Abstract
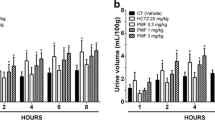
The objective of this study briefly focus on the evaluation of diuretic activity and its possible mechanism of action of methanolic extract of Syzygium cumini (MESCS) seeds. The MESCS doses (150 and 300 mg/kg) were orally administered to male Wistar albino rats. Urine volume, urinary excretion, diuretic action, diuretic activity, electrolyte levels in urine, natriuretic, saluretic, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity, were measured in of saline loaded rats at 5 and 24th hour. Plasma creatinine and uric acid were also measured at 24th hour. The oral administration of MESCS increased the urine volume and electrolyte excretion at the 24th hour compared to 5th hour. To assess the involvement of the prostaglandin system in the mechanism of action, oral administration of methanolic extract of S. cumini (300 mg/kg) in association with Lornoxicam (3 mg/kg) reduced urinary and sodium, potassium, and chlorine excretion when compared to MESCS group. The results concluded that MESCS shown maximum diuretic activity at a dose of 300 mg/kg 24th hour and its mechanism involved prostaglandin system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishek KS, Vinod KV (2011) Syzygium cumini: an oveview. J Chem Pharm Res 3:108–11
Al-Ali M, Wahbi S, Twaij H, Al-Badr A (2003) Tribulus terrestris: preliminary study of its diuretic and contractile effects and comparison with Zea mays. J Ethanopharmacol 85:257–260
Alvarez ME, Maria AOM, Villegas O, Saad JR (2003) Evaluation of diuretic activit of the constituents of Clematis monteridensis Spreng in Rats. Phytotheraphy Res 17:958–60
Amuthan A, Bharathi C, Bairy KL, Sudhakar, Prakash M (2012) Evaluation of diuretic activity of Amaranthus spinoosus Linn. aqueous extract in Wistar rats. J Ethanopharmacol 140:424–27
Benjumea D, Abdala S, Hernandez-Luis F, Perez-Paz P, Martin-Herrera D (2005) Diuretic activity of Artemisia thuscula, an endemic canary species. J Ethnopharmacol 100:205–209
Bernard N, Sacquet J, Benzoni D, Sassard J (2000) Cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 and thromboxane synthase in kidneys of lyon hypertensive rats. American J Hypertens 13:404–409
Demaria AN, Weir MR (2003) Loxibs beyond the gastro intestinal tract: renal and cardiovascular issues. J Pain Symptom Manag 25:41–49
Indian Pharmacopoeia (1996) Publications and information directorate (CSIR), New Delhi, India 2: 689
Jorge VG, Rolffy OA, Julio RL, Patricia CE, Rafael VM, Maximiliano IB et al (2010) Vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effects of methanolic extract from roots of Laelia anceps are mediated by Ca+2channel antagonism. Fitoterapia 81:350–357
Lipschitz WL, Hadidian Z, Kerpesar A (1943) Bioassay of diuretics. Pharmacol Ex Therap 79:97–110
Mamun MM, Billah MM, Ashek MA, Ahasan MM, Hossai MJ, Sultana T (2003) Evaluation of diuretic activity of Ipomoea aquatic in mice model study. J Med Sci 9:395–400
Modi DC, Patel JK, Shah BN, Nayak BS (2010) Pharmacognostic studies of the seed of Syzygium cumini Linn. Int J Pharmaceutical Sci 1:113–125
Mukherjee PK, Pal M, Saha K, Saha BP (1996) Diuretic activity of extract of the rhizomes of Nelumbonucifera gaertn. Phytotherapy Res 10:424–25
Murugesan T, Manikandan L, Suresh KB, Pal M, Saha BP (2000) Evaluation of diuretic potentials of Jussiaea suffruticosa Linn extracts in rats. Indian J Pharma Sci 62:150–151
OECD (2001) Guidline for testing of chemicals. 425:1–26
Ratrasooriya WD, Pieris KP, Samaratunga U, Jayakody JR (2004) Diuretic activity of Spilanthus acmella flowers in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 91:317–320
Satoa M, Nakayama T, Soma M, Aoia N, Kusugeb K, Haketab A et al. (2007) Association between prostaglandin E2 receptor gene and essential hypertension prostaglandins, leukotrienes and essential fatty acids 77: 15–20
Soleimani M, Barone S, Xu J, Shull GE, Siddiqui F, Zahedi K, Amlal H (2012) Double knockout of pendrin and Na-Cl co-transporter (NCC) causes severe salt wasting, volume depletion, and renal failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:13368–13373
Somova LI, Shode FO, Ramanan P, Nadar A (2003) Antihypertensive, antiatherosclerotic and antioxidant activity of triterpenoids isolated from Oleaeuropaea subspecies Africana leaves. J Ethanopharmacol 84:299–305
Stanic G, Samarzija I, Blazevic N (1998) Time dependent diuretic response in rats treated with Juniper berry preparations. Phytotherap Res 12:494–97
Twaij HAA, Elisha EE, Al-Jeboory AA (1985) Screening of Iraqi medicinal plants for diuretic activity. Indian J Pharmac 17:73–76
Venkateshwarlu E, Sharvana BS, Umasankar K, Venkateshwar Rao J (2013) Evaluation of diuretic activity of Isatin derivatives in Wistar rats. J Pharm Nutri Sci 3:141–148
Whelton A, Hamilton CW (1991) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug: effects on kidney function. J Cli Pharmacol 31:588–598
Yasar S, Lin FM, Fried LP, Kawas CH, Sink KM, DeKosky ST, Carlson MC (2012) Diuretic use is associated with better learning and memory in older adults in the Ginkgo evaluation of memory study. Alzheimers Dement 8:188–19
Conflict of Interests
No conflict of interests. No financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkateshwarlu, E., Bhava, B.S.S., Kumar, R.S. et al. Evaluation of diuretic activity of Syzygium cumini and its effect on prostaglandin system. Orient Pharm Exp Med 15, 45–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-015-0179-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-015-0179-5