Abstract
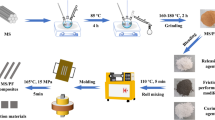
Perforative silica microspheres (PSMs) were prepared by an emulsion method coupled with sol–gel technology and phase separation. Next, phenolphthalein-based poly(arylene ether sulfone)/PSM composites (PES-C/PSM) were fabricated. PSM was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method. The as-synthesized PSM exhibited a spherical shape with an external diameter of 2–10 µm, surface area of 166.5 m2/g and pore volume of 1.35 cm3/g. SEM and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (energy-dispersive spectroscopy) were used to characterize the morphology and the composition of the composite, respectively. Both SEM and energy-dispersive spectroscopy results revealed that the PES-C polymer chains penetrated into the PSM pores. In addition, the effect of PSM weight content on the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the composites was characterized by tensile tests and thermal analysis, respectively. A 19% increase in tensile strength and a 29% increase in breaking elongation of PES-C were achieved by the addition of 0.50 wt% PSM. Moreover, the thermal oxidative stability of PES-C was remarkably improved with the incorporation of PSM. Compared with pristine PES-C, the final degradation temperature was enhanced by 42 °C at 1.0 wt% PSM loading. Our studies have indicated that PSM is a kind of promising reinforcement for improvement of tensile and thermal properties of engineering plastics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng S, Guo Q, Mi Y (2003) Miscibility and phase behavior in blends of phenolphthalein poly(ether sulfone) and poly(hydroxyether of bisphenol-A). Polymer 44:867–876
Wang Z, Chen T, Xu J (2000) Gas transport properties of novel cardo poly(aryl ether ketone)s with pendant alkyl groups. Macromolecules 33:5672–5679
Chen G, Zhang X, Zhang S, Chen T, Wu Y (2007) Synthesis, properties, and gas permeation performance of cardo poly(arylene ether sulfone)s containing phthalimide side groups. J Appl Polym Sci 106:2808–2816
Sugama T (1998) Polyphenylethersulfone adhesive for EPDM elastomer-to-stainless steel joints in a hydrothermal environment. J Mater Sci 33:5095–5102
Wang G, Fu G, Gao T, Kuang H, Wang R, Yang F, Jiao W, Hao L, Liu W (2016) Preparation and characterization of novel film adhesives based on cyanate ester resin for bonding advanced radome. Int J Adhes Adhes 68:80–86
Wang M, Wu LG, Mo HX, Gao CH (2006) The preparation and characterization of novel charged polyacrylonitrile/PES-C blend membranes used for ultrafiltration. JMembr Sci 274:200–208
Blanco JF, Nguyen QT, Schaetzel P (2001) Novel hydrophilic membrane materials: sulfonated polyethersulfone cardo. J Membr Sci 186:267–279
Bolong N, Ismail AF, Salim MR, Rana D, Matsuura T, Tabe-Mohammadi A (2010) Negatively charged polyethersulfone hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of bisphenol-A from wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 73:92–99
Lin CX, Zhuo YZ, Lai AN, Zhang QG, Zhu AM, Liu QL (2016) Comb-shaped phenolphthalein-based poly(ether sulfone)s as anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells. RSC Adv 6:17269–17279
Rao AHN, Kim HJ, Nam S, Kim TH (2013) Cardo poly(arylene ether sulfone) block copolymers with pendant imidazolium side chains as novel anion exchange membranes for direct methanol alkaline fuel cell. Polymer 54:6918–6928
Lai AN, Zhuo YZ, Lin CX, Zhang QG, Zhu AM, Ye ML, Liu QL (2016) Side-chain-type phenolphthalein-based poly(arylene ether sulfone nitrile)s anion exchange membrane for fuel cells. J Membr Sci 502:94–105
Dong X, Hou S, Mao H, Zheng J, Zhang S (2016) Novel hydrophilic-hydrophobic block copolymer based on cardo poly (arylene ether sulfone)s with bis-quaternary ammonium moieties for anion exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 518:31–39
Kishi H, Shi YB, Huang J, Yee AF (1997) Shear ductility and toughenability study of highly cross-linked epoxy/polyethersulphone. J Mater Sci 32:761–771
Yang Y, Li B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhuang G (1995) Thermal and mechanical properties of phenolphthalein polyethersulfone/poly (phenylene sulfide) blends. J Appl Polym Sci 55:633–639
Mi Y, Feng J, Chan C-M, Guo Q (1997) Blends of phenolphthalein poly (ether ether sulfone) with a thermotropic liquid crystalline copolyester. J Macromol Sci Part B Phys 36:153–167
Li G, Yin J, Li B, Zhuang G, Yang Y, Nicolais L (1995) In situ composite: phenolphthalein polyethersulfone—thermotropic liquid crystalline polymer blends. Polym Eng Sci 35:658–665
Sharma M, Bijwe J, Singh K (2011) Studies for wear property correlation for carbon fabric-reinforced PES composites. Tribo Lett 43:267
Zhang SL, Yin SB, Rong CR, Huo PF, Jiang ZH, Wang GB (2013) Synergistic effects of functionalized graphene and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the electrical and mechanical properties of poly(ether sulfone) composites. Eur Polym J 49:3125–3134
Zinadini S, Zinatizadeh AA, Rahimi M, Vatanpour V, Zangeneh H (2014) Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J Membr Sci 453:292–301
Celik E, Park H, Choi H, Choi H (2011) Carbon nanotube blended polyethersulfone membranes for fouling control in water treatment. Water Res 45:274–282
Li L, Wang YX (2006) Proton conducting composite membranes from sulfonated polyethersulfone cardo and phosphotungstic acid for fuel cell application. J Power Sources 162:541–546
Yu J, Li L, Liu N, Lee R (2013) An approach to prepare defect-free PES/MFI-type zeolite mixed matrix membranes for CO2/N2separation. J Mater Sci 48:3782–3788
Asadi V, Jafari SH, Khonakdar HA, Haeussler L, Wagenknecht U (2016) Poly(ethylene succinate) nanocomposites containing inorganic WS2 nanotubes with improved thermal properties: a kinetic study. Composites Part B98:496–507
Shariatmadar F, Mohsen-Nia M (2012) PES/SiO2nanocomposite by in situ polymerization: synthesis, structure, properties, and new applications. Polym Compos 33:1188–1196
Teng S, Qiu Z (2017) Enhanced crystallization and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(ethylene succinate) by octaisobutyl-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes in their nanocomposites. Thermochim Acta 649:22–30
Peydayesh M, Mohammadi T, Bakhtiari O (2018) Effective treatment of dye wastewater via positively charged TETA-MWCNT/PEShybrid nanofiltration membranes. Sep Purif Technol 194:488–502
Shi ZG, Feng YQ (2008) Synthesis and characterization of hierarchically porous silica microspheres with penetrable macropores and tunable mesopores. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 116:701–704
Wang L, Liu XH, Wang X, Yang XJ, Lu LD (2011) Gelatin-assisted porous expansion of mesoporous silica. J Mater Sci 46:634–640
Sun ZQ, Fan JM, Hu P, Ding F, Yang J, Yuan FL (2017) A novel low-temperature strategy for synthesis of alumina ceramics with uniform and interconnected pores by silica coating. J Mater Sci 52:1603–1616
Shi ZG, Guo QZ, Liu YT, Xiao YX, Xu L (2011) Drug delivery devices based on macroporous silica spheres. Mater Chem Phys 126:826–831
Long T, Guo QZ, Xu LY (2011) Fast separation of sulfanilamides using macroporous silica spheres as the separation media. J Liq Chromatogr Related Technol 34:1391–1398
Ma LY, Li J, Zhao J, Liao H, Xu L, Shi ZG (2016) Penetrable silica microspheres for immobilization of bovine serum albumin and their application to the study of the interaction between imatinib mesylate and protein by frontal affinity chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:805–814
Lu L, Teng F, Qi D, Wang L, Zhang J (2015) Synthesis of visible-light driven CrxOy TiO2 binary photocatalyst based on hierarchical macro-mesoporous silica. Appl Catal B 163:9–15
Pan YT, Trempont C, Wang DY (2016) Hierarchical nanoporous silica doped with tin as novel multifunctional hybrid material to flexible poly(vinyl chloride) with greatly improved flame retardancy and mechanical properties. Chem Eng J 295:451–460
Nhat Tri V, Patra AK, Kim D (2017) Pore size and concentration effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the coefficient of thermal expansion and optical transparency of poly(ether sulfone) films. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:1937–1944
Tanimoto Y, Kitagawa T, Aida M, Nishiyama N (2006) Experimental and computational approach for evaluating the mechanical characteristics of dental composite resins with various filler sizes. Acta Biomater 2:633–639
Kissinger HE (1957) Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem 29:1702–1706
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural National Science Foundation of China (51503165) and the Youth Science Foundation of Wuhan Institute of Technology, China (Q201701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Hu, L., Fan, C. et al. Perforative silica microsphere-modified phenolphthalein-based poly(arylene ether sulfone) composites: tensile and thermal properties. Iran Polym J 27, 611–619 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-018-0637-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-018-0637-2