Abstract
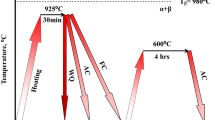
Static and fatigue characteristics of Ti–6Al–3Mo–2Zr–2Sn–2Nb–1.5Cr–0.1Si (TC21 Ti-alloy) in as-received and heat-treated conditions were investigated at ambient temperature. Two solution treatment cycles were applied on as-received TC21 samples. The first treatment was done below β-transus temperature (Tβ) at 920 °C/15 min and the second one above β-transus temperature (Tβ) at 1020 °C/15 min followed by water quenching. Both groups of samples were aged at 600 °C for 4 h before being air-cooled. The treated samples at 920 °C showed an equiaxed α + β structure. However, a complete martensitic structure was obtained in the treated samples at 1020 °C. In addition, secondary α-platelets (αs) precipitated inside retained β-phase (βr) due to aging process. The treated samples at 920 °C revealed the best tensile properties (tensile strength, 1447 MPa, and elongation, 8%). Theoretical study using Solidworks simulation program showed a fatigue limit of 709 MPa for as-received smooth samples. The treated samples at 920 °C obtained the highest fatigue limit of 866.5 MPa. However, the treated samples at 1020 °C revealed the lowest fatigue limit of 598.5 MPa. The as-received notched samples recorded a fatigue limit of 392 MPa by a decrease in the fatigue limit of about 45% compared with the as-received smooth samples. The experimental study using rotary bending fatigue machine recorded the best fatigue limit of 782.5 MPa for treated samples at 920 °C. As-received and treated samples at 1020 °C achieved fatigue limits of 651 and 546 MPa, respectively. The as-received notched samples showed a reduction in fatigue limit by approximately 43% from 625 to 359 MPa. Hence, the treated samples at 920 °C showed the best fatigue properties. The difference between theoretical and experimental fatigue values was less than 10% in four studied conditions.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Y. Li, X.L. Liu, G.Q. Wu, Z. Huang, Fretting fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 25, 64–70 (2019)
Y.C. Lin, Y. Tang, X.Y. Zhang, C. Chen, H. Yang, K.C. Zhou, Effects of solution temperature and cooling rate on the microstructure and micro-hardness of a hot compressed Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Vacuum. 159, 191–199 (2019)
H. Shao, Y. Zhao, P. Ge, W. Zeng, Crack initation and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy with equiaxed microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 586, 215–222 (2013)
C. Tan, Q. Sun, L. Xiao, Y. Zhao, J. Sun, Characterization of deformation in primary α phase and crack initiation and propagation of TC21 alloy using in-situ SEM experiments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 725, 33–42 (2018)
C. Tan, Q. Sun, L. Xiao, Y. Zhao, J. Sun, Cyclic deformation and microcrack initiation during stress controlled high cycle fatigue of a titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 711, 212–222 (2018)
G. Li, S. Qu, S. Guan, F. Wang, Study on the tensile and fatigue properties of the heat-treated HIP Ti-6Al-4V alloy after ultrasonic surface rolling treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 379, 124971 (2019)
A.S. Anoushe, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi, A. Barabi, C. Huang, F. Berto, On the microstructure evolution during isothermal low cycle fatigue of β-annealed Ti-6242S titanium alloy: internal damage mechanism, substructure development and early globularization. Int. J. Fatigue. 116, 592–601 (2018)
Committee, ASM Handbook Volume 19 Fatigue and Fracture (ASM International, Ohio, 1996), p. 2136
P. Zhao, B. Chen, J. Kelleher, G. Yuan, B. Guan, X. Zhang, S. Tu, High-cycle-fatigue induced continuous grain growth in ultrafine-grained titanium. Acta Mater. 174, 29–42 (2019)
I. Altenberger, R.K. Nalla, Y. Sano, L. Wagner, R.O. Ritchie, On the effect of deep-rolling and laser-peening on the stress-controlled low- and high-cycle fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V at elevated temperatures up to 550°C. Int. J. Fatigue. 44, 292–302 (2012)
S. Zhang, Y. Liang, Q. Xia, M. Ouzhao, Study on tensile deformation behavior of TC21 titaniumalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28, 1581–1590 (2019)
Z. Shi, H. Guo, R. Liu, X. Wang, Z. Yao, Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy by near-isothermal forging. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China. 25, 72–79 (2015)
T. Kakiuchi, R. Kawaguchi, M. Nakajima, M. Hojo, K. Fujimoto, Y. Uematsu, Perdication of fatigue limit in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy at elevated temperature. Int. J. Fatigue. 126, 55–61 (2019)
C. Tan, X. Li, Q. Sun, L. Xiao, Y. Zaho, J. Sun, Effect of α-phase morphology on low cycle fatigue behavior of TC21 alloy. Int. J. Fatigue. 75, 1–9 (2015)
R. Santhosh, M. Geetha, V.K. Saxena, R.M. Nageswara, Effect of duplex aging on microstructure and mechanical behavior of beta titanium alloy Ti–15V–3Cr–3Al–3Sn under unidirectional and cyclic loading conditions. Int. J. Fatigue. 73, 88–97 (2015)
X. Shi, W. Zeng, S. Xue, Z. Jia, The crack initiation behavior and the fatigue limit of Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–1Cr–1Fe titanium alloy with basket-weave microstructure. J. Alloy Compd. 631, 340–349 (2015)
Z.F. Shi, H.Z. Guo, J.W. Zhang, J.N. Yin, Microstructure-fracture toughness relations and toughening mechanism of TC21 titanium alloy with lamellar microstructure. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China. 28, 2440–2448 (2018)
N. Baohua, Z. Zihua, O. Yongzhong, C. Dongchu, C. Hong, S. Haibo, L. Shu, Effect of LCF pre-damage on very high cycle fatigue behavior of TC21 titanium alloy. Materials. 10, 1–14 (2017)
B. Nie, D. Chen, Z. Zhao, J. Zhang, Y. Meng, G. Gao, Notch effect on the fatigue behavior of a TC21 titanium alloy in very high cycle regime. Appl. Sci. 8, 1–13 (2018)
R.N. Elshaer, K.M. Ibrahim, A.F. Barakat, R.R. Abbas, Determination of phase transformation for TC21 Ti-alloy by dilatometry method. Open J. Met. 9, 1–10 (2019)
R.N. Elshaer, K.M. Ibrahim, Effect of cold deformation and heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 Ti alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China. 30, 1290–1299 (2020)
R.N. Elshaer, K.M. Ibrahim, M.A. Ahmed, I. Ahmed, Effect of cooling rate and aging process on wear behavior of TC21 Ti-alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 835, 265–273 (2020)
G. Lütjering, J.C. Williams, Titanium, 2nd edn (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, 2007)
H. Zhimin, Z. Yongqing, Z. Weidong, M. Xiaonan, L. Wenguang, Z. Pengsheng, Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure development of TC21 alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 46(8), 2087–2091 (2017)
Y. Xu, H. Liu, D. Yi, Z. Zhu, F. Zheng, Antiphase boundary-like structure in α′′ martensite of TC21 titanium alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China. 22, 1366–1371 (2012)
D. Jeong, Y. Kwon, M. Goto, S. Kim, High cycle fatigue and fatigue crack propagation behaviour of β-annealed Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 12, 1–10 (2017)
M. Janecek, F. Novy, P. Harcuba, J. Strasky, L. Trsko, M. Mhaede, L. Wagner, The very high cycle fatigue behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on physics of materials (ISPMA13), vol. 128(4), pp. 497–502 (2015)
T. Morita, S. Tanaka, S. Ninomiya, Improvement in fatigue strength of notched Ti-6Al-4V alloy by short-time heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 669, 127–133 (2016)
X. Peng, H. Guo, Z. Shi, C. Qjn, Z. Zhao, Microstructure characterization and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy after thermomechanical treatment. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China. 24, 682–689 (2014)
W. Ziaja, J. Sieniawski, K. Kubiak, M. Motyka, Fatigue and microstructure of two-phase titanium alloys. Inż. Mater. 22(5), 981–985 (2001)
S.S. Kim, J.K. Kwon, Y.J. Kim, W.K. Jang, S.G. Lee, J.K. Choi, Factors influencing fatigue crack propagation behavior of austenitic steels. Met. Mater. Int. 19(4), 683–690 (2013)
H.K. Sung, D.H. Jeong, T.D. Park, J.S. Lee, S.S. Kim, S-N fatigue behavior of Fe25Mn steel and its weld at 298 and 110 K. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 755–763 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elshaer, R.N., Abdelhameed, M., Ibrahim, K.M. et al. Static and Fatigue Characteristics of Heat-Treated Ti–6Al–3Mo–2Zr–2Sn–2Nb–1.5Cr–0.1Si Alloy. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 11, 443–453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-022-00856-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-022-00856-9