Abstract
Purpose
Conformality index of the 50% prescription isodose volume (CI50) is an important variable in lung stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) planning but has not been previously correlated to radiation pneumonitis (RP). We hypothesized that adherence to recommended CI50 for patients undergoing lung SBRT would result in decreased incidence and/or severity of RP compared to that for patients with minimal deviations and unacceptable deviations.
Methods and materials
We retrospectively identified patients treated between 2006 and 2016, with > 3 months follow up from lung SBRT treatment. CTCAE v4.0 toxicity grades were used to classify RP. Clinically significant RP was defined as grade ≥ 2 toxicity. Using Radiation Therapy Oncology Group CI50 planning guidelines, patients were separated into three groups: acceptable, minor deviation, and unacceptable deviation. CI25 and CI75 values in patients with and without clinically significant RP were also reported in this study.
Results
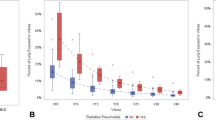
One hundred seventy-four patients with a median follow-up time of 26.8 months were included in this analysis. Overall incidence of grade ≥ 2 RP was 12.7%. Thirty-eight (21.8%) patients had acceptable CI50, 100 (57.5%) had minor deviations, and 36 (20.7%) had unacceptable deviations. Incidence of RP did not significantly differ between patients with acceptable, minor deviation, and unacceptable CI50. Additionally, CI25 and CI75 did not significantly differ between patients with and without clinically significant RP.
Conclusions
Adhering to recommended CI50 values does not significantly decrease the incidence of clinically significant RP in patients with NSCLC treated with SBRT. To the authors’ knowledge, this observation has not been published previously.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hernando ML et al (2001) Radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity: a dose-volume histogram analysis in 201 patients with lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51(3):650–659
Barriger RB et al (2012) A dose-volume analysis of radiation pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(1):457–462
Tsoutsou PG, Koukourakis MI (2006) Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis: mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(5):1281–1293
Timmerman R et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. Jama 303(11):1070–1076
US Department of Health and Human Services (2009) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 4.0. National Cancer Institute:09–5410
A phase II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in the treatment of patients with medically inoperable stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer. (2009). Retrieved from https://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable/StudyDetails.aspx?study=0236. (Identification No. RTOG 0236)
Yirmibesoglu E et al (2012) Challenges scoring radiation pneumonitis in patients irradiated for lung cancer. Lung Cancer 76(3):350–353
Marks LB et al (2010) Radiation dose-volume effects in the lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3):S70–S76
Guckenberger M et al (2010) Dose–response relationship for radiation-induced pneumonitis after pulmonary stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 97(1):65-70
Takeda A et al (2012) Comparison of clinical, tumour-related and dosimetric factors in grade 0–1, grade 2 and grade 3 radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumours. Br J Radiol 85(1013):636–642
Jo I-Y et al (2013) Significance of low-dose radiation distribution in development of radiation pneumonitis after helical-tomotherapy-based hypofractionated radiotherapy for pulmonary metastases. J Radiat Res 55(1):105–112
Harder EM et al (2016) Pulmonary dose-volume predictors of radiation pneumonitis following stereotactic body radiation therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol 6(6):e353–e359
Petras K et al (2016) Predictors of post-treatment symptomatic pneumonitis in lung SBRT patients through decision tree analysis. J Radiat Oncol 5(3):273–278
Ong CL et al (2010) Treatment of large stage I–II lung tumors using stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT): planning considerations and early toxicity. Radiother Oncol 97(3):431–436
Baker R et al (2013) Clinical and dosimetric predictors of radiation pneumonitis in a large series of patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy to the lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(1):190–195
Yamashita H et al (2007) Exceptionally high incidence of symptomatic grade 2–5 radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic radiation therapy for lung tumors. Radiat Oncol 2(1):21
Funding
This work was supported by the Department of Radiation Oncology, Loyola University Chicago in Chicago, IL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutten, R., Surucu, M., Joyce, C. et al. Association of conformality index and post-treatment radiation pneumonitis in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Radiat Oncol 7, 63–67 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-018-0342-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-018-0342-y