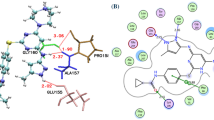
Abstract
The Aurora kinases play crucial roles in regulating mitotic progression and have implications in various diseases, including cancer. In this study, we explored the potential of depsidone analogues as inhibitors of Aurora A kinase through computational methods. A molecular docking studies of 260 depsidone molecules against Aurora A kinase, were conducted using extra precision docking mode of Glide. Three molecules, parmosidone A, chaetosidone A, and parmosidone E, showed promising docking scores compared to the reference inhibitor. These compounds exhibited strong interactions with the binding site of Aurora A kinase, involving hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. To further evaluate the stability of these interactions, we performed molecular dynamics simulations for 100 nanoseconds. RMSD analysis indicated that all compounds maintained relatively stable interactions with the protein throughout the simulation period. Notably, parmosidone A and chaetosidone A exhibited minimal fluctuations after an initial equilibration phase. RMSF analysis revealed that certain protein residues showed high fluctuations but were not crucial for inhibitor binding. Protein-ligand interaction analysis demonstrated that water bridges and hydrogen bonds played significant roles in the interactions between the compounds and Aurora A kinase. Overall, our computational assessments suggest that depsidone analogues, particularly parmosidone A and chaetosidone A, have potential as inhibitors of Aurora A kinase. These findings provide insights into the molecular interactions of these compounds and open new avenues for targeting Aurora A kinase in cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data related to the current study are included in this article.
References
Alzain AA, Elbadwi FA (2021) Identification of Novel TMPRSS2 inhibitors for COVID-19 using e-Pharmacophore modelling, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics and Quantum Mechanics Studies. Inf Med Unlocked 26:100758
Alzain AA et al (2023) Modulation of NRF2/KEAP1-Mediated Oxidative Stress for Cancer Treatment by Natural Products Using Pharmacophore-Based Screening, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 28(16)
Andrews PD (2005) Aurora Kinases: Shining Lights on the Therapeutic Horizon? Oncogene 2005 24:32 24(32): 5005–15
Assefa ST et al (2020) Alpha glucosidase inhibitory activities of plants with Focus on Common vegetables. Plants 9(1)
Badar M, Sufian S, Shamsi J, Ahmed, Md (2022) Afshar Alam. Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Concept, Methods, and Applications. (August): 131–51
Bay M, Van et al (2020) Theoretical study on the antioxidant activity of natural depsidones. ACS Omega 5(14):7895–7902
Beard H et al (2013) Applying physics-based scoring to calculate free energies of binding for single amino acid mutations in protein-protein complexes. PLoS ONE 8(12):1–11
Bioinformatics
Bowers KJ et al (2007) Scalable Algorithms for Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Commodity clusters.: 43–43
Carmena M, Earnshaw WC, Glover DM (2015) The Dawn of Aurora Kinase Research: from fly Genetics to the clinic. Front Cell Dev Biology 3(NOV):1–5
Carpentier C et al (2018) Lobaric Acid and pseudodepsidones inhibit NF-ΚB signaling pathway by activation of PPAR-γ. Bioorg Med Chem 26(22):5845–5851
Darden T, York D, and Lee Pedersen (1993) Particle Mesh Ewald: an N⋅log(N) method for Ewald Sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092
Devi A, Paramita et al (2020) Salazinic acid-derived depsidones and diphenylethers with α -Glucosidase inhibitory activity from the Lichen Parmotrema Dilatatum. Planta Med 86(16):1216–1224
Dhasmana A et al (2018) New look to Phytomedicine: advancements in Herbal products as Novel Drug leads high-throughput virtual screening (HTVS) of natural compounds and Exploration of their Biomolecular mechanisms: an. Silico Approach. Elsevier Inc
Ding Y et al (2019) Curdepsidones B-G, Six Depsidones with Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Marine-Derived Fungus Curvularia Sp. IFB-Z10. Marine Drugs 17(5)
Du R et al (2021) Targeting AURKA in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Opportunities for Cancer Therapy. Molecular cancer 20(1)
Elamin EM et al (2023) Discovery of Dual-Target Natural Antimalarial Agents against DHODH and PMT of Plasmodium Falciparum: Pharmacophore Modelling, Molecular Docking, Quantum Mechanics, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research
Eltaib L, Alzain AA (2022) Targeting the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 with phytochemicals from Saudi Medicinal plants: molecular docking combined with Molecular Dynamics investigations. J Biomol Struct Dynamics 0(0):1–13
Essmann U et al (1995) A smooth particle Mesh Ewald Method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593
Feng J et al (2008) Discovery of Alogliptin: A Potent, Selective, Bioavailable, and Efficacious Inhibitor of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2007) 50, (2297–2300)). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51(14): 4357
Friesner RA et al (2006) Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49(21):6177–6196
Giet Régis, Petretti C, and Claude Prigent (2005) Aurora Kinases, Aneuploidy and Cancer, a coincidence or a real link? Trends Cell Biol 15(5):241–250
Gong Y et al (2012) Tanshinones inhibit the growth of breast Cancer cells through epigenetic modification of Aurora A expression and function. PLoS ONE 7(4)
Hoang NT, My et al (2016) In Vitro characterization of Derrone as an Aurora kinase inhibitor. Biol Pharm Bull 39(6):935–945
Hontz AE et al (2007) Aurora A and B overexpression and centrosome amplification in Early Estrogen-Induced Tumor Foci in the Syrian Hamster kidney: implications for chromosomal instability, Aneuploidy, and Neoplasia. Cancer Res 67(7):2957–2963
Howard S et al (2009) Fragment-based Discovery of the pyrazol-4-Yl urea (AT9283), a Multitargeted kinase inhibitor with potent Aurora kinase activity. J Med Chem 52(2):379–388
Ibrahim, Sabrin RM et al (2018) Biologically active fungal depsidones: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Structural characterization, and Bioactivities. Fitoterapia 129:317–365
Irwin JJ, Brian KS (2016) Docking screens for Novel ligands Conferring New Biology. J Med Chem 59(9):4103–4120
Jackson JR, Denis R, Patrick MM, Dar (2007) and Pearl S. Huang. Targeted Anti-Mitotic Therapies: Can We Improve on Tubulin Agents? Nature Reviews Cancer 2007 7:2 7(2): 107–17
Jorgensen WL et al (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating Liquid Water. J Chem Phys 79(2):926–935
Keen N, and Stephen Taylor (2004) Aurora-kinase inhibitors as Anticancer agents. Nat Rev Cancer 4(12):927–936
Khayat MT et al (2023) Recent advances on natural depsidones: sources, biosynthesis, structure-activity relationship, and Bioactivities. PeerJ 11:e15394
Khazir J et al (2014) Anticancer agents from Diverse Natural sources. Nat Prod Commun 9(11):1655–1669
Kuzmanic A, and Bojan Zagrovic (2010) Determination of ensemble-average pairwise Root Mean-Square deviation from experimental B-Factors. Biophysj 98(5):861–871
Lu M, Wang C, Wang J (2016) Tanshinone I induces human colorectal Cancer cell apoptosis: the potential roles of Aurora A-P53 and survivin-mediated signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 49(2):603–610
Lu C et al (2021) OPLS4: improving Force Field Accuracy on challenging regimes of Chemical Space. J Chem Theory Comput 17(7):4291–4300
Ma Z, Liang et al (2015) Tanshinones Suppress AURKA through Up-Regulation of MiR-32 expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 6(24):20111–20120
Majolo F et al (2019) Medicinal plants and Bioactive Natural compounds for Cancer Treatment: important advances for Drug Discovery. Phytochem Lett 31:196–207. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1874390018304968
Martyna GJ, Klein ML, and Mark Tuckerman (1992) Nosé-Hoover Chains: the canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. J Chem Phys 97(4):2635–2643
Martyna GJ, Douglas J, Tobias, and Michael L Klein (1994) Constant pressure Molecular Dynamics algorithms. J Chem Phys 101:4177–4189
Mohamed GA et al (2023) Structure-based virtual screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Assessments of Depsidones as possible selective cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonists. Molecules 28(4)
Newman DJ, Gordon MC (2020) Natural products as sources of New drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J Nat Prod 83(3):770–803
Pradhan T, Gupta O, Singh G, and Vikramdeep Monga (2021) Aurora Kinase Inhibitors as potential Anticancer agents: recent advances. Eur J Med Chem 221
Repasky MP et al (2012) Docking performance of the Glide Program as evaluated on the astex and DUD datasets: a Complete Set of Glide SP results and selected results for a new scoring function integrating WaterMap and Glide. J Comput Aided Mol Des 26(6):787–799
Ryckaert J-P, Ciccotti G, Herman JC, Berendsen (1977) Numerical Integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular Dynamics of n-Alkanes. J Comput Phys 23(3):327–341
Santos LHS, Rafaela S, Ferreira, Ernesto RC (2019) Chapter 2. 2053
Sargsyan K, Grauffel Cédric, Lim C (2017) How molecular size impacts RMSD applications in Molecular Dynamics simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 13(4):1518–1524
Saur IML, Panstruga R, Paul Schulze-Lefert (2021) NOD-like receptor-mediated plant immunity: from structure to cell death. Nat Rev Immunol 21(5):305–318
Schrödinger (2021c) Schrödinger | Schrödinger Is the Scientific Leader in Developing State-of-the-Art Chemical Simulation Software for Use in Pharmaceutical, Biotechnology, and Materials Research
Schrödinger (2021b) MacroModel | Schrödinger.
Schrödinger (2021a) LigPrep | Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2018-1
Shaik B, Baba NK, Katari, Sreekantha Babu J (2022) Role of Natural products in developing Novel Anticancer agents: a perspective. Chem Biodivers 19(11):e202200535. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202200535
Shen B (2015) A New Golden Age of Natural products Drug Discovery. Cell 163(6):1297–1300
Shoaib TH et al (2023) Exploring the potential of approved drugs for triple-negative breast Cancer Treatment by Targeting Casein kinase 2: insights from computational studies ed. Wagdy Mohamed Eldehna. PLoS ONE 18(8):e0289887
Stojanovic G, Stojanovic I, and Andrija Smelcerovic (2012) Lichen Depsidones as potential Novel pharmacologically active compounds. Mini-Rev Org Chem 9(2):178–184
Van Anh C et al (2022) Antibacterial and cytotoxic phenolic polyketides from two marine-derived fungal strains of Aspergillus Unguis. Pharmaceuticals 15(1)
Varney MD et al (1992) 4/JLo*. (3)
Venera C et al (2022) Physodic acid sensitizes LNCaP prostate Cancer cells to TRAIL-Induced apoptosis. Toxicol in Vitro 84
Veselovsky AV, Ivanov AS (2003) Strategy of computer-aided Drug Design. Curr Drug Targets - Infect Disorders 3(1):33–40
Von Itzstein M et al (1993) Rational design of potent sialidase-based inhibitors of Influenza Virus Replication. Nature 363(6428):418–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Author disclosure statement
The authors declare they have no conflicting financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almogaddam, M.A., Shoaib, T.H., Mohamed, S.G.A. et al. Computational screening identifies depsidones as promising Aurora A kinase inhibitors: extra precision docking and molecular dynamics studies. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 13, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-024-00451-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-024-00451-8