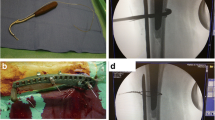
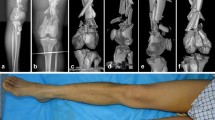
Abstract
Minimally invasive plate ostesynthesis (MIPO) is not just a technique, it is a method of treatment for metadiaphyseal fractures that has three elements: small incisions, indirect functional reduction and flexible fixation. In an elderly patient, the osteoporotic fracture doesn't accept absolute stability well, because the bone cannot withstand interfragmentary compression. MIPO is a biologically friendly approach, preserving the blood supply of the soft tissues and the bone, allowing a better healing process, and less risk of non-union and infection. These are important factors in elderly patients because they are more likely to develop delayed healing and non-union, as well as infection due to deficiency of the immune system. This article presents the best way to reduce the fracture and place the plate in the bone to achieve the best construct. An angular, stable plate with a screw locking feature has brought mechanical and biological advantages to MIPO fixation. Clinical results are presented for the humeral, femoral and tibial fractures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Riggs BL, Melton III LJ. The prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:620–7.
Aharonoff GB, Koval KJ, Skovron ML, et al. Hip fracture in the elderly. Predictors of one year mortality. J Orthop Trauma. 1997;11:162–5.
Johnell O, Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17:1726–33.
Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fracture of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1058–64.
Mazees RB. On aging bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982;165:239–52.
Chan GK, Duque G. Age-related bone loss: old bone, new facts. Gerontology. 2002;48:62–71.
Giannoudis P, Tzioupis C, Almalki T, Buckley R. Fracture healing in osteoporotic fractures: is it really different? A basic science perspective. Injury. 2007;38(S1):90–9.
Wang JW, Li W, Xu SW, et al. Osteoporosis influences the middle and late periods of fracture healing in a rat osteoporotic model. Clin J Trumatol. 2005;8:111–6.
Islam AA, Rasubala L, Yoshikawa H, et al. Healing of fractures in osteoporotic rat mandible shown by the expression of bone morphogenetical protein-2 and tumor necorsis fractor-alpha. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;43:383–91.
Lill CA, Hesseln J, Schlegel U, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of healing in a non-critical defect in a large animal model of osteoporosis. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:836–42.
Freeman AL, Tornetta III P, Schmidt A, et al. How much do locked screws add to the fixation of “hybrid plate constructs in osteoporotic bone? J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24:163–9. Interesting study regarding the bioimechanics and function of the locking plate.
Fulkerson E, Egol KA, Kubiak EN, et al. Fixation of diaphyseal fractures with segmental defect: a biomechanical comparison of locked and conventional plating techniques. J Trauma. 2006;60:830–5.
Blatter G, Konig H, Hanssen M, et al. Primary femoral shortening osteosynthesis in the management of comminuted supracondylar femoral fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1994;113:134–7.
Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Distale femurfraktturen. transartikulare rekonstruktion, perkutane plattenosteosynthese und retrograde nagelung. Unfallchirurg. 1996;99:2–10.
Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J. Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia – results in 20 patients. Injury. 2006;37:877–87.
Cornell CN, Ayalon O. Evidence for success with locking plates for fragility fractures. HSSJ. 2011;7:164–9. Article about the use of locking plate in osteoporotic fractures.
Faruok O, Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Guy P, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and vascularity: preliminary results of a cadaver infection study. Injury. 1997;28:SA7–SA12.
Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fractures: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007;38:365–70.
Navaratnarajah A, Stephen JHD. The physiology of ageing. Medicine. 2013;41:5–8. Comprehensive article about he physiology of ageing and its consequences on the different systems.
Ellis T, Bourgeault CA, Kyle RF. Screw position affects dynamic compression plate strain in an in vitro fracture model. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15:333–7.
Törnkvist H, Heam TC, Schatzker J. The strength of plate fixation in relation to the number and spacing of bone screws. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10:204–8.
Cornell CN. Techniques for fixation of long bone fractures in patients with osteoporosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11:109–19.
Gautier E, Perren SM, Cordey J. Effect of plate position relative to bending direction on the rigidity of a plate osteosynthesis. A theoretical analysis. Injury. 2000;31 suppl 3:C14–20.
Cordey J, Borgeaud M, Perren SM. Force transfer between the plate and the bone: relative importance of the bending stiffness of the screws friction between plate and bone. Injury. 2000;31 suppl 3:C21–8.
Egol KA, Kubiak EN, Fulkerson E, et al. Biomechanics of locking plates and screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:488–93.
Tejwani NC, Guerado E. Improving fixation of the osteoprotic fracture: the role of the locked plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25:S56–60. The article describes how helpful the locking plates have been in the treatment of fractures in elderly. And aware about the complications with both the technique and implants.
Arumilli B, Suhm N, Marcel J, Rikli D. Long Philos plate fixation in a series of humeral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;10:1324–9.
Zhou ZB, Gao YS, Tang MJ, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis for proximal humeral shaft fractures with Philos through the deltopectoral approach. Int Orthop. 2012;36:2341–5.
Rancan M, Dietrich M, Lamdark T, et al. Miimal invasive long Philos-plate osteosynthesis in metapdiaphyseal fractures of the proximal humerus. Injury. 2010;41:1277–83.
Doshi HK, Wenxian P, Burgula MV, Murphy DP. Clinical outcomes of distal femoral fractures in the geriatric population using locking plates with a minimally invasive approach. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehab. 2013;4:16–20.
Vallier A, Immler W. Comparison of the 95-degree angled blade pate and the locking condylar plate for the treatment of distal femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26:327–33.
Kao FC, Tu YK, Su JY, et al. Treatment of distal femoral fracture by minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis: comparison between the dynamic condylar screw and the less invasive stabilization system. J Trauma. 2009;67:719–26.
Hou Z, Bowen TR, Irgit K, et al. Locked plating of periprosthetic femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26:427–32.
Hoffmann MF, Jones CB, Sietsema DL, Koenig SJ, Tornetta III P. Outcome of periprothetic distal femoral fractures following knee arthroplasty. Injury. 2012;43:1084–9. Article discussing the treatment of distal femoral fractures over a total knee arthroplasty.
Ehlinger M, Czekaj J, Adam P, et al. Minimally invasive fixation of type B and C interprosthetic femoral fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99:563–9.
Naik MA, Arora G, Tripathy SK, et al. Clinical and radiological outcome of percutaneous plating in extra-articular proximal tibia fractures: a prospective study. Injury. 2013;44:1081–6. Prospective study of the fixation of the proximal extra-articular tibia fracture with MIPO.
Sitnik AA, Beletsky AV. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of tibia fractures: results in 80 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471:2783–9.
Li B, Yang Y, Jiang LS. Plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing for displaced extra-articular distal tibia fractures: a system review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;10:1362–73. A systematic review of the comparison between intramedullary nailing and plate fixation for extra-articular distal tibia fracture.
Ehlinger M, Adam P, Abane L, et al. Minimally invasive internal fixation of extra-articular distal femur fractures using a locking plate: tricks of the trade. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97:201–5. This article discuss the fixation of the distal femoral fracture with bridge plate fixation.
Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures: the scientific basis of biological internal fixation. Choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2002;84:1093–110.
Kottmeier SA, Jones CB, Tornetta III P, Russel TA. Locked and minimally invasive plating: a paradigm shift? Metadiaphyseal site-specific concerns and controversies. Instr Course Lect. 2013;62:41–59. The authors review the use of the locking plate in the minimally invasive osteosynthesis enfacizing the current controversies and concerns.
Sanders R. When evolution begets revolution. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:481–2.
Rijal L, Sagar G, Mani K, et al. Minimizing radiation and incision in minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) of distal tibial fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23:361–5. This article reviews the technique of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the tiba and also how to minimize the radiation during the procedure.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Kodi Edson Kojima and Jorge dos Santos Silva declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, K.E., dos Santos Silva, J. Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Elderly Patient. Curr Geri Rep 3, 115–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-014-0085-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-014-0085-6