Abstract
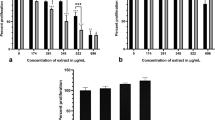
Complex synergistic interplay of the composite mixture of compounds present in plants may be the reason of their beneficial effects. In this perspective an important yet not well studied ethnomedicinal plant Lasiosiphon glaucus was subjected to invitro anticancer analysis. The flowcytometry study revealed that the plant has cytotoxic effect against breast cancer cells (MCF-7) acting upon multiple pathways, inhibiting cell proliferation (Downregulation of Bcl2 and Akt) and inducing apoptosis (Mitochondrial membrane depolarisation, Upregulation of p53, caspase 8, caspases 3 and DNA fragmentation). It is interesting that the plant activated both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways while inhibiting cancer cell proliferation. The study, a first report, highlights the use of L. glaucus in ethnomedicine for treating cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhilash N, Ramesh KV (2017) Gas chromatography-mass spectrometric analysis, adsorption distribution metabolism excretion and toxicity analysis and molecular docking studies of phytochemicals of ethno botanical medicinal plant Laciocephon glaucus. Intern J Pharma Bio Sci 8:742–749
Abhilash N, Ramesh KV (2018) Lasiosiphon glaucus: Preliminary Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant Activity and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Ethnomedicinal Plant. Research and Reviews: J of Herbal Sci 7:1-7
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Jain AK, Jaiswal AK, Aggarwal BB (2006) Genetic Deletion of NAD(P)H:Quinone Oxidoreductase 1 Abrogates Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB, IκBα Kinase, c-Jun N-terminal Kinase, Akt, p38, and p44/42 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases and Potentiates Apoptosis. The J Biol Chemis 281:19798–19808
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2007) Simvastatin potentiates TNFalpha-induced apoptosis through the down‐regulation of NFkappaB‐dependent antiapoptotic gene products: role of IkappaBalpha kinase and TGF‐beta‐activated kinase‐1. J Immunol 178:2507–2516
Artun FT, Karagoz A, Ozcan G, Melikoglu G, Anil S, Kultur S, Sutlupinar N (2016) In vitro anticancer and cytotoxic activities of some plant extracts on HeLa and Vero cell lines. JBUON 21:720–5
Atanasov AG, Zotchev SB, Dirsch VM, the International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce, Supuran CT (2021) Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20(3):200–216
Burgering BM, Coffer PJ (1995) Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 376:599–602
Chu PS, Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN (1989) Trilostane with hydrocortisone in treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 13:117–121
Czerski L, Nunez G (2004) Apoptosome formation and Caspase activation: is it different in the heart? J of Mol Cell Cardio 37:643–652
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Davis RE, Staudt LM (2002) Molecular diagnosis of lymphoid malignancies by gene expression profiling. Cur Opini Hemato 9:333–338
Elisavet Paplomata and Ruth O’Regan (2014) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer: targets, trials and biomarkers. Therap Adv Med Oncol 6:154–166
Fridman JS, Lowe SW (2003) Control of apoptosis by p53. Oncogene 22:9030–9040
Gowrish A, Vagdevi HM, Rajashekar H, Vijaya Kumar ML, Shobha KS (2013) In-Vitro Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activity of Gnidia glauca (Fresen) Gilg Root Extract. J Appli Chemistry 2:1362–1369
Karna P, Chagani S, Gundala SR (2012) Benefits of whole ginger extract in prostate cancer. British J of Nutri 107:473–484
Kominami K, Nakabayashi J, Nagai T, Tsujimura Y, Chiba K, Kimura H, Miyawaki A, Sawasaki T, Yokota H, Manabe N, Sakamaki K (2012) The molecular mechanism of apoptosis upon caspase-8 activation: Quantitative experimental validation of a mathematical model. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:1825–1840
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Chang CH, Lin CC (2005) The mechanism of ellipticine-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human breast MCF-7 cancer cells. Cancer Lett 223:293–301
Kwan YP, Saito T, Ibrahim D, Saleh Al-Hassan FM, Oon CE, Chen Y, Jothy SL, Kanwar JR, Sasidharan S (2016) Evaluation of the cytotoxicity, cell-cycle arrest, and apoptotic induction by Euphorbia hirta in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Pharma Biol 54:1223–1236
Liu RH (2003) Health benefits of fruit and vegetables are from additive and synergistic combinations of phytochemicals. American J Clini Nutri 78:517S–520S
Lockshin RA, Williams CM (1965)) “Programmed cell death-I. Cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental muscles of the Pernyi silkmoth., ” J Insect Physiol 11:123–133
Luo J, Manning BD, Cantley LC (2003) Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 4:257–262
Martin S, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC, Fitzgerald P, Green DR (2000) p53 Induces Apoptosis by Caspase Activation through Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Release. The J Biol Chem 275:7337–7342
Manosroiab J, Dhumtanoma P, Manosroiab A (2006) Anti-proliferative activity of essential oil extracted from Thai medicinal plants on KB and P388 cell lines. Cancer Letters 235(1):114–120
Miyashita T, Reed JC (1995) Tumor Suppressor p53 Is a Direct Transcriptional Activator of the Human bax Gene. Cell 80:293–299
Mortenson MM, Galante JG, Gilad O, Schlieman MG, Virudachalam S, Kung HJ, Bold RJ (2007) BCL-2 Functions as an Activator of the AKT Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer J Cellu. Biochem 102:1171–1179
Mykhaylo S, Frasinyuk, Galyna PM, Svitlana P, Bondarenko VM, Sviripa, Zhang W, Cai X, Michael VF, Mohler JL, Liube C, David SW (2015) Application of Mannich bases to the synthesis of hydroxymethylated isoflavonoids as potential antineoplastic agents. Organic Biomol Chem 13:11292–11301
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM (2003) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat Prod 66:1022–1037
Österberg F, Morris GM, Sanner MF, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2001) Automated Docking to Multiple Target Structures: Incorporation of Protein Mobility and structural water heterogeneity in AutoDock. Proteins 46:34–40
Puar YR, Shanmugam MK, Fan L, Arfuso F, Sethi G, Tergaonkar V (2018) Evidence for the Involvement of the Master Transcription Factor NF-κB in Cancer Initiation and Progression.Biomedicines6:82
Roy MJ, Vom A, Czabotar PE, Lessene G (2014) Cell death and the mitochondria: therapeutic targeting of the BCL-2 family-driven pathway. British J Pharmaco 171:1973–1987
Sanchez-Beato M, Sanchez-Aguilera A, Piris MA (2003) Cell cycle deregulation in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 101:1220–1235
Solowey E, Lichtenstein M, Sallon S, Paavilainen H, Solowey E, Lorberboum-Galski H (2014) Evaluating Medicinal Plants for Anticancer Activity. Scientif World J
Suffness M, Pezzuto JM (1990) Assays related to cancer drug discovery. In: In: Hostettmann K (ed) Methods in plant biochemistry: assay for bioactivity. Academic Press, London, pp 71–133
Taylor WR, Stark GR (2001) Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene 20:1803–1815
Weinstein IB (2002) Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes-the Achilles heal of cancer. Science 297:63–64
Wolf BB, Schuler M, Echeverri F, Greeni DR (1999) Caspase-3 Is the Primary Activator of Apoptotic DNA Fragmentation via DNA Fragmentation Factor-45/Inhibitor of Caspase-activated DNase Inactivation. The J Biolo Chem 274:30651–30656
Yin C, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Dyke TV (1995) Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosis in vivo. Cell 80:293–299
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Ramesh Kudlutota for sharing his knowledge on plant collection, identification and guidance. Also, thankful to the Principal of SDMRIBS, Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara University, Dharwad, India for his support.
Funding
No financial support from any government / private organizations had been received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
We have not used any animal models in this study, however, have used MCF-7 cell lines which was purchased from the National Centre for Cell Science, Pune, India.
Conflict of interest
N. Abhilash has no conflict of interest. S. K. Ajay has no conflict of interest. K. V. Ramesh has no conflict of interest. Renukaradhya K. Math has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abhilash, N., Ajay, S.K., Ramesh, K.V. et al. Lasiosiphon glaucus a potent ethnobotanical medicinal plant against breast cancer targeting multiple pathways: an invitro study. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 23, 557–564 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-021-00624-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-021-00624-0