Abstract
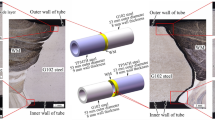
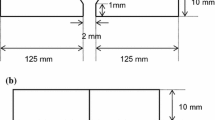
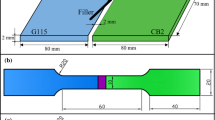
In liquid metal cooled fast breeder reactors (LMFBR), modified 9Cr–1Mo ferritic steel (P91 or Grade 91) is a preferred material for constructing steam generators due to its creep strength and stress corrosion cracking resistance. The austenitic stainless steels (SS 316LN and SS 304LN) are widely used for primary and secondary piping systems because of its oxidation resistance and excellent creep strength. So, the dissimilar metal weld joint (DMWJ) between P91 and SS 316LN is inevitable. Nickel-based consumables (Alloy 82 and Alloy 182) are preferred to join these materials. The DMWJ will experience the temperature up to 550 °C. For accurate integrity assessment, the mechanical properties of individual regions are to be evaluated at room temperature (RT) and 550 °C. Hence, the present investigation is focused on evaluating the mechanical properties of various regions of DMWJ at RT and 550 °C. From this investigation, it is understood that the tensile properties are heterogeneous across the DMWJ at RT and 550 °C. The high-temperature (550 °C) tensile properties are significantly lower with respect to the RT properties. The development of complex microstructures at the interfaces will alter the mechanical properties across the DMWJ.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Kumar, A. Pai, An overview of welding aspects and challenges during manufacture of intermediate heat exchangers for 500 MWe prototype fast breeder reactor. Proc. Eng. 86(Ic), 173–183 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.026
P. Puthiyavinayagam, P. Selvaraj, V. Balasubramaniyan, S. Raghupathy, K. Velusamy, K. Devan et al., Development of fast breeder reactor technology in India. Prog. Nucl. Energy (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2017.03.015
R.W. Swindeman, M.L. Santella, P.J. Maziasz, B.W. Roberts, K. Coleman, Issues in replacing Cr–Mo steels and stainless steels with 9Cr–1Mo–V steel. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 81(6), 507–512 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2003.12.009
K. Velusamy, P. Chellapandi, S.C. Chetal, B. Raj, Overview of pool hydraulic design of Indian prototype fast breeder reactor. Sadhana—Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 35(2), 97–128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-010-0022-0
A.K. Bhaduri, S. Venkadesan, P. Rodriguez, P.G. Mukunda, Transition metal joints for steam generators—an overview. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 58(3), 251–265 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-0161(94)90061-2
T. Sarikka, M. Ahonen, R. Mouginot, P. Nevasmaa, P. Karjalainen-Roikonen, U. Ehrnstén, H. Hänninen, Microstructural, mechanical, and fracture mechanical characterization of SA 508-alloy 182 dissimilar metal weld in view of mismatch state. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 145, 13–22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2016.06.004
S. Kumar, P.K. Singh, K.N. Karn, V. Bhasin, Experimental investigation of local tensile and fracture resistance behaviour of dissimilar metal weld joint: SA508 Gr.3 Cl.1 and SA312 type 304LN. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 40, 190–206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12484
H.T. Wang, G.Z. Wang, F.Z. Xuan, C.J. Liu, S.T. Tu, Local mechanical properties of a dissimilar metal welded joint in nuclear powersystems. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 568, 108–117 (2013)
D.W. Rathod, S. Pandey, P.K. Singh, R. Prasad, Mechanical properties variations and comparative analysis of dissimilar metal pipe welds in pressure vessel system of nuclear plants. J. Pressure Vessel Technol. 138(1), 11403 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4031129
J.W. Kim, K. Lee, J.S. Kim, T.S. Byun, Local mechanical properties of alloy 82/182 dissimilar weld joint between SA508 Gr.1a and F316 SS at RT and 320 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 384(3), 212–221 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.11.019
M. Sireesha, S.K. Albert, S. Sundaresan, Metallurgical changes and mechanical behaviour during high temperature aging of welds between alloy 800 and 316LN austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 19, 1411–1417 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1179/026708303225006042
M. Sireesha, S.K. Albert, S. Sundaresan, Influence of high-temperature exposure on the microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar metal welds between modified 9Cr–1Mo steel and alloy 800. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 10–12 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0241-x
M. Sireesha, S.K. Albert, V. Shankar, S. Sundaresan, A comparative evaluation of welding consumables for dissimilar welds between 316LN austenitic stainless steel and Alloy 800. J. Nucl. Mater. 279, 65–76 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3115(99)00275-5
M. Sireesha, V. Shankar, S.K. Albert, S. Sundaresan, Microstructural features of dissimilar welds between 316LN austenitic stainless steel and alloy 800. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 292, 74–82 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00969-2
M. Sireesha, S.K. Albert, S. Sundaresan, Thermal cycling of transition joints between modified 9Cr–1Mo steel and Alloy 800 for steam generator application. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 79, 819–827 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-0161(02)00104-7
H.Y. Lee, S.H. Lee, J.B. Kim, J.H. Lee, Creep-fatigue damage for a structure with dissimilar metal welds of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel and 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 29, 1868–1879 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.02.009
D.W. Rathod, R.K.R. Singh, S. Pandey, S. Aravindan, P.K. Singh, Influence of graded compositions and carbon diffusivities in buttering on structural integrity of dissimilar metal welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 702, 289–300 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.07.036
T. Böllinghaus, H. Herold, Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds (Springer, 2005), https://books.google.co.in/books?id=OveDQzH5fPwC
J.N. DuPont, S.W. Banovic, A.R. Marder, Microstructural evolution and weldability of dissimilar welds between a super austenitic stainless steel and nickel-based alloys. Weld. J. 82(6), 125–135 (2003)
D. Rathod, S. Aravindan, P.K. Singh, S. Pandey, Metallurgical characterization and diffusion studies of successively buttered deposit of Ni–Fe alloy and inconel on SA508 ferritic steel. ISIJ Int. 54(8), 1866–1875 (2014)
C. Sudha, A.L.E. Terrance, S.K. Albert, M. Vijayalakshmi, Systematic study of formation of soft and hard zones in the dissimilar weldments of Cr–Mo steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 302, 193–205 (2002)
R. Lin, H. Cui, F. Lu, X. Huo, P. Wang, Study on the microstructure and toughness of dissimilarly welded joints of advanced 9Cr/CrMoV. J. Mater. Res. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.381
H. Ming, Z. Zhang, J. Wang, E.H. Han, P. Wang, Z. Sun, Microstructure of a safe-end dissimilar metal weld joint (SA508-52-316L) prepared by narrow-gap GTAW. Mater. Charact. 123, 233–243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2016.11.029
S.C. Yoo, K.J. Choi, C.B. Bahn, S.H. Kim, J.Y. Kim, J.H. Kim, Effects of thermal aging on the microstructure of type-II boundaries in dissimilar metal weld joints. J. Nucl. Mater. 459, 2–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.01.009
H. Ming, Z. Zhang, J. Wang, E.H. Han, W. Ke, Microstructural characterization of an SA508-309L/308L-316L domestic dissimilar metal welded safe-end joint. Mater. Charact. 97, 101–115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.08.023
S. Kou, Welding Metallurgy, (Wiley, 2003), https://books.google.co.in/books?id=FQSEfRigyNUC
V.T. Paul, S. Saroja, P. Hariharan, A. Rajadurai, M. Vijayalakshmi, Identification of microstructural zones and thermal cycles in a weldment of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel. J. Mater. Sci. 42(14), 5700–5713 (2007)
V.D. Vijayanand, V. Ganesan, K. Laha, New insights to damage initiation during creep deformation of stainless steel weld joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 703(June), 37–44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.07.057
C.F. Etienne, D.V. Rossum, F. Roode, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Aspects of Creep, University of Sheffield, vol. 2 (1980), pp. 113–121
R. Mittal, B.S. Sidhu, Microstructures and mechanical properties of dissimilar T91/347H steel weldments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 220, 76–86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.01.008
D.J. Abson, J.S. Rothwell, Review of type IV cracking of weldments in 9–12%Cr creep strength enhanced ferritic steels. Int. Mater. Rev. 58(8), 437–473 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280412Y.0000000016
K.S. Chandravathi, K. Laha, K.B.S. Rao, S.L. Mannan, Microstructure and tensile properties of modified 9Cr–1Mo steel (grade 91). Mater. Sci. Technol. 17(May), 559–565 (2001)
K. Laha, K.S. Chandravathi, P. Parameswaran, K.B.S. Rao, S.L. Mannan, Characterization of microstructures across the heat-affected zone of the modified 9Cr–1Mo weld joint to understand its role in promoting type IV Cracking. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 38(1), 58–68 (2007)
G.E. Dieter, D. Bacon, Mechanical Metallurgy, (McGraw-Hill, 1988), https://books.google.co.in/books?id=hlabmB3e8XwC
A. Laukkanen, P. Nevasmaa, U. Ehrnstén, R. Rintamaa, Characteristics relevant to ductile failure of bimetallic welds and evaluation of transferability of fracture properties. Nucl. Eng. Des. 237(1), 1–15 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to UGC-DAE CSR (Kalpakkam node) for providing financial assistance (Project No. CSR-KN/CRS-56/2013-14/655) to carry out this investigation. Authors wish to record their sincere thanks to M/s. Mailam India Pvt. Limited, Pondicherry, for the consumables supply. Authors are also thankful to The Director, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), Kalpakkam, for providing base metals for carrying out this investigation. Authors are thankful to Director, Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL), Ambernath, for providing hot tensile test facility. The technical supports rendered by Mr. S. A. Krishnan, Scientist-E and Dr. G. Sasikala, Scientist-H+ from IGCAR, Kalpakkam, are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karthick, K., Malarvizhi, S., Balasubramanian, V. et al. Tensile Properties Variation Across the Dissimilar Metal Weld Joint Between Modified 9Cr–1Mo Ferritic Steel and 316LN Stainless Steel at RT and 550 °C. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 7, 209–221 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-018-0430-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-018-0430-9