Abstract
Purpose of Review
The purpose of this article is to review current understanding of the role of IL-23 in psoriasis and the available results to date on clinical trials establishing the efficacy and safety of IL-23 inhibitors for use in adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
Recent Findings
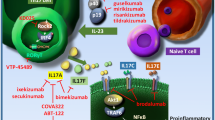
Interleukin-23, a cytokine involved in activation and maintenance of the T-helper 17 pathway, plays a key role in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. While antibodies to IL-12 and IL-23 have been approved in psoriasis treatment for several years, robust evidence on the key role of IL-23 has led to the newest class of biologics for the treatment of psoriasis specifically targeting only IL-23. Guselkumab, tildrakizumab, risankizumab, and mirikizumab are fully human (guselkumab) or humanized (tildrakizumab, risankizumab, and mirikizumab) monoclonal antibodies that bind to the unique p19 subunit of IL-23. Guselkumab was recently approved for use in psoriasis, while the three others remain under investigation in clinical trials.
Summary
Early data from clinical trials shows high efficacy and low short-term safety risks of IL-23 inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(3):512–6.
Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, Mehta NN, Ogdie A, Van Voorhees AS, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):377–90.
Rapp SR, Feldman SR, Exum ML, Fleischer AB, Reboussin DM. Psoriasis causes as much disability as other major medical diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41(3):401–7.
Pearce DJ, Singh S, Balkrishnan R, Kulkarni A, Fleischer Jr AB, Feldman SR. The negative impact of psoriasis on the workplace. J Dermatol Treat. 2006;17(1):24–8.
Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol. 2009;129(6):1339–50.
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, et al. Novel p 19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13(5):715–25.
Gerosa F, Baldani-Guerra B, Lyakh LA, Batoni G, Esin S, Winkler-Pickett RT, et al. Differential regulation of interleukin 12 and interleukin 23 production in human dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2008;205(6):1447–61.
Piskin G, Tursen U, Sylva-Steenland R, Bos J, Teunissen M. Clinical improvement in chronic plaque-type psoriasis lesions after narrow-band UVB therapy is accompanied by a decrease in the expression of IFN-γ inducers–IL-12, IL-18 and IL-23. Exp Dermatol. 2004;13(12):764–72.
Chan JR, Blumenschein W, Murphy E, Diveu C, Wiekowski M, Abbondanzo S, et al. IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2–dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Exp Med. 2006;203(12):2577–87.
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL, Pittman D, Wang F, Chamian F, et al. Increased expression of interleukin 23 p 19 and p 40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med. 2004;199(1):125–30.
Rizzo HL, Kagami S, Phillips KG, Kurtz SE, Jacques SL, Blauvelt A. IL-23–mediated psoriasis-like epidermal hyperplasia is dependent on IL-17A. J Immunol. 2011;186(3):1495–502.
Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J, et al. Interleukin-22, a T H 17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature. 2007;445(7128):648–51.
Tonel G, Conrad C, Laggner U, Di Meglio P, Grys K, McClanahan TK, et al. Cutting edge: a critical functional role for IL-23 in psoriasis. J Immunol. 2010;185(10):5688–91.
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W, Zaba LC, Duan S, Gardner J, et al. A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(4):e1000041.
Duvallet E, Semerano L, Assier E, Falgarone G, Boissier M-C. Interleukin-23: a key cytokine in inflammatory diseases. Ann Med. 2011;43(7):503–11.
Sherlock JP, Joyce-Shaikh B, Turner SP, Chao C-C, Sathe M, Grein J, et al. IL-23 induces spondyloarthropathy by acting on ROR-γt+ CD3+ CD4− CD8− entheseal resident T cells. Nat Med. 2012;18(7):1069–76.
Krueger GG, Langley RG, Leonardi C, Yeilding N, Guzzo C, Wang Y, et al. A human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(6):580–92.
Levin AA, Gottlieb AB. Specific targeting of interleukin-23p19 as effective treatment for psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(3):555–61.
Kulig P, Musiol S, Freiberger SN, Schreiner B, Gyülveszi G, Russo G, et al. IL-12 protects from psoriasiform skin inflammation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13466.
Gaspari AA, Tyring S. New and emerging biologic therapies for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: mechanistic rationales and recent clinical data for IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28(4):179–93.
Tugues S, Burkhard S, Ohs I, Vrohlings M, Nussbaum K, Vom Berg J, et al. New insights into IL-12-mediated tumor suppression. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(2):237–46.
Köck K, Pan W, Gow J, Horner M, Gibbs J, Colbert A, et al. Preclinical development of AMG 139, a human antibody specifically targeting IL-23. Br J Pharmacol. 2015;172(1):159–72.
Tremfya (guselkumab) [prescribing information]. Horsham PJB, Inc; October 2017.
•• Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Griffiths CE, Randazzo B, Wasfi Y, Shen Y-K, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo-and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):405–17. Phase III clinical trial of guselkumab.
•• Reich K, Armstrong AW, Foley P, Song M, Wasfi Y, Randazzo B, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis with randomized withdrawal and retreatment: Results from the phase III, double-blind, placebo-and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 2 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):418–31. Phase III clinical trial of guselkumab.
Reich K, Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Tyring SK, Sinclair R, Thaçi D, et al. Tildrakizumab versus placebo or etanercept for chronic plaque psoriasis (reSURFACE 1 and reSURFACE 2): results from two randomised controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2017;390(10091):276–88.
Gordon KB, et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab: results from two double-blind, placebo- and ustekinumab-controlled, phase 3 trials in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Presented at: 2018 American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting. February 16–20, 2017; San Diego, CA. Abstract 6495.
AbbVie. Risankizumab meets all co-primary and ranked secondary endpoints, achieving significantly greater efficacy versus standard biologic therapies in three pivotal phase 3 psoriasis studies. [Online Press Release]. https://news.abbvie.com/news/risankizumab-meets-all-co-primary-and-ranked-secondary-endpoints-achieving-significantly-greater-efficacy-versus-standard-biologic-therapies-in-three-pivotal-phase-3-psoriasis-studies.htm. Accessed 1 February 2018.
Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Gooderham M, Langley R, Leonardi C, Lacour J-P et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab, an interleukin-23 inhibitor in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis: 16-week results from the phase III IMMhance trial [Abstract] FC29. Psoriasis: From Gene to Clinic International Congress, London, 2nd December 2017, 1115. 2017:69.
Gordon K MA, Ferris L, Martorell A, Kim B, Song M, Wasfi Y, You Y, Shen YK, Langley R. Consistency of response (PASI 90 or 100 and IGA 0 or 0/1) in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated with guselkumab: results from the VOYAGE 1 and 2 trials. AAD Anual Meeting. [Poster presentation]. 2018.
Gordon K, Blauvelt A, Foley P, Song M, Wasfi Y, Randazzo B, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab in subpopulations of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a pooled analysis of the phase III VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 studies. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(1):132–9.
•• Langley RG, Tsai TF, Flavin S, Song M, Randazzo B, Wasfi Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: results of the randomized, double-blind, phase III NAVIGATE trial. The British journal of dermatology. 2018;178(1):114–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15750. Phase III clinical trial of guselkumab in patients without complete response to ustekinumab.
•• Terui T, Kobayashi S, Okubo Y, Murakami M, Hirose K, Kubo H. Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab, an Anti-interleukin 23 Monoclonal Antibody, for Palmoplantar Pustulosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(3):309–16. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5937. Phase III clinical trials of tildrakizumab.
•• Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Bukhalo M, Gooderham M, Krueger JG, Lacour J-P, et al. Risankizumab versus ustekinumab for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(16):1551–60. Phase II clinical trial of risankizumab.
Krueger JG, Ferris LK, Menter A, Wagner F, White A, Visvanathan S, et al. Anti–IL-23A mAb BI 655066 for treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis: safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and biomarker results of a single-rising-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136(1):116–24. e7.
Rich P, Maari C, Leonardi C, Klekotka P, Patel D, Li J et al. Efficacy, safety, and quality of life in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis treated with mirikizumab (LY3074828) in a phase 2 study [Meeting Abstract]. AAD Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA; February 16–20, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Psoriasis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, K.M., Yang, E.J., Sekhon, S. et al. IL-23 Inhibitors for Psoriasis. Curr Derm Rep 7, 119–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13671-018-0216-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13671-018-0216-y