Abstract
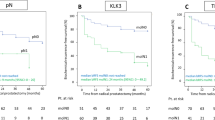
Resistance to or relapse after androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) remains a significant problem in patients with prostate cancer. Several studies have hypothesized that the overexpression of MET and the activating signaling axis in prostate cancer cells are associated with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). On the other hand, the expression of human kallikrein 1-related peptidase (KLK) 4, which activates plasma HGF activator zymogen, in prostate cancer patients with bone metastasis or advanced stage has also been reported. In this study, we analyzed the expression and phosphorylation of MET along with KLK4 by immunohistochemistry in 62 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of prostate cancer collected by needle biopsy at our hospital between 2006 and 2011. As a result, the phosphorylation of MET was observed in 56 % (35 of 62 cases) and positively correlated with worsening PSA relapse rate in a group of ADT-treated patients (P = 0.0445), suggesting significant correlation with CRPC. Overexpression of KLK4 was observed in patients with high T stage (P = 0.0001) and high Gleason score (P = 0.0146), and the expression was correlated with the phosphorylation of MET (P = 0.0002). Pathologically, strong MET phosphorylation observed in specific architectures in prostate cancer, such as cribriform structures, ill-defined glands or solid patterns, suggested the significance of MET activation in promoting the architectural formation of prostate cancer. In addition, high positivity rate (80 %) of phospho-MET staining at high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) may indicate the importance of the activating signaling axis in the carcinogenesis of prostate cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsuda A, Matsuda T, Shibata A, Katanoda K, Sobue T, Nishimoto H, The Japan Cancer Surveillance Research Group. Cancer incidence and incidence rates in japan in 2008: a study of 25 population-based cancer registries for the monitoring of cancer incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013;44(4):388–96.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29.
Center MM, Jemal A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Ward E, Ferlay J, Brawley O, Bray F. International variation in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2012;61(6):1079–92.
Wozney JL, Antonarakis ES. Growth factor and signaling pathways and their relevance to prostate cancer therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33(2–3):581–94.
Kataoka H, Miyata S, Uchinokura S, Itoh H. Roles of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activator and HGF activator inhibitor in the pericellular activation of HGF/scatter factor. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22(2–3):223–36.
Kataoka H, Kawaguchi M. Hepatocyte growth factor activator (HGFA): pathophysiological functions in vivo. FEBS J. 2010;277(10):2230–7.
Lee SL, Dickson RB, Lin CY. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor and urokinase/plasminogen activator by matriptase, an epithelial membrane serine protease. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36720–5.
Kirchhofer D, Peek M, Lipari MT, Billeci K, Fan B, Moran P. Hepsin activates pro-hepatocyte growth factor and is inhibited by hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1B (HAI-1B) and HAI-2. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(9):1945–50.
Shimomura T, Kondo J, Ochiai M, Naka D, Miyazawa K, Morimoto Y, Kitamura N. Activation of the zymogen of hepatocyte growth factor activator by thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(30):22927–32.
Mukai S, Fukushima T, Naka D, Tanaka H, Osada Y, Kataoka H. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor activator zymogen (pro-HGFA) by human kallikrein 1-related peptidases. FEBS J. 2008;275(5):1003–17.
Borgono CA, Diamandis EP. The emerging roles of human tissue kallikreins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;11:876–90.
Gao J, Collard RL, Bui L, Herington AC, Nicol DL, Clements JA. Kallikrein 4 is a potential mediator of cellular interactions between cancer cells and osteoblasts in metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate. 2007;67(4):348–60.
Avgeris M, Stravodimos K, Scorilas A. Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 gene (KLK4) in prostate tumors: quantitative expression analysis and evaluation of its clinical significance. Prostate. 2011;71(16):1780–9.
Knudsen BS, Edlund M. Prostate cancer and the met hepatocyte growth factor receptor. Adv Cancer Res. 2004;91:31–67.
Knudsen BS, Gmyrek GA, Inra J, Scherr DS, Vaughan ED, Nanus DM, Kattan MW, Gerald WL, Vande Woude GF. High expression of the Met receptor in prostate cancer metastasisto bone. Urology. 2002;60(6):1113–7.
Smith MR, Sweeney CJ, Corn PG, Rathkopf DE, Smith DC, Hussain M, George DJ, Higano CS, Harzstark AL, Sartor AO, Vogelzang NJ, Gordon MS, de Bono JS, Haas NB, Logothetis CJ, Elfiky A, Scheffold C, Laird AD, Schimmoller F, Basch EM, Scher HI. Cabozantinib in chemotherapy-pretreated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: results of a phase II nonrandomized expansion study. J Clin Oncol. 2014; pii: JCO.2013.54.5954.
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Publishing; 2004. p. 281–90.
Mukai S, Yorita K, Kawagoe Y, Katayama Y, Nakahara K, Kamibeppu T, Sugie S, Tukino H, Kamoto T, Kataoka H. Matriptase and MET are prominently expressed at the site of bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma: immunohistochemical analysis. Hum Cell. 2015;28(1):44–50.
Inoue T, Kataoka H, Goto K, Nagaike K, Igami K, Naka D, Kitamura N, Miyazawa K. Activation of c-Met (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) in human gastric cancer tissue. Cancer Sci. 2004;95(10):803–8.
Han SW, Hwang PG, Chung DH, Kim DW, Im SA, Kim YT, Kim TY. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) downstream molecules as response predictive markers for gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) in chemotherapy-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;113(1):109–15.
Nakamura Y, Niki T, Goto A, Morikawa T, Miyazawa K, Nakajima J, Fukayama M. c-Met activation in lung adenocarcinoma tissues: an immunohistochemical analysis. Cancer Sci. 2007;98(7):1006–13 [Epub 2007 Apr 24].
Ma PC, Maulik G, Christensen J, Salgia R. c-Met: structure, functions and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22(4):309–25.
Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Comoglio PM. MET signalling: principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(12):834–48.
Benvenuti S, Comoglio PM. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase in invasion and metastasis.J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(2):316–25. Review.
Scagliotti GV, Novello S, von Pawel J. The emerging role of MET/HGF inhibitors in oncology. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39(7):793–801.
Russo AL, Jedlicka K, Wernick M, McNally D, Kirk M, Sproull M, Smith S, Shankavaram U, Kaushal A, Figg WD, Dahut W, Citrin D, Bottaro DP, Albert PS, Tofilon PJ, Camphausen K. Urine analysis and protein networking identify met as a marker of metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(13):4292–8.
Verras M, Lee J, Xue H, Li T, Wang Y, et al. The androgen receptor negatively regulates the expression of c-Met: implications for a novel mechanism of prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2007;67(3):697–975.
Maeda A, Nakashiro K, Hara S, Ssaki T, Miwa Y, Tanji N, Yokoyama M, Hamakawa H, Oyasu R. Inactivation of AR activates HGF/c-Met system in human prostatic carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;347:1158–65.
Nishida S, Hirohashi Y, Torigoe T, Inoue R, Kitamura H, Tanaka T, Takahashi A, Asanuma H, Masumori N, Tsukamoto T, Sato N. Prostate cancer stem-like cells/cancer-initiating cells have an autocrine system of hepatocyte growth factor. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(4):431–6.
Yasuda K, Nagakawa O, Akashi T, Fujiuchi Y, Koizumi K, Komiya A, Saiki I, Fuse H. Serum active hepatocyte growth factor (AHGF) in benign prostatic disease and prostate cancer. Prostate. 2009;69(4):346–51.
Warren M, Twohig M, Pier T, Eickhoff J, Lin CY, Jarrard D, Huang W. Protein expression of matriptase and its cognate inhibitor HAI-1 in human prostate cancer: a tissue microarray and automated quantitative analysis. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2009;17(1):23–30.
Schalken JA, Van Leenders G. Cellular and molecular biology of the prostate: stem cell biology. Urology. 2003;62:11–20.
van Leenders G, van Balken B, Aalders T, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa C, Ruiter D, Schalken J. Intermediate cells in normal and malignant prostate epithelium express c-MET: implications for prostate cancer invasion. Prostate. 2002;51(2):98–107.
Wang W, Bergh A, Damber JE. Morphological transition of proliferative inflammatory atrophy to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer in human prostate. Prostate. 2009;69(13):1378–86.
Dorn J, Bayani J, Yousef GM, Yang F, Magdolen V, Kiechle M, Diamandis EP, Schmitt M. Clinical utility of kallikrein-related peptidases (KLK) in urogenital malignancies. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110(3):408–22.
Liu J, Brown RE. Immunohistochemical expressions of fatty acid synthase and phosphorylatedc-Met in thyroid carcinomas of follicular origin. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(8):755–64.
Jeffers M, Schmidt L, Nakaigawa N, Webb CP, Weirich G, et al. Activating mutations for the met tyrosine kinase receptor in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(21):445–50.
Koga K, Hamasaki M, Kato F, Aoki M, Hayashi H, Iwasaki A, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K. Association of c-Met phosphorylation with micropapillary pattern and small cluster invasion in pT1-size lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2013;82(3):413–9.
Dong Y, Bui LT, Odorico DM, Tan OL, Myers SA, Samaratunga H, Gardiner RA, Clements JA. Compartmentalized expression of kallikrein 4 (KLK4/hK4) isoforms in prostate cancer: nuclear, cytoplasmic and secreted forms. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(4):875–89.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ms. Yukari Kawagoe and Ms. Yasuko Tobayashi for their technical assistance with immunohistochemical staining. This study was supported in part by a grant for clinical research from Miyazaki University Hospital.
Conflict of interest
This study was supported in part by a grant for clinical research from Miyazaki University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukai, S., Yorita, K., Yamasaki, K. et al. Expression of human kallikrein 1-related peptidase 4 (KLK4) and MET phosphorylation in prostate cancer tissue: immunohistochemical analysis. Human Cell 28, 133–142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-015-0114-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-015-0114-6