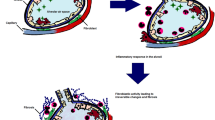
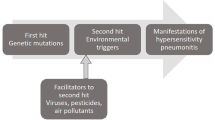
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This article aims to provide an overview on the diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP). We will focus on the issues surrounding the lack of an international consensus on the diagnosis of HP, and review the existing treatment options for HP.
Recent Findings
There is emerging international consensus that HP should be classified based on clinical, radiologic, and pathologic features and not solely on disease duration. Environmental assessment and antigen avoidance remains the most important step in managing HP. Antifibrotics may soon become a viable option for chronic HP in the near future. Well-designed prospective controlled studies are underway.
Summary
Substantial gaps still remain in our understanding of the diagnosis and management of HP. Further research should focus on establishing internationally accepted diagnostic criteria and clinical practice guidelines to aid the clinician in the challenging treatment of patients with HP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
•• Vasakova M, Selman M, Morell F, Sterclova M, Molina-Molina M, Raghu G. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts of pathogenesis and potential targets for treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Medicine. 2019;200:301–8. Important review on our current understanding of HP pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of HP.
Pérez ER, Swigris JJ, Forssén AV, Tourin O, Solomon JJ, Huie TJ, et al. Identifying an inciting antigen is associated with improved survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2013;144(5):1644–51.
Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U, Dalphin JC, Morell F, Erkinjuntti-Pekkanen R, et al. Classification of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. International archives of allergy and immunology. 2009;149(2):161–6.
Zacharisen MC, Schlueter DP, Kurup VP, Fink JN. The long-term outcome in acute, subacute, and chronic forms of pigeon breeder’s disease hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2002;88(2):175–82.
Ohtani Y, Saiki S, Sumi Y, Inase N, Miyake S, Costabel U, et al. Clinical features of recurrent and insidious chronic bird fancier's lung. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2003;90(6):604–10.
Tateishi T, Ohtani Y, Takemura T, Akashi T, Miyazaki Y, Inase N, et al. Serial high-resolution computed tomography findings of acute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by avian antigen. Journal of computer assisted tomography. 2011;35(2):272–9.
•• Vasakova M, Morell F, Walsh S, Leslie K, Raghu G. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: perspectives in diagnosis and management. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2017;196(6):680–9. Key review on HP that proposed classification schema for HP as “acute/inflammatory” vs. “chronic/fibrotic”.
•• Salisbury ML, Myers JL, Belloli EA, Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Flaherty KR. Diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia. Where we stand and where we need to go. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2017;196(6):690–9. Key review on HP. Recommends treating HP according to whether inflammatory features are present or not.
Pérez-Padilla R, Salas J, Chapela R, Sánchez M, Carrillo G, Pérez R, et al. Mortality in Mexican patients with chronic pigeon breeder’s lung compared with those with usual interstitial pneumonia. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1993;148:49.
Ohtani Y, Saiki S, Kitaichi M, Usui Y, Inase N, Costabel U, et al. Chronic bird fancier’s lung: histopathological and clinical correlation. An application of the 2002 ATS/ERS consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Thorax. 2005;60(8):665–71.
Churg A, Muller NL, Flint J, Wright JL. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2006;30(2):201–8.
Chiba S, Tsuchiya K, Akashi T, Ishizuka M, Okamoto T, Furusawa H, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis with a usual interstitial pneumonia-like pattern: correlation between histopathologic and clinical findings. Chest. 2016;149(6):1473–81.
Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Cherniack RM, Curran-Everett D, Cool CD, Tuder RM, et al. The effect of pulmonary fibrosis on survival in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. The American journal of medicine. 2004;116(10):662–8.
Pérez F, Evans R, et al. Epidemiology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis among an insured population in the United States: a claims-based cohort analysis. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 2018;15.4:460–9.
Solaymani-Dodaran M, West J, Smith C, Hubbard R. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis: incidence and mortality in the general population. QJM: An International Journal of Medicine. 2007;100(4):233–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcm008.
Nogueira R, Melo N, e Bastos HN, Martins N, Delgado L, Morais A, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: antigen diversity and disease implications. Pulmonology. 2019;25(2):97–108.
Girard M, Lacasse Y, Cormier Y. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergy. 2009;64:322–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.01949.x.
Bourke SJ, Dalphin JC, Boyd G, McSharry C, Baldwin CI, Calvert JE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts. European Respiratory Journal. 2001;18(32 suppl):81s–92s.
Reich JM. Chirping rales in bird-fancier’s lung. Chest. 1993;104(1):326–7.
Fenoglio CM, Reboux G, Sudre B, Mercier M, Roussel S, Cordier JF, et al. Diagnostic value of serum precipitins to mould antigens in active hypersensitivity pneumonitis. European Respiratory Journal. 2007;29(4):706–12.
Van Hoeyveld E, Dupont L, Bossuyt X. Quantification of IgG antibodies to Aspergillus fumigatus and pigeon antigens by ImmunoCAP technology: an alternative to the precipitation technique? Clinical chemistry. 2006;52(9):1785–93.
Raulf M, Joest M, Sander I, Hoffmeyer F, Nowak D, Ochmann U, Preisser A, Schreiber J, Sennekamp J, Koschel D. Update of reference values for IgG antibodies against typical antigens of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergo J Int. 2019;1–2.
Lynch DA, Newell JD, Logan PM, King TE Jr, Müller NL. Can CT distinguish hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 1995;165(4):807–11.
Silva CI, Muller NL, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, Brown KK, Lee KS, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: differentiation from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia by using thin-section CT. Radiology. 2008;246(1):288–97.
Hansell DM, Wells AU, Padley SP, Müller NL. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: correlation of individual CT patterns with functional abnormalities. Radiology. 1996;199(1):123–8.
Lynch DA, Rose CS. Way D, King Jr TE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: sensitivity of high-resolution CT in a population-based study. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 1992;159(3):469–72.
Silva CI, Churg A, Müller NL. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: spectrum of high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2007;188(2):334–44.
Sahin H, Brown KK, Curran-Everett D, Hale V, Cool CD, Vourlekis JS, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: CT features—comparison with pathologic evidence of fibrosis and survival. Radiology. 2007;244(2):591–8.
Chung JH, Zhan X, Cao M, Koelsch TL, Manjarres DC, Brown KK, et al. Presence of air trapping and mosaic attenuation on chest computed tomography predicts survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 2017;14(10):1533–8.
• Barnett J, Molyneaux PL, Rawal B, Abdullah R, Hare SS, Vancheeswaran R, et al. Variable utility of mosaic attenuation to distinguish fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. European Respiratory Journal. 2019;54(1):1900531. Interesting study that noted the presence of mosaic attenuation in 51% of IPF patients and found the “headcheese sign” to be a highly specific radiologic finding for fibrotic HP.
Aburto M, Herráez I, Iturbe D, Jiménez-Romero A. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: differential diagnosis. Medical Sciences. 2018;6(3):73.
Ohshimo S, Bonella F, Cui A, Beume M, Kohno N, Guzman J, et al. Significance of bronchoalveolar lavage for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2009;179(11):1043–7.
• Morisset J, Johannson KA, Jones KD, Wolters PJ, Collard HR, Walsh SL, et al. Identification of diagnostic criteria for chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. An International Modified Delphi Survey. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2018;197(8):1036–44. Recent Delphi survey among international HP experts on consensus diagnostic features of chronic HP.
Meyer KC, Raghu G, Baughman RP, Brown KK, Costabel U, du Bois RM, et al. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: the clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular analysis in interstitial lung disease. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2012;185(9):1004–14.
• Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2018;198(5):e44–68. Most recent IPF clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis of IPF.
Adams TN, Newton CA, Batra K, Abu-Hijleh M, Barbera T, Torrealba J, et al. Utility of bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Lung. 2018;196(5):617–22.
Trahan S, Hanak V, Ryu JH, Myers JL. Role of surgical lung biopsy in separating chronic hypersensitivity pneumonia from usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis*: analysis of 31 biopsies from 15 patients. Chest. 2008;134(1):126–32.
Sharp C, McCabe M, Adamali H, Medford AR. Use of transbronchial cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease—a systematic review and cost analysis. QJM: An International Journal of Medicine. 2016;110(4):207–14.
Takemura T, Akashi T, Ohtani Y, Inase N, Yoshizawa Y. Pathology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008;14(5):440–54.
Churg A, Sin DD, Everett D, Brown K, Cool C. Pathologic patterns and survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:1765–70.
Ohtani Y, Kojima K, Sumi Y, Sawada M, Inase N, Miyake S, et al. Inhalation provocation tests in chronic bird fancier’s lung. Chest. 2000;118:1382–9.
Walsh SL, Sverzellati N, Devaraj A, Wells AU, Hansell DM. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: high resolution computed tomography patterns and pulmonary function indices as prognostic determinants. European radiology. 2012;22(8):1672–9.
Morell F, Villar A, Montero MÁ, Muñoz X, Colby TV, Pipvath S, et al. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective case-cohort study. The lancet Respiratory medicine. 2013;1(9):685–94.
• Ryerson CJ, Corte TJ, Lee JS, Richeldi L, Walsh SL, Myers JL, et al. A standardized diagnostic ontology for fibrotic interstitial lung disease. An international working group perspective. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2017;196(10):1249–54. Provides a framework for the standardization of diagnostic confidence in ILD.
Elicker BM, Jones KD, Henry TS, Collard HR. Multidisciplinary approach to hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Journal of thoracic imaging. 2016;31(2):92–103.
Sema M, Miyazaki Y, Tsutsui T, Tomita M, Eishi Y, Inase N. Environmental levels of avian antigen are relevant to the progression of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis during antigen avoidance. Immunity, inflammation and disease. 2018;6(1):154–62.
De Gracia J, Morell F, Bofill JM, Curull V, Orriols R. Time of exposure as a prognostic factor in avian hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respiratory medicine. 1989;83(2):139–43.
Quirce S, Vandenplas O, Campo P, Cruz MJ, de Blay F, Koschel D, et al. Occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis: an EAACI position paper. Allergy. 2016;71(6):765–79.
Millerick-May ML, Mulks MH, Gerlach J, Flaherty KR, Schmidt SL, Martinez FJ, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis and antigen identification–an alternate approach. Respiratory medicine. 2016;112:97–105.
Craig TJ, Hershey J, Engler RJ, Davis W, Carpenter GB, Salata K. Bird antigen persistence in the home environment after removal of the bird. Annals of allergy. 1992;69(6):510–2.
Ohshimo S, Bonella F, Guzman J, Costabel U. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Immunology and Allergy Clinics. 2012;32(4):537–56.
Kokkarinen JI, Tukiainen HO, Terho EO. Effect of corticosteroid treatment on the recovery of pulmonary function in farmer’s lung 1-3. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145:3–5.
Mönkäre S. Influence of corticosteroid treatment on the course of farmer’s lung. European journal of respiratory diseases. 1983;64(4):283–93.
De Sadeleer L, Hermans F, De Dycker E, Yserbyt J, Verschakelen J, Verbeken E, et al. Effects of corticosteroid treatment and antigen avoidance in a large hypersensitivity pneumonitis cohort: a single-centre cohort study. Journal of clinical medicine. 2019;8(1):14.
Morisset J, Johannson KA, Vittinghoff E, Aravena C, Elicker BM, Jones KD, et al. Use of mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine for the management of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2017;151(3):619–25.
Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, Pérez ER, Hamblin M, Patel N, Tener M, et al. Outcomes of immunosuppressive therapy in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ERJ open research. 2017;3(3):00016–2017.
Keir GJ, Maher TM, Ming D, Abdullah R, de Lauretis A, Wickremasinghe M, et al. Rituximab in severe, treatment-refractory interstitial lung disease. Respirology. 2014 Apr;19(3):353–9.
Cottin V, Hirani NA, Hotchkin DL, Nambiar AM, et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27:180076.
Shibata S, Furusawa H, Inase N. Pirfenidone in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a real-life experience. Sarcoidosis vasculitis and diffuse lung disease. 2018;35(2):139–42.
Behr J, Neuser P, Prasse A, Kreuter M, Rabe K, Schade-Brittinger C, et al. Exploring efficacy and safety of oral pirfenidone for progressive, non-IPF lung fibrosis (RELIEF): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, multi-center, phase II trial. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17:122.
Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Wells AU, Clerisme-Beaty E, Collard HR, Cottin V, et al. Design of the PF-ILD trial: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial of nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease. BMJ open respiratory research. 2017;4(1):e000212.
Kern RM, Singer JP, Koth L, Mooney J, Golden J, Hays S, et al. Lung transplantation for hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2015;147(6):1558–65.
Sansores R, Salas J, Chapela R, Barquin N, Selman M. Clubbing in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: its prevalence and possible prognostic role. Archives of internal medicine. 1990;150(9):1849–51.
Gimenez A, Storrer K, Kuranishi L, Soares MR, Ferreira RG, Pereira CA. Change in FVC and survival in chronic fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Thorax. 2018;73(4):391–2.
Miyazaki Y, Tateishi T, Akashi T, Ohtani Y, Inase N, Yoshizawa Y. Clinical predictors and histologic appearance of acute exacerbations in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2008;134(6):1265–70.
Ryerson CJ, Vittinghoff E, Ley B, Lee JS, Mooney JJ, Jones KD, et al. Predicting survival across chronic interstitial lung disease: the ILD-GAP model. Chest. 2014;145(4):723–8.
Mooney JJ, Elicker BM, Urbania TH, Agarwal MR, Ryerson CJ, Nguyen ML, et al. Radiographic fibrosis score predicts survival in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2013;144(2):586–92.
Hanak V, Golbin JM, Hartman TE, Ryu JH. High-resolution CT findings of parenchymal fibrosis correlate with prognosis in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2008;134(1):133–8.
• Salisbury ML, Gu T, Murray S, Gross BH, Chughtai A, Sayyouh M, et al. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: radiologic phenotypes are associated with distinct survival time and pulmonary function trajectory. Chest. 2019;155(4):699–711. Recent paper on classifying HRCT findings of HP patients into three phenotypes.
Wang P, Jones KD, Urisman A, Elicker BM, Urbania T, Johannson KA, et al. Pathologic findings and prognosis in a large prospective cohort of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 2017;152(3):502–9.
Nukui Y, Miyazaki Y, Masuo M, Okamoto T, Furusawa H, Tateishi T, Kishino M, Tateishi U, Ono J, Ohta S, Izuhara K. Periostin as a predictor of prognosis in chronic bird-related hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Allergology International. 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Anoop Nambiar reports research grants and personal fees from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech/Roche, Veractye, Nitto Denko, and Galapagos outside of the submitted work.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Interstitial Lung Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tam, W.S., Islam, T. & Nambiar, A.M. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (Including Environmental Assessment): Diagnosis and Management. Curr Pulmonol Rep 8, 131–138 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13665-019-00239-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13665-019-00239-6