Abstract
Oncofetal reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment is clinically relevant. This study used the non-negative matrix factorial (NMF) algorithm for single-cell RNA sequencing data of gastric cancer (GC) based on embryonic stem genes. Pseudotime analysis, cell–cell interaction analysis, and SCENIC analysis revealed that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), tumor-associated endothelial cells (TECs), and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) have different oncofetal reprogramming that affects cell function, enhances intercellular communication, and activates multiple transcription factors in these cells. Furthermore, based on the signatures of the newly defined oncofetal cell subtypes and expression profiles of large cohorts in GC patients, we determined that GJA1 + TEC-C2, IFITM1 + CAF-C3, PODXL + TEC-C1, SFRP2 + CAF-C2, and SRSF7 + CAF-C1 are crucial prognostic factors for GC patients and predictors of immune checkpoint blockade in GC. Cell subtypes were validated by immunohistochemical methods. Our novel, profound, and systematic analysis of the oncofetal reprogramming of GC may facilitate the development of improved drugs for treating GC.






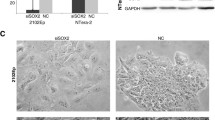
(source HPA ID: GCAB010753. Patient ID: 2066, male, age 76). Panel2: IFITM1 + fibroblasts were marked with a black arrow. Protein was mainly expressed on cell membrane (source HPA ID: HPA004810. Patient ID: 2105, male, age 62 years). Panel3: PODXL + endothelial cells were marked with a black arrow. Protein was mainly expressed on cell membrane (source HPA ID: HPA002110. Patient ID: 2626, female, age 79 years). Panel4: SRSF7 + fibroblasts were marked with black arrows. Protein was mainly expressed in the nucleus (source HPA ID: HPA056926. Patient ID: 650, male, age 68 years)
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated for this study can be found in the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) and Xena GDC TCGA (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/). IHC images can be publicly downloaded from The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) database (https://www.proteinatlas.org).
Code availability
R and other custom scripts for analyzing data are available upon request.
Change history
16 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-00879-6
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. 2021;71:209–49.
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Manzo G. Similarities between embryo development and cancer process suggest new strategies for research and therapy of tumors: a new point of view. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:20.
Sharma A, Blériot C, Currenti J, Ginhoux F. Oncofetal reprogramming in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:593–602.
Peng H, Wang X, Du J, Cui Q, Huang Y, Jin H. Metabolic reprogramming of vascular endothelial cells: basic research and clinical applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 626047.
Sharma A, Seow JJW, Dutertre CA, et al. Onco-fetal reprogramming of endothelial cells drives immunosuppressive macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. 2020;183:377-94.e21.
Devalaraja S, To TKJ, Folkert IW, et al. Tumor-derived retinoic acid regulates intratumoral monocyte differentiation to promote immune suppression. Cell. 2020;180:1098-114.e16.
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419.
Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E, Satija R. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36:411–20.
Mo S, Dai L, Wang Y, Song B, Yang Z, Gu W. Comprehensive analysis of the systemic transcriptomic alternations and inflammatory response during the occurrence and progress of COVID-19. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:9998697.
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P, Pachter L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34:525–7.
Vento-Tormo R, Efremova M, Botting RA, et al. Single-cell reconstruction of the early maternal-fetal interface in humans. Nature. 2018;563:347–53.
Fu Y, Guo Z, Wang Y, et al. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals the shared mechanisms inducing cognitive impairment between COVID-19 and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 967356.
Guan X, Polesso F, Wang C, et al. Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy. Nature. 2022;606:791–6.
Van de Sande B, Flerin C, Davie K, et al. A scalable SCENIC workflow for single-cell gene regulatory network analysis. Nat Protoc. 2020;15:2247–76.
Imrichova H, Hulselmans G, Atak ZK, Potier D, Aerts S. i-cisTarget 2015 update: generalized cis-regulatory enrichment analysis in human, mouse and fly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W57-64.
Gu W, Mo S, Wang Y, et al. Robust validation and comprehensive analysis of a novel signature derived from crucial metabolic pathways of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071825.
Mo S, Song B, Wang Y. Transcriptomic analysis and novel gene pair-based signatures for hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2021;31:37–53.
Galbo PM Jr, Zang X, Zheng D. Molecular features of cancer-associated fibroblast subtypes and their implication on cancer pathogenesis, prognosis, and immunotherapy resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:2636–47.
Bischoff P, Trinks A, Obermayer B, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct tumor microenvironmental patterns in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2021;40:6748–58.
Maeser D, Gruener RF, Huang RS. oncoPredict: an R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief Bioinform. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab260.
Yang W, Soares J, Greninger P, et al. Genomics of drug sensitivity in cancer (GDSC): a resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D955–61.
Gu W, Kim M, Wang L, Yang Z, Nakajima T, Tsushima Y. Multi-omics analysis of ferroptosis regulation patterns and characterization of tumor microenvironment in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:3476–92.
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, et al. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:131.
Kasashima H, Duran A, Martinez-Ordonez A, et al. Stromal SOX2 upregulation promotes tumorigenesis through the generation of a SFRP1/2-expressing cancer-associated fibroblast population. Dev Cell. 2021;56(95–110): e10.
Affo S, Nair A, Brundu F, et al. Promotion of cholangiocarcinoma growth by diverse cancer-associated fibroblast subpopulations. Cancer Cell. 2021;39(866–82): e11.
Zhuo H, Zhao Y, Cheng X, et al. Tumor endothelial cell-derived cadherin-2 promotes angiogenesis and has prognostic significance for lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:34.
Wu Y, Yang S, Ma J, et al. Spatiotemporal immune landscape of colorectal cancer liver metastasis at single-cell level. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:134–53.
Chen Y, McAndrews KM, Kalluri R. Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:792–804.
Janssens R, Struyf S, Proost P. The unique structural and functional features of CXCL12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018;15:299–311.
Liew FY, Girard JP, Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:676–89.
Marković I, Savvides SN. Modulation of signaling mediated by TSLP and IL-7 in inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1557.
Dong Z, Nör JE. Transcriptional targeting of tumor endothelial cells for gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:542–53.
Verdegem D, Moens S, Stapor P, Carmeliet P. Endothelial cell metabolism: parallels and divergences with cancer cell metabolism. Cancer Metab. 2014;2:19.
Heusschen R, Schulkens IA, van Beijnum J, Griffioen AW, Thijssen VL. Endothelial LGALS9 splice variant expression in endothelial cell biology and angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:284–92.
Filippou PS, Karagiannis GS, Constantinidou A. Midkine (MDK) growth factor: a key player in cancer progression and a promising therapeutic target. Oncogene. 2020;39:2040–54.
Wieland E, Rodriguez-Vita J, Liebler SS, et al. Endothelial notch1 activity facilitates metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:355–67.
Mulder K, Patel AA, Kong WT, et al. Cross-tissue single-cell landscape of human monocytes and macrophages in health and disease. Immunity. 2021;54:1883-900.e5.
Yan S, Wan G. Tumor-associated macrophages in immunotherapy. FEBS J. 2021;288:6174–86.
Becker-Santos DD, Thu KL, English JC, et al. Developmental transcription factor NFIB is a putative target of oncofetal miRNAs and is associated with tumour aggressiveness in lung adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 2016;240:161–72.
Suphakhong K, Terashima M, Wanna-Udom S, et al. m6A RNA methylation regulates the transcription factors JUN and JUNB in TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102554.
Wang H, Lu J, Mandel JA, et al. Patient-derived mutant forms of NFE2L2/NRF2 drive aggressive murine hepatoblastomas. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12:199–228.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all our team members at Bioinfo_composer, the leading bioinformatics platform in China, for their selfless help.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP22K20814.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SCM and WCG analyzed the data and presented the results. WCG designed the research. XS wrote the introduction and discussion of the manuscript. YLW modified the manuscript to the submission format and made a flowchart. YPL and ZCY assisted with the literature search. TS and TN provided suggestions on data analysis. WCG and TN obtained the grant.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to retrospective open access cancellation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, S., Shen, X., Wang, Y. et al. Systematic single-cell dissecting reveals heterogeneous oncofetal reprogramming in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. Human Cell 36, 689–701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-00856-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-00856-z