Abstract
This study explores the effects of halibut oil cream on different phases of wound healing and assess its potential as a supplement for promoting wound healing in rats. The study randomly assigned five groups of male wistar rats to receive different treatments: a vehicle-control group (water-soluble cream base), a positive-control group (Povidone-iodine ointment, PI-5%), and three halibut oil cream formulation (HBOF) treatment groups with strengths of 3, 9, and 27%. An excision wound model was used to induce injury and daily as well as terminal wound healing indices such as wound area contraction, relative wound area percentage, inflammatory and proliferative phases, oxidative stress, and cytokine levels were recorded. Compared to the vehicle control group, both the PI-5% and HBOF treatment groups significantly promoted wound healing. They demonstrated reduced wound size and oxidative stress in regenerated skin tissue. Histopathological examination revealed a marked increase in collagen production, and analysis of cytokine levels indicated enhanced efficacy. These effects can be attributed to the high hydroxyproline content of halibut oil. The findings of this study suggest that topically applying halibut oil cream may serve as a useful supplement for promoting wound healing in rats. The omega-3 fatty acids and other components present such as vitamin A and D in the cream formulation demonstrated beneficial effects on wound size reduction, oxidative stress reduction, collagen production, and cytokine efficacy.
Graphical abstract

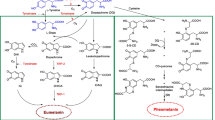
Graphical Abstract depicting the experimental procedure for studying wound healing. Albino Wistar rats were utilized to create a 500 mm2 wound, with varying concentrations of HBOF applied topically from day (D) 1 to 15. The control group received treatment with a water-soluble cream base, while the standard group was treated with Povidone Iodine 5%. On day 16, the skin surrounding the wounds of all animals was carefully dissected, and biochemical, cytokine level, and histopathological evaluations were performed on the skin specimens. Throughout the study, measurements were taken for body weight, the inflammatory phase (D1-5), the proliferative phase (D5-15), and wound area contraction (D1-15).




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HBOF:
-
Halibut Oil Cream Formulation
- RT:
-
Retention Time
- D:
-
Day
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- SOD:
-
Superoxide Dismutase
- GSH:
-
Reduced Glutathione
- NBT:
-
Nitroblue Tetrazolium
- TMB:
-
3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine
- ROS:
-
Reactive Oxygen Species
- KOH:
-
Potassium hydroxide
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric Acid
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme‐Linked Immunosorbent Assay
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β and TGF-β: Transforming growth factor‐beta
- PI-5%:
-
Povidone Iodine 5% w/w
- H&E Stain:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin Stain
- CCSEA:
-
Committee for the control and supervision of experiments on animals
- PRC:
-
Pretox Research Centre
- hrs:
-
Hours
- Secs:
-
Seconds
- SEM:
-
Standard Error Mean
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of Variance
- HPLC:
-
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- GC:
-
Gas Chromatography
- FID:
-
Flame Ionized Detector
References
Abramov Y, Golden B, Sullivan M, Botros SM, Miller JR, Alshahrour A, Sand PK (2007) Histologic characterization of vaginal vs. abdominal surgical wound healing in a rabbit model. Wound Repair Regen 15(1):80–86
Al-Khalaifah H (2020) Modulatory effect of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids on immunity, represented by phagocytic activity. Front Veterinary Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.569939
Alinafiah SM, Azlan A, Ismail A, Rashid NKMA (2021) Method development and validation for omega-3 fatty acids (Dha and epa) in fish using gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (gc-fid). Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216592
Andritoiu CV, Andriescu CE, Ibanescu C, Lungu C, Ivanescu B, Vlase L, Popa M (2020) Effects and characterization of some topical ointments based on vegetal extracts on incision, excision, and thermal wound models. Molecules 25(22):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES25225356
Arantes EL, Dragano N, Ramalho A, Vitorino D, de-Souza GF, Lima MHM, Araújo EP (2016) Topical docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) accelerates skin wound healing in rats and activates GPR120. Biol Res Nurs 18(4):411–419
Asadi SY, Parsaei P, Karimi M, Ezzati S, Zamiri A, Mohammadizadeh F, Rafieian-kopaei M (2013) Effect of green tea (Camellia sinensis) extract on healing process of surgical wounds in rat. Int J Surg 11(4):332–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.02.014
Baum CL, Arpey CJ (2005) Normal cutaneous wound healing: clinical correlation with cellular and molecular events. Dermatol Surg 31(6):674–686
Bawn CSH (1987) Encyclopedia of polymer science and engineering. Polymer. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(87)90274-6
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44(1):276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Bhagavathula N, Warner RL, Dasilva M, McClintock SD, Barron A, Aslam MN, Varani J (2009) A combination of curcumin and ginger extract improves abrasion wound healing in corticosteroid-impaired hairless rat skin. Wound Repair Regen 17(3):360–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2009.00483.x
Builders PF, Kabele-Toge B, Builders M, Chindo BA, Anwunobi PA, Isimi YC (2013) Wound healing potential of formulated extract from hibiscus sabdariffa calyx. Indian J Pharm Sci 75(1):45
Childs DR, Murthy AS (2017) Overview of wound healing and management. Surg Clin North Am 97(1):189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2016.08.013
El Kahi CG, Atiyeh BS, Abdallah Hajj Hussein I, Jurjus R, Dibo SA, Jurjus A, Jurjus A (2009) Modulation of wound contracture α-smooth muscle actin and multispecific vitronectin receptor integrin αvβ3 in the rabbit’s experimental model. Int Wound J 6(3):214–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-481X.2009.00597.x
Emmett AD, Bird OD, Nielsen C, Cannon HJ (1932) A study of Halibut-liver oil: I. With respect to its vitamin potency, physical constants, and tolerance. Ind Eng Chem Res 24(9):1073–1077. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50273a025
Fronza M, Caetano GF, Leite MN, Bitencourt CS, Paula-Silva FWG, Andrade TAM, Faccioli LH (2014) Hyaluronidase modulates inflammatory response and accelerates the cutaneous wound healing. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112297
Fujiwara T, Duscher D, Rustad KC, Kosaraju R, Rodrigues M, Whittam AJ, Gurtner GC (2016) Extracellular superoxide dismutase deficiency impairs wound healing in advanced age by reducing neovascularization and fibroblast function. Exp Dermatol 25(3):206–211
Gabbiani G (2003) The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. The J Pathol: A J Pathol Soc Great Br Irel 200(4):500–503
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74(1):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90326-2
Iftikhar F, Arshad M, Rasheed F, Amraiz D, Anwar P, Gulfraz M (2010) Effects of Acacia honey on wound healing in various rat models. Phytother Res 24(4):583–586. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2990
Karoud W, Ghlissi Z, Krichen F, Kallel R, Bougatef H, Zarai Z, Bougatef A (2020) Oil from hake (Merluccius merluccius): characterization, antioxidant activity, wound healing and anti-inflammatory effects. J Tissue Viability 29(2):138–147
Khan AA, Alsahli MA, Rahmani AH (2018) Myeloperoxidase as an active disease biomarker: recent biochemical and pathological perspectives. Med Sci 6(2):33
Khazaeli P, Alaei M, Khaksarihadad M, Ranjbar M (2020) Preparation of PLA/chitosan nanoscaffolds containing cod liver oil and experimental diabetic wound healing in male rats study. J Nanobiotechnol 18(1):1–9
Kunkemoeller B, Kyriakides TR (2017) Redox signaling in diabetic wound healing regulates extracellular matrix deposition. Antioxid Redox Signal 27(12):823–838. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7263
Landén NX, Li D, Ståhle M (2016) Transition from inflammation to proliferation: a critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(20):3861–3885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2268-0
Levenson SM, Gruber CA, Rettura G, Gruber DK, Demetriou AA, Seifter E (1984) Supplemental vitamin A prevents the acute radiation-induced defect in wound healing. Ann Surg 200(4):494–512. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-198410000-00011
Li J, Chen J, Kirsner R (2007) Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin Dermatol 25(1):9–18
Liu Y, Li Y, Li N, Teng W, Wang M, Zhang Y, Xiao Z (2016) TGF-β1 promotes scar fibroblasts proliferation and transdifferentiation via up-regulating MicroRNA-21. Sci Rep 6(1):32231
Mahboub M, Attari AMA, Sheikhalipour Z, Attari MMA, Davami B, Amidfar A, Lotfi M (2022) A comparative study of the impacts of aloe vera gel and silver sulfadiazine cream 1% on healing, itching and pain of burn wounds: a randomized clinical trial. J Caring Sci 11(3):132–138. https://doi.org/10.34172/jcs.2021.036
Mann PC, Vahle J, Keenan CM, Baker JF, Bradley AE, Goodman DG, Tanaka T (2012) International harmonization of toxicologic pathology nomenclature: an overview and review of basic principles. Toxicol Pathol 40(4):7S-13S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312438738
Manzuoerh R, Farahpour MR, Oryan A, Sonboli A (2019) Effectiveness of topical administration of Anethum graveolens essential oil on MRSA-infected wounds. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1650–1658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.117
Masson-Meyers DS, Andrade TAM, Caetano GF, Guimaraes FR, Leite MN, Leite SN, Frade MAC (2020) Experimental models and methods for cutaneous wound healing assessment. Int J Exp Pathol 101(1–2):21–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/iep.12346
Masson-Meyers DS, Bumah VV, Enwemeka CS (2016) Blue light does not impair wound healing in vitro. J Photochem Photobiol, B 160:53–60
McDaniel JC, Belury M, Ahijevych K, Blakely W (2008) Omega-3 fatty acids effect on wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 16(3):337–345
McDaniel JC, Massey K, Nicolaou A (2011) Fish oil supplementation alters levels of lipid mediators of inflammation in microenvironment of acute human wounds. Wound Repair Regen: Offl Publ Wound Heal Soc Eur Tissue Repair Soc 19(2):189. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1524-475X.2010.00659.X
McDaniel JC, Rausch J, Tan A (2020) Impact of omega-3 fatty acid oral therapy on healing of chronic venous leg ulcers in older adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled single-center trial. Trials. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3970-7
Mori R, Kondo T, Nishie T, Ohshima T, Asano M (2004) Impairment of skin wound healing in β-1, 4-galactosyltransferase-deficient mice with reduced leukocyte recruitment. Am J Pathol 164(4):1303–1314
Morton JJ, Malone MH (1972) Evaluation of vulneray activity by an open wound procedure in rats. Archiv Int De Pharmacodyn Et De Ther 196(1):117–126
Ortonne JP, Clévy JP (1994) Physiology of cutaneous cicatrization. Rev Prat 44(13):1733–1737
Patriche EL, Croitoru O, Coman G, Stefan CS, Tutunaru D, Cuciureanu R (2014) Validation of HPLC method for the determination of retinol in different dietary supplements. Roman Biotechnol Lett 19(6):9875–9882
Pizzimenti S, Toaldo C, Pettazzoni P, Dianzani MU, Barrera G (2010) The “Two-Faced” effects of reactive oxygen species and the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal in the hallmarks of cancer. Cancers 2:338–363. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2020338
Prockop DJ, Udenfriend S (1960) A specific method for the analysis of hydroxyproline in tissues and urine. Anal Biochem 1(3):228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(60)90050-6
Razzaghi R, Pourbagheri H, Momen-Heravi M, Bahmani F, Shadi J, Soleimani Z, Asemi Z (2017) The effects of vitamin D supplementation on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Diabetes Compl 31(4):766–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.06.017
Shackelford C, Long G, Wolf J, Okerberg C, Herbert R (2002) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nonneoplastic lesions in toxicology studies. Toxicol Pathol 30(1):93–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230252824761
Shukla A, Rasik AM, Patnaik GK (1997) Depletion of reduced glutathione, ascorbic acid, vitamin E and antioxidant defence enzymes in a healing cutaneous wound. Free Radical Res 26(2):93–101. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715769709097788
Siregar FD, Hidayat W (2023) The role of vitamin D on the wound healing process: a case series. Int Med Case Rep J 16:227–232. https://doi.org/10.2147/IMCRJ.S402005
Sun ML, Zhao F, Chen XL, Zhang XY, Zhang YZ, Song XY, Yang J (2020) Promotion of wound healing and prevention of frostbite injury in rat skin by exopolysaccharide from the Arctic marine bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010048
Temova Ž, Roškar R (2016) Stability-indicating HPLC-UV method for vitamin D3 determination in solutions, nutritional supplements and pharmaceuticals. J Chromatogr Sci 54(7):1180–1186. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmw048
Terkelsen LH, Eskild-Jensen A, Kjeldsen H, Barker JH, Hjortdal VE (2000) Topical application of cod liver oil ointment accelerates wound healing: an experimental study in wounds in the ears of hairless mice. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 34(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/02844310050160123
Truzzi C, Illuminati S, Annibaldi A, Antonucci M, Scarponi G (2017) Quantification of fatty acids in the muscle of Antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: optimization of the analytical methodology. Chemosphere 173:116–123
Yin K, Agrawal DK (2014) Vitamin D and inflammatory diseases. J Inflamm Res 7(1):69–87. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S63898
Zinder R, Cooley R, Vlad LG, Molnar JA (2019) Vitamin A and wound healing. Nutr Clin Pract 34(6):839–849. https://doi.org/10.1002/ncp.10420
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Shri JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, for providing the necessary facilities and support to carry out this research project. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Avijit Choudhury and Mr. Vishal Patel for their valuable support in carrying out the research work at Pretox Research Centre.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
STS: conceptualized, planned, and performed the project, developed the methodology, performed the formal analysis and data visualization, and wrote the original draft and edited the final manuscript. AK, SAA, and DK developed and supervised the methodology, performed the investigation and, edited and reviewed the manuscript. SKD conceptualized, visualized, data curation and supervised the project and edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Animal experiment protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Animal Committee (Approval No: PRC/IAEC/2023/01/XIV/001), formed under the regulation of CCSEA, INDIA.
Competing interests
S. T. Shukla has no conflict of interest. Anu Kaushik has no conflict of interest. Samiullah Allahbaksh Auti has no conflict of interest. Dinesh Kumar has no conflict of interest. Supriya Kumar Das has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, S.T., Kaushik, A., Auti, S.A. et al. In-vivo assessment of wound healing activity of halibut oil cream in rat model of excision wound. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-024-00748-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-024-00748-z