Abstract
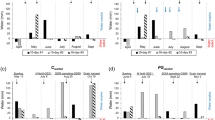
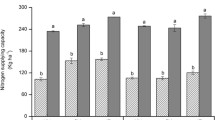
Efficient fertilization is a central topic in sustainable agriculture since fertilization strongly influences both crop performances and environmental impact. In several Mediterranean regions, globe artichoke fertilization is still empirically oriented toward nitrogen overdressing and insufficient phosphorus supply. To date, there is a lack of systematic research on the relationships between nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizations, especially in terms of nutrient efficiency. Here, in a 2-year experiment, we studied the effects of two phosphorus fertilization rates, 50 and 150 kg P2O5 ha−1, and four nitrogen fertilization rates, 0, 150, 300 and 450 kg N ha−1, on earliness, yield characteristics and nutrient efficiency indices of two globe artichoke genotypes: the traditional vegetatively propagated ‘Violetto di Sicilia’ and the modern ‘seed’-propagated ‘Opal F1’. The nutrient efficiency indices included partial factor productivity of nitrogen (PFPN), total factor productivity (TFP) and nitrogen agronomic efficiency (NAE). Results show that the highest phosphorus rate allowed to reduce nitrogen supply from 450 to 300 kg ha−1 without compromising earliness or yield of the crop. The highest phosphorus rate also increased PFPN up to 6.9 kg heads dry weight ha−1 kg−1 and NAE up to 2.5 Δ kg dry weight ha−1 kg−1, thus indicating a better nitrogen utilization of the crop, especially at lower doses. ‘Opal F1’, as compared to ‘Violetto di Sicilia’, showed higher PFPN of 8.1 versus 5.2 kg heads dry weight ha−1 kg−1 and TFP of 4.0 versus 2.4 kg heads dry weight ha−1 kg−1, especially at low nitrogen supplies. We conclude that balancing nitrogen and phosphorus supplies, together with the adoption of globe artichoke genotypes characterized by more efficient utilization of soil mineral nutrients, are effective tools to promote both yield performances and a more sustainable nitrogen fertilization of the crop.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M, Shabaz M, Ashraf MY (2001) Influence of nitrogen supply and water stress on growth and nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and calcium contents in pearl millet. Biol Plantarum 44:459–462
Basnizki Y, Zohary D (1994) Breeding of seed planted artichoke. Pl Breed Rev 12:253–269
Bhattacharyya R, Kundu S, Prakash V, Gupta HS (2008) Sustainability under combined application of mineral and organic fertilizers in a rainfed soybean–wheat system of the Indian Himalayas. Eur J Agron 28:33–46
Calabrese N, De Palma E, Bianco VV (2004) Yield and quality of new commercial seed grown artichoke hybrids. Acta Hort 660:77–82
Cassman KG, Gines GC, Dizon MA, Samson MI, Alcantara JM (1996) Nitrogen-use efficiency in tropical lowland rice systems: contribution from indigenous and applied nitrogen. Field Crop Res 47:1–12
Cosentino S, Mauromicale G (1990) Transpiration and plant water status of globe artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) grown from seed and from vegetative organs with two water regimes. Acta Hort 278:261–270
Ehaliotis C, Massas I, Pavlou G (2010) Efficient urea-N and KNO3-N uptake by vegetable plants using fertigation. Agron Sustain Dev 30:763–768
Elia A, Conversa G (2007) Mineral nutrition aspects in artichoke growing. Acta Hort 630:239–249
FAOSTAT (2008) Crops statistical database of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://faostat.fao.org/. Assessed 18 February 2011
Foti S, Mauromicale G, Ierna A (2005) Response of seed-grown globe artichoke to different levels of nitrogen fertilization and water supplies. Acta Hort 681:237–242
Gonzalez-Dugo V, Durand JL, Gastal F (2010) Water deficit and nitrogen nutrition in of crops. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:529–544
Khayyo S, Pérez-Lotz J, Ramos C (2004) Application of the Nmin nitrogen fertilizer recommendation system in artichoke in the Valencian community. Acta Hort 660:261–266
Magnifico V (1987) Aspetti agronomici della coltivazione del carciofo. Inf Agr 43:57–66
Mauro R, Portis E, Acquadro A, Lombardo S, Mauromicale G, Lanteri S (2009) Genetic diversity of globe artichoke landraces from Sicilian small-holdings: implications for evolution and domestication of the species. Conserv Genet 10:431–440
Mauromicale G, Ierna A (1995) Effects of gibberellic acid and sowing date on harvesting time and yield of seed-grown globe artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). Agronomie 15:527–538
Mauromicale G, Ierna A (2000) Characteristics of heads of seed-grown globe artichoke [Cynara cardunculus L. var. scolymus (L.) Fiori] as affected by harvest period, sowing date and gibberellic acid. Agronomie 20:197–204
Mauromicale G, Ierna A, Licandro P, Maugeri R, Scandurra S (2004) Il carciofo: una coltura “nuova” per la valorizzazione delle aree irrigue della collina interna siciliana. Italus Hortus 11:53–59
Novoa R, Loomis RS (1981) Nitrogen and plant production. Plant Soil 58:177–204
Pandino G, Courts FL, Lombardo S, Mauromicale G, Williamson G (2010) Caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids in the immature inflorescence of globe artichoke, wild cardoon, and cultivated cardoon. J Agric Food Chem 58:1026–1031
Portis E, Mauromicale G, Barchi L, Mauro R, Lanteri S (2005) Population structure and genetic variation in autochthonous globe artichoke germplasm from Sicily Island. Plant Sci 168:1591–1598
Rincón L, Pérez A, Pellicer C, Abadia A, Sáez J (2007) Nutrient uptake by artichoke. Acta Hort 730:287–292
Ryan J (1998) Changes in organic carbon in long-term rotation and tillage trials in Northern Syria. In: Lal R, Kimble JM, Follett RF, Stewart BA (eds) Management of carbon sequestration in soil. Advances in Soil Science CRC Publisher, Boca Raton, pp 285–295
Ryan J, Masri S, Ceccarelli S, Grando S, Ibrikci H (2008) Differential responses of barley landraces and improved barley cultivars to nitrogen–phosphorus fertilizer. J Plant Nutr 31:381–393
Società Italiana Scienza del Suolo (1985) Metodi normalizzati di analisi del suolo. Edagricole, Bologna, p 100
Spiertz JHJ (2010) Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:43–55
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080
Yadav RL (2003) Assessing on-farm efficiency and economics of fertilizer N, P and K in rice wheat systems of India. Field Crop Res 81:39–51
Zubillaga MM, Aristi JP, Lavado RS (2002) Effect of phosphorus and nitrogen fertilization on sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) nitrogen uptake and yield. J Agron Crop Sci 188:267–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ierna, A., Mauro, R.P. & Mauromicale, G. Improved yield and nutrient efficiency in two globe artichoke genotypes by balancing nitrogen and phosphorus supply. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 773–780 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0048-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0048-7