Abstract
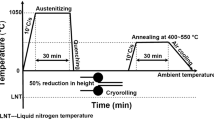
The microstructures and properties of the ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel were investigated. Martensite microstructure was obtained by quenching a low-carbon steel, followed by 50% strain cold rolling and then annealing at 500–650 °C for 2 and 30 min, respectively. Microstructures were observed, and tensile properties were measured for the specimens treated with cold rolling and annealing. The effects of annealing parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties were analyzed. It shows that the microstructure of specimen annealed at 550 °C for 30 min consists of ferrite grains with an average size of 330 nm. The ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel exhibits not only high tensile strength (867 MPa), but also good elongation (16.7%).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.L. Shaw, Processing nanostructured materials: an overview. JOM 52(12), 41–45 (2000)
R. Saha, R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, Fully recrystallized nanostructure fabricated without severe plastic deformation in high-Mn austenitic steel. Scripta Mater. 68(10), 813–816 (2013)
Y.Z. Tian, L.J. Zhao, S. Chen, D. Terada, A. Shibata, N. Tsuji, Optimizing strength and ductility in Cu–Al alloy with recrystallized nanostructures formed by simple cold rolling and annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 49(19), 6629–6639 (2014)
J. Hu, L.X. Du, H. Xie, P. Yu, R.D.K. Misra, A nanograined/ultrafine-grained low-carbon microalloyed steel processed by warm rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 605(605), 186–191 (2014)
N. Tsuji, K. Shiotsuki, H. Utsunomiya, Y. Satio, Low temperature superplasticity of ultra-fine grained 5083 aluminium alloy produced by accumulative roll-bonding. Mater. Sci. Forum 304, 73–78 (1999)
Y. Saito, N. Tsuji, H. Utsunomiya, T. Sakai, R.G. Hong, Ultrafine grained bulk aluminum produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scripta Mater. 39(9), 1221–1227 (1998)
R.Z. Valiev, A.V. Korznikov, R.R. Mulyukov, Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained materials produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 168(2), 141–148 (1993)
M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, Fabrication of submicrometer-grained Zn–22% Al by torsion straining. J. Mater. Res. 11(9), 2128–2130 (1996)
Y. Iwahashi, J. Wang, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, T.G. Langdon, Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultra-fine grained materials. Scripta Mater. 35(2), 143–146 (1996)
A. Belyakov, Y. Sakai, T. Hara, Y. Kimura, K. Tsuzaki, Effect of dispersed particles on microstructure evolved in iron under mechanical milling followed by consolidating rolling. Metal. Mater. Trans. A 32(7), 1769–1776 (2001)
Y. Okitsu, N. Takata, N. Tsuji, A new route to fabricate ultrafine-grained structures in carbon steels without severe plastic deformation. Scripta Mater. 60(2), 76–79 (2009)
L.X. Sun, N.R. Tao, M. Kuntz, J.Q. Yu, K. Luet, Annealing-induced hardening in a nanostructured low-carbon steel prepared by using dynamic plastic deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30(8), 731–735 (2014)
N. Tsuji, R. Ueji, Y. Minamino, Y. Saito, A new and simple process to obtain nano-structured bulk low-carbon steel with superior mechanical property. Scripta Mater. 46(4), 305–310 (2002)
R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, Y. Minamino, Y. Koizumi, Ultragrain refinement of plain low carbon steel by cold-rolling and annealing of martensite. Acta Mater. 50(16), 4177–4189 (2002)
M. Hamzeh, A. Kermanpur, A. Najafizadeh, Fabrication of the ultrafine-grained ferrite with good resistance to grain growth and evaluation of its tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 593(2), 24–30 (2014)
H. Ashrafi, A. Najafizadeh, Fabrication of the ultrafine grained low carbon steel by cold compression and annealing of martensite. T. Indian I. Metals 69(8), 1467–1473 (2016)
S. Morito, H. Saito, T. Ogawa, T. Furuhara, T. Maki, Effect of austenite grain size on the morphology and crystallography of lath martensite in low carbon steels. ISIJ Int. 45(1), 91–94 (2005)
A.S. Schulz-Beenken, Martensite in steels: its significance, recent developments and trends. J. Phys. IV 7(5), 657–665 (1997)
H.F. Lan, W.J. Liu, X.H. Liu, Ultrafine ferrite grains produced by tempering cold-rolled Martensite in low carbon and microalloyed steels. ISIJ Int. 47(11), 1652–1657 (2007)
M. Takahashi, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Model for transition from upper to lower bainite. Mat. Sci. Tech. 6(7), 592–603 (1990)
M. Najafi, H. Mirzadeh, M. Alibeyki, Toward unraveling the mechanisms responsible for the formation of ultrafine grained microstructure during tempering of cold rolled martensite. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 670, 252–255 (2016)
F.J. Humphreys, M. Hatherly, Chapter 9–Recrystallization of Two-Phase Alloys. Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena: second edition, (2004), pp. 285–319
W. Lei, T.S. Wang, Z. Li, X.J. Zhang, Q.F. Wang, F.C. Zhang, A new process to fabricate ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel with high strength and high elongation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528(2), 784–787 (2010)
T.S. Wang, Z. Li, B. Zhang, X.J. Zhang, J.M. Deng, F.C. Zhang, High tensile ductility and high strength in ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527(10–11), 2798–2801 (2010)
Z.W. Hu, G. Xu, H. Yang, C. Zhang, R. Yu, The effects of cooling mode on precipitation and mechanical properties of a Ti–Nb microalloyed steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(12), 4216–4222 (2014)
F. Liu, G. Xu, Y.L. Zhang, H.J. Hu, L.X. Zhou, Z.L. Xue, In situ observations of austenite grain growth in Fe–C–Mn–Si super bainitic steel. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20(11), 1060–1066 (2013)
M.A. Neri, R. Colás, Analysis of a martensitic stainless steel that failed due to the presence of coarse carbides. Mater. Charact. 47(3), 283–289 (2001)
C.Y. Lee, J. Jeong, J. Han, S.J. Lee, S. Lee, Y.K. Lee, Coupled strengthening in a medium manganese lightweight steel with an inhomogeneously grained structure of austenite. Acta Mater. 84, 1–8 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 51274154), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA03A504), and State Key Laboratory of Development and Application Technology of Automotive Steels (Baosteel Group).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Xu, G., Liang, W. et al. Effect of Annealing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Low-Carbon Steel with Ultrafine Grains. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 6, 233–239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-017-0350-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-017-0350-0