Abstract
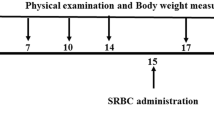
Chai-Ling-Tang (CLT) is a traditional Chinese herbal decoction consisting of twelve different herbs, and it has been used to treat a number of immune related disorders. However, the mechanism for its clinical effectiveness was not fully understood. In this study, CLT’s effect on the immune system of female B6C3F1 mice was evaluated by examining the IgM antibody forming cell (AFC) response; natural killer (NK) cell activity; the expression of splenocyte surface markers; concanavalin (Con) A and anti-CD3 antibody-mediated T-lymphocyte proliferation; lipopolysaccharide-mediated-B cell proliferation, and the host resistances to the Listeria monocytogenes bacterial infection and B16F10 melanoma. The results from these studies suggest that the administration of CLT at doses between 400 and 800 mg/kg/day by gavage for 28 days modulates the immune response in female B6C3F1 mice by increasing the number, percentage, and activity of NK cells, both Con A and anti-CD3 antibody-mediated T-cell proliferation, the number of neutrophils, and the host resistance to L. monocytogenes infection. On the other hand, B cell activity was decreased at the 800 mg/kg dose level. In conclusion, CLT produced an enhancement of host resistance to Listeria monocytogenes infection possibly through modulating the function of neutrophils, T cells and NK cells in female B6C3F1 mice using a T regulatory cell-related mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFC:
-
antibody forming cell
- CLT:
-
Chai-Ling-Tang
- Con A:
-
concanavalin A
- EBSS:
-
Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- NK cells:
-
natural killer cells
- sRBCs:
-
sheep red blood cells
References
Cheers C, McKenzie IF, Pavlov H, Waid C, York J (1978) Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: course of listeriosis in resistant or susceptible mice. Infect Immun 19:763
Chi RP, White KL Jr, Guo TL (2004) Immunomodulation by Chai-Ling-Tang, a formula consisting of twelve Chinese herbs. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol 18:146–151
Czuprynski CJ, Brown JF, Wagner RD, Steinberg H (1994) Administration of antigranulocyte monoclonal antibody RB6-8C5 prevents expression of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes infection in previously immunized mice. Infect Immun 62:5161
Dai ZJ, Liu XX, Tang W, Xue Q, Wang XJ, Ji ZZ, Kang HF, Diao Y (2008) Antitumor and immune-modulating effects of Scutellaria barbata extract in mice bearing hepatocarcinoma H22 cells-derived tumor. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28(10):1835–1837
Dobrzanski MJ, Reome JB, Dutton RW (2001) Role of effector cell-derived IL-4, IL-5, and perforin in early and late stages of type 2 CD8 effector cell-mediated tumor rejection. J Immunol 167:424–434
Egawa Y, Suzuki I, Nagi N, Yadomae T, Kawakita T, Kikuchi S, Nomoto K (1991) Chai-ling-tang (Japanese name: sairei-to) as an oral adjuvant. Int J Immunopharmacol 13:1031–1036
Fujii T, Hamai Y, Kozuma S, Miki A, Yamashita T, Hyodo H, Unno N, Taketani Y (1999) Effects of sairei-to and tokishakuyaku-san on cytokine release from peripheral blood mononuclear cells upon recognition of HLA-G protein in the treatment of recurrent abortion. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 21:261–264
Fujii T, Kanai T, Kozuma S, Hamai Y, Hyodo H, Yamashita T, Miki A, Unno N, Taketani Y (2000) Theoretical basis for herbal medicines, Tokishakuyaku-san and Sairei-to, in the treatment of autoimmunity-related recurrent abortion by correcting T helper-1/T helper-2 balance. Am J Reprod Immunol 44:342–346
Guo TL, McCay JA, Zhang LX, Brown RD, You L, Karrow NA, Germolec DR, White KL Jr (2001) Genistein modulates immune responses and increases host resistance to B16F10 tumor in adult female B6C3F1 mice. J Nutr 131(12):3251–3258
Guo TL, Chi RP, Karrow NA, Zhang LX, Pruett SB, Germolec DR, White KL Jr (2005) Thalidomide enhances both primary and secondary host resistances to Listeria monocytogenes infection by a neutrophil-related mechanism in female B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209(3):244–254
Hagiwara A, Sano M, Tanaka H, Kawabe M, Tamano S, Kadota T, Yanagisawa T, Maemura S, Ito N, Shirai T (2002) Lack of enhancing effect of two Kampo medicines, Sho-saiko-to (TJ-9) and Sairei-to (TJ-114), on rat urinary bladder carcinogenesis initiated with N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 22(1):41–50
Hattori T, Shindo S (1995) Effects of sairei-to (TJ-114) on the expression of adhesion molecule in anti-GBM nephritic rats. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 37:373–383
Hattori T, Nishimura H, Makino B, Shindo S, Kawamura H (1998) Sairei-to inhibits the production of endothelin-1 by nephritic glomeruli(2): alisols, possible candidates as active compounds. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 40:33–41
Holsapple MP, Munson AE, Munson JA, Bick PH (1983) Suppression of cell-mediated immunocompetence after subchronic exposure to diethylstilbestrol in female B6C3F1 mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:130–138
Horikoshi A, Shida M, Abe M, Hosokawa Y, Sawada S, Horie T (1995) A case of Evans’s syndrome in which thrombocytopenia and hemolysis was improved by Sairei-to. Rinsho Ketsueki 36:1237–1239
Ikeda K, Takasaka T (1988) Treatment of secretory otitis media with kampo medicine. Treatment of secretory otitis media with kampo medicine. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 245:234–236
Ikeda N, Hayasaka S, Nagaki Y, Hayasaka Y, Kadoi C, Matsumoto M (2001) Effects of traditional Sino-Japanese herbal medicines on aqueous flare elevation after small-incision cataract surgery. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 17:59–65
Ito T, Seo N, Yagi H, Ohtani T, Tokura Y, Takigawa M, Furukawa F (1985) Unique therapeutic effects of the Japanese-Chinese herbal medicine, Sairei-to, on Th1/Th2 cytokines balance of the autoimmunity of MRL/lpr mice. Dermatol Sci 28:198–210
Ito T, Seo N, Yagi H, Ohtani T, Tokura Y, Takigawa M, Furukawa F (2002) Unique therapeutic effects of the Japanese-Chinese herbal medicine, Sairei-to, on Th1/Th2 cytokines balance of the autoimmunity of MRL/lpr mice. J Dermatol Sci 28(3):198–210
Jerne NK, Nordin AA (1963) Plaque formation in agar by single antibody-producing cells. Science 140:405
Jin Z (1994) Chai ling tang in the treatment of steroid-dependent nephrosis syndrome. J Tradit Chin Med 14:254–258
Kanauchi H, Imamura S, Takigawa M, Furukawa F (1994) Evaluation of the Japanese-Chinese herbal medicine, kampo, for the treatment of lupus dermatoses in autoimmune prone MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. J Dermatol 21:935–939
Kanzaki J, O-uchi T, Tsuchihashi N (1993) Steroid-responsive sensorineural hearing loss: combination therapy with prednisolone and Sairei-to. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 55:24–29
Kimura K, Nanba S, Tojo A, Matsuoka H, Sugimoto T (1990) Effects of sairei-to on the relapse of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Am J Chin Med 18:45–50
Liu XY (1995) Therapeutic effect of chai-ling-tang (sairei-to) on the steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Am J Chin Med 23:255–260
Morahan PS, Klykken PC, Smith SH, Harris LS, Munson AE (1979) Effects of cannabinoids on host resistance to Listeria monocytogenes and herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun 23:670–674
Motoo Y, Taga H, Yamaguchi Y, Watanabe H, Okai T, Sawabu N (1997) Effect of niuche-shen-qi-wan on painful muscle cramps in patients with liver cirrhosis: a preliminary report. Am J Chin Med 25:97–102
Murray MJ, Kerkvliet NI, Ward EC, Dean JH (1985) Models for the evaluation of tumor resistance following chemical or drug exposure. In: Dean JH, Luster MI, Munson AE, Amos H (eds) Immunotoxicology and immunopharmacology. Raven, New York, pp 113–122
Nakayama S, Matsushita A, Ichiba S, Yabe H, Nagai K (1992) Clinical evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine for chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Rinsho Ketsueki 33:157–161
O-Uchi T, Kanzaki J, Tsuchihashi N (1993) Clinical analysis of steroid-responsive sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 20:79–93
Rakhmilevich AL (1995) Neutrophils are essential for resolution of primary and secondary infection with Listeria monocytogenes. J Leukoc Biol 57:827
Rogers HW, Unanue ER (1993) Neutrophils are involved in acute, nonspecific resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice. Infect Immun 61:5090
See DM, Broumand N, Sahl L, Tilles JG (1997) In vitro effects of echinacea and ginseng on natural killer and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in healthy subjects and chronic fatigue syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients. Immunopharmacology 35(3):229–235
Shida K, Imamura K, Katayama T, Machida T, Ohkawa T, Ishibashi A (1994) Clinical efficacy of sairei-to in various urinary tract diseases centering on fibrosis. Hinyokika Kiyo 40:1049–1057
Sugiyama T, Oonishi N, Onoe M, Kurita T (2002) Kampo preparations for prostatic hyperplasia: usefulness of Saireito for nocturia. Hinyokika Kiyo 48:343–346
Sun HX (2006) Haemolytic activities and adjuvant effect of Bupleurum chinense saponins on the immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 24(9):1324–1331
Suzuki T, Ono S, Oshima Y (1990) Effects of Sairei-to on Lupus erythematosus, Medicines of Plant Origin in Modern Therapy, Oxford Clinical Communications, pp 46–47
Takakuwa K, Yasuda M, Hataya I, Sekizuka N, Tamura M, Arakawa M, Higashino M, Hasegawa I, Tanaka K (1996) Treatment for patients with recurrent abortion with positive antiphospholipid antibodies using a traditional Chinese herbal medicine. J Perinat Med 24:489–494
Takakuwa K, Arakawa M, Honda K, Imai T, Tamura M, Yasuda M, Tanaka K (1997a) Alterations of lymphocyte subsets in patients with recurrent fetal wastage positive for antiphospholipid antibodies treated with Chinese herbal medicine. J Perinat Med 25:385–387
Takakuwa K, Arakawa M, Honda K, Imai T, Tamura M, Kurabayashi T, Tanaka K (1997b) Immunosuppressive therapy for recurrent aborters with positive antiphospholipid antibodies and alteration of 6ketoPGF1 alpha/TXB2 ratio. J Perinat Med 25:509–511
Tanaka H (1990) Remission-inducing effects of Sairei-to in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicines of Plant Origin in Modern Therapy, Oxford Clinical Communications, Oxford, pp 46–47
Wilson SD, McCay JA, Butterworth LF, Munson AE, White KL Jr (2001) Correlation of suppressed natural killer cell activity with altered host resistance models in B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177(3):208–218
Yano H, Hiraki S, Hayasaka S (1999) Effects of Kakkon-to and Sairei-to on experimental elevation of aqueous flare in pigmented rabbits. Jpn J Ophthalmol 43:279–284
Yoshikawa N, Ito H, Takekoshi Y, Honda M, Awazu M, Iijima K, Nakamura H, Seino Y, Takeda N, Hattori S, Matsuda I (1998) Standard versus long-term prednisolone with sairei-to for initial therapy in childhood steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome: a prospective controlled study. Nippon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 40:587–590
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported in part by the NIEHS contract NO1-ES-55538. The authors would like to thank D.L. Musgrove and R.D. Brown for their technical help.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, T.L., Chi, R.P., Fu, J. et al. Immunomodulation in female B6C3F1 mice following treatment with Chai-Ling-Tang, a formula consisting of twelve herbs. Orient Pharm Exp Med 11, 91–99 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0017-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0017-3