, Liu C, Li B, Shen Y, Wang H, Ji K, Mao X, Wei L, Sun R, Zhou F (2023) Electrospun PVDF-based piezoelectric nanofibers: materials, structures, and applications. Nanoscale Adv 5:1043–1059. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2na00773h
Beermann F, Schwakenberg M, Voigt AL, Ehrmann A (2018) Influence of substrate materials on electrospun pan nanofiber mats. IEEE NAP. https://doi.org/10.1109/NAP.2018.8914823
Avvari VD, Olejnik R, Danova R, Matyas J, Slobodian P, Adamek M, Kimmer D (2020) Poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun non-woven nanofibers based piezoelectric nanogenerator. IEEE NEMS. https://doi.org/10.1109/NEMS50311.2020.9265569
Varesano A, Rombaldoni F, Mazzuchetti G, Tonin C, Comotto R (2010) Multi-jet nozzle electrospinning on textile substrates: observations on process and nanofibre mat deposition. Polym Int 59:1606–1615. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2893
Drioli E, Giorno L (eds) (2016) Encyclopedia of membranes. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40872-4_2196-1
Mohammadpourfazeli S, Arash S, Ansari A, Yang S, Mallick K, Bagherzadeh R (2023) Future prospects and recent developments of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric polymer; fabrication methods, structure, and electro-mechanical properties. RSC Adv 13:370–387. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra06774a
Cirqueira SS, Tanabe EH, Aguiar ML (2019) Experimental investigation of particle deposition in filter media during filtration cycles with regeneration by pulse jet cleaning. Process Saf Environ Prot 127:288–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.05.013
Chinaglia DL, Gregorio R Jr, Stefanello JC, Pisani Altafim RA, Wirges W, Wang F, Gerhard R (2010) Influence of the solvent evaporation rate on the crystalline phases of solution-cast poly(vinylidene fluoride) films. J Appl Polym Sci 116:785–791. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.31488
Adeli B, Gharehaghaji AA, Jeddi AA (2021) A feasibility study on production and optimization of PVDF/PU polyblend nanofiber layers using expert design analysis. Iran Polym J 30:535–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00910-3
Soin N, Anand SC, Shah TH (2016) Energy harvesting and storage textiles. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, pp 357–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-465-9.00012-4
Bairagi S, Shahadat M, Mulvihill DM, Ali W (2023) Mechanical energy harvesting and self-powered electronic applications of textile-based piezoelectric nanogenerators: a systematic review. Nano Energy 111:108414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108414
He Z, Rault F, Lewandowski M, Mohsenzadeh E, Salaün F (2021) Electrospun PVDF nanofibers for piezoelectric applications: a review of the influence of electrospinning parameters on the β phase and crystallinity enhancement. Polymers 13:174. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020174
Tiwari S, Dubey DK, Prakash O, Das S, Maiti P (2023) Effect of functionalization on electrospun PVDF nanohybrid for piezoelectric energy harvesting applications. Energy 275:127492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127492
Mahato PK, Seal A, Garain SE, Sen S (2015) Effect of fabrication technique on the crystalline phase and electrical properties of PVDF films. Mater Sci Pol 33:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1515/msp-2015-0020
Wang X, Hsiao BS (2016) Electrospun nanofiber membranes. Curr Opin Chem Eng 12:62–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2016.03.001
Ke G, Jin X, Hu H (2020) Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/polyacrylonitrile composite fibers: fabrication and characterization. Iran Polym J 29:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-019-00773-9
Yao M, Woo YC, Tijing LD, Shim WG, Choi JS, Kim SH, Shon HK (2016) Effect of heat-press conditions on electrospun membranes for desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 378:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.09.025
Kanafchian M, Valizadeh M, Haghi AK (2011) Fabrication of nanostructured and multicompartmental fabrics based on electrospun nanofibers. Korean J Chem Eng 28:763–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0449-3
Yalcinkaya F, Hruza J (2018) Effect of laminating pressure on polymeric multilayer nanofibrous membranes for liquid filtration. Nanomaterials 8:272. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050272
He T, Li X, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Wang X, Wang Z, Tavajohi N, Cui Z (2022) Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membrane fabrication with an ionic liquid via non-solvent thermally induced phase separation. Appl Water Sci 12:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01499-x
Zhou Y, Liu Y, Zhang M, Feng Z, Yu DG, Wang K (2022) Electrospun nanofiber membranes for air filtration: a review. Nanomaterials 12:1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071077
Sudha RK, Shruthi I, Varsha K, Vidya AN, Kumari UM, Shireesha G (2020) Simulation and optimization of stacked PVDF membrane for piezoelectric application. IJEAT 9:551–555. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijeat.E9653.069520
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Vincent. Ivo, and Lovecká. Lenka for their valuable contribution in this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avvari, V.D., Kimmer, D., Sahu, S.K. et al. Influence of non-woven antistatic substrate materials on polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun nanofibers: fabrication, characterization, and performance evaluation. Iran Polym J (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-024-01312-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-024-01312-x