Abstract
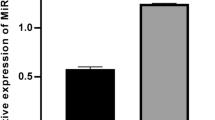
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases. An increasing body of evidence has indicated the critical roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating the progression of DLBCL. In this study, we found that miR-645 was up-regulated in DLBCL tissues and cell lines. Down-regulation of miR-645 significantly inhibited the proliferation, cell cycle progression and promoted the apoptosis of DLBCL cells. Experimental study identified Dachshund family transcription factor 1 (DACH1) as a target of miR-645. MiR-645 bound the 3′-untranslated region of DACH1 and reduced the expression of DACH1 in DLBCL cells. Decreased expression of DACH1 was inversely correlated with that of miR-645 in DLBCL tissues. The promoting effect of miR-645 on the proliferation of DLBCL cells was attenuated with the overexpression of DACH1. These results demonstrated the novel mechanism of miR-645 in DLBCL, which indicated miR-645 as a potential target for the diagnosis and prognostics of DLBCL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li S, Young KH, Medeiros LJ. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology. 2018;50:74–87.
Chiappella A, Santambrogio E, Castellino A, Nicolosi M, Vitolo U. Integrating novel drugs to chemoimmunotherapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017;10:697–705.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Mohr AM, Mott JL. Overview of microRNA biology. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:3–11.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5.
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351–79.
Kwak PB, Iwasaki S, Tomari Y. The microRNA pathway and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:2309–15.
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T. miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 2011;223:102–15.
Qu H, Xu W, Huang Y, Yang S. Circulating miRNAs: promising biomarkers of human cancer. Asian PAC J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:1117–25.
Gentilin E, Degli Uberti E, Zatelli MC. Strategies to use microRNAs as therapeutic targets. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;30:629–39.
Momtazi AA, Shahabipour F, Khatibi S, Johnston TP, Pirro M, Sahebkar A. Curcumin as a microRNA regulator in cancer: a review. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;171:1–38.
Huang Y, Zou Y, Lin L, Ma X, Zheng R. miR101 regulates the cell proliferation and apoptosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma by targeting MEK1 via regulation of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2019;41:377–86.
He B, Yan F, Wu C. Overexpressed miR-195 attenuated immune escape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by targeting PD-L1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;98:95–101.
Li J, Fu R, Yang L, Tu W. miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:15019–24.
Song J, Shao Q, Li C, Liu H, Li J, Wang Y, et al. Effects of microRNA-21 on apoptosis by regulating the expression of PTEN in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e7952.
Chen J, Shu Y, Yu Q, Shen W. MicroRNA-645 promotes cell metastasis and proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma by targeting GK5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:4557–655.
Cai Y, Li WF, Sun Y, Liu K. Downregulation of microRNA-645 suppresses breast cancer cell metastasis via targeting DCDC2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:4129–36.
Guo ST, Guo XY, Wang J, Wang CY, Yang RH, Wang FH, et al. MicroRNA-645 is an oncogenic regulator in colon cancer. Oncogenesis. 2017;6:e335.
Feng X, Wang Y, Ma Z, Yang R, Liang S, Zhang M, et al. MicroRNA-645, up-regulated in human adencarcinoma of gastric esophageal junction, inhibits apoptosis by targeting tumor suppressor IFIT2. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:633.
Shih KK, Qin LX, Tanner EJ, Zhou Q, Bisogna M, Dao F, et al. A microRNA survival signature (MiSS) for advanced ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121:444–50.
Xu H, Yu S, Yuan X, Xiong J, Kuang D, Pestell RG, et al. DACH1 suppresses breast cancer as a negative regulator of CD44. Sci Rep. 2017;7:4361.
Han N, Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Chu Q, Guo M, et al. DACH1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma invasion and tumor growth by repressing CXCL5 signaling. Oncotarget. 2015;6:5877–88.
Zhang J, Ren X, Wang B, Cao J, Tian L, Liu M. Effect of DACH1 on proliferation and invasion of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Face Med. 2018;14:20.
Cao J, Yan XR, Liu T, Han XB, Yu JJ, Liu SH, et al. MicroRNA-552 promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting DACH1 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:3795–802.
Lu GF, Geng F, Xiao Z, Chen YS, Han Y, You CY, et al. MicroRNA-6807-3p promotes the tumorigenesis of glioma by targeting downstream DACH1. Brain Res. 2019;1708:47–57.
Cao W, Sun J. MicroRNA-200c promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting dachshund family transcription factor 1 by the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs. 2019;30:218–24.
Kubuschok B, Held G, Pfreundschuh M. Management of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Cancer Treat Res. 2015;165:271–88.
Yan W, Wu K, Herman JG, Brock MV, Fuks F, Yang L, et al. Epigenetic regulation of DACH1, a novel Wnt signaling component in colorectal cancer. Epigenetics. 2013;8:1373–83.
Wu K, Li A, Rao M, Liu M, Dailey V, Yang Y, et al. DACH1 is a cell fate determination factor that inhibits cyclin D1 and breast tumor growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:7116–299.
Chen K, Wu K, Cai S, Zhang W, Zhou J, Wang J, et al. Dachshund binds p53 to block the growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3262–74.
Cheng Q, Ning D, Chen J, Li X, Chen XP, Jiang L. SIX1 and DACH1 influence the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating p53. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19:381–90.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Cangzhou Science and Technology Support Technology Project (No. 141302108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Shen, J., Su, N. et al. MiR-645 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by targeting DACH1. Human Cell 33, 1091–1098 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00321-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00321-1