Abstract
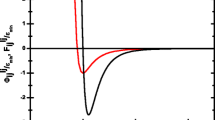
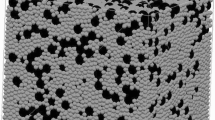
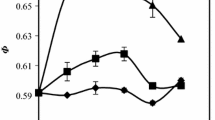
Random packing of binary mixtures of spherical particles in viscous fluid is numerically investigated via CFD-DEM, where moderate size ratios (d/D) are specially considered. Results indicate that binary packing in fluid is much looser than that in the absence of fluid, and two distinct phenomena can be identified as the global packing density varies with the volume fraction of coarse particle (XD). For small size ratios, the global packing density first increases with increasing XD due to the occupation mechanism, and then it reaches the maximum value when XD ≈ 0.6, beyond which the global packing density decreases as XD increases further. However, for large size ratios, the global packing density always decreases with increasing XD. These phenomena are further discussed by using the local packing density determined by Voronoi tessellation, the mean and local coordination number, and radial distribution function, with which the particle arrangements within binary mixtures are well identified.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
F. Podczeck, M. Sharma, The influence of particle size and shape of components of binary powder mixtures on the maximum volume reduction due to packing. Int. J. Pharm. 137, 41–47 (1996)
I. Biazzo, F. Caltagirone, G. Parisi, F. Zamponi, Theory of amorphous packings of binary mixtures of hard spheres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 195701 (2009)
H.J.H. Brouwers, Particle-size distribution and packing fraction of geometric random packings. Phys. Rev. E 74, 031309 (2006)
A.S. Clarke, J.D. Wiley, Numerical simulation of the dense random packing of a binary mixture of hard spheres: amorphous metals. Phys. Rev. B 35, 7350–7356 (1987)
M.D. Eldridge, P.A. Madden, D. Frenkel, Entropy-driven formation of a superlattice in a hard-sphere binary mixture. Nature 365, 35–37 (1993)
S. Pillitteri, E. Opsomer, G. Lumay, N. Vandewalle, How size ratio and segregation affect the packing of binary granular mixtures. Soft Matter 16, 9094–9100 (2020)
J. Zheng, W.B. Carlson, J.S. Reed, The packing density of binary powder mixtures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 15, 479–483 (1995)
R. Al-Raoush, M. Alsaleh, Simulation of random packing of polydisperse particles. Powder Technol. 176, 47–55 (2007)
W. Liu, S. Chen, C.-Y. Wu, S. Li, Unified size-density and size-topology relations in random packings of dry adhesive polydisperse spheres. Phys. Rev. E 99, 022901 (2019)
E.I. Corwin, M. Clusel, A.O.N. Siemens, J. Brujic, Model for random packing of polydisperse frictionless spheres. Soft Matter 6, 2949–2959 (2010)
V. Baranau, U. Tallarek, Random-close packing limits for monodisperse and polydisperse hard spheres. Soft Matter 10, 3826–3841 (2014)
V. Ogarko, S. Luding, Prediction of polydisperse hard-sphere mixture behavior using tridisperse systems. Soft Matter 9, 9530–9534 (2013)
Y. Rouault, S. Assouline, Modeling the disordered dense phase in the packing of binary mixtures of spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 204, 87–92 (1998)
G.E. Schröder-Turk, W. Mickel, M. Schröter, G.W. Delaney, M. Saadatfar, T.J. Senden, K. Mecke, T. Aste, Disordered spherical bead packs are anisotropic. EPL 90, 34001 (2010)
M. Jerkins, M. Schröter, H.L. Swinney, Onset of mechanical stability in random packings of frictional spheres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 018301 (2008)
C.S. Chang, Y. Deng, Packing potential index for binary mixtures of granular soil. Powder Technol. 372, 148–160 (2020)
I. Prasad, C. Santangelo, G. Grason, Subjamming transition in binary sphere mixtures. Phys. Rev. E 96, 052905 (2017)
S. Liu, Z. Ha, Prediction of random packing limit for multimodal particle mixtures. Powder Technol. 126, 283–296 (2002)
L. Meng, P. Lu, S. Li, Packing properties of binary mixtures in disordered sphere systems. Particuology 16, 155–166 (2014)
S. Yerazunis, S.W. Cornell, B. Wintner, Dense random packing pf binary mixtures of spheres. Nature 207, 835–837 (1965)
D. Pinson, R.P. Zou, A.B. Yu, P. Zulli, M.J. McCarthy, Coordination number of binary mixtures of spheres. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 31, 457–462 (1998)
Y. Guo, C.-Y. Wu, K.D. Kafui, C. Thornton, 3D DEM/CFD analysis of size-induced segregation during die filling. Powder Technol. 206, 177–188 (2011)
F. Qian, N. Huang, J. Lu, Y. Han, CFD–DEM simulation of the filtration performance for fibrous mediabased on the mimic structure. Comput. Chem. Eng. 71, 478–488 (2014)
J.S. Marshall, Discrete-element modeling of particulate aerosol flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 1541–1561 (2009)
K.D. Kafui, C. Thornton, M.J. Adams, Discrete particle-continuum fluid modelling of gas-solid fluidised beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 57, 2395–2410 (2002)
H. Chen, Granular vortex ring formed by penetration into loose granular medium: structure identification. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 127, 107542 (2023)
H. Chen, L. Xia, C. Li, Z. Zheng, Penetration into a granular bed in the presence of upward gas flows. Particuology 82, 1–12 (2022)
J.S. Marshall, S. Li, Adhesive particle flow: a discrete-element approach (Cambridge University Press, New York, 2014)
A.B. Yu, N. Standish, Estimation of the porosity of particle mixtures by a linear-mixture packing model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 30, 1372–1385 (1991)
R.P. Dias, J.A. Teixeira, M.G. Mota, A.I. Yelshin, Particulate binary mixtures: dependence of packing porosity on particle size ratio. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43, 7912–7919 (2004)
M. Mota, J. Teixeira, A. Yelshin, Binary spherical particle mixed beds porosity and permeability relationship measurement. The transactions of the Filtration Society 1, 101–106 (2001)
H.Y. Sohn, C. Moreland, The effect of particle size distribution on packing density. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 46, 162–167 (1968)
S. Yerazunis, J.W. Bartlett, A.H. Nissan, Packing of binary mixtures of spheres and irregular particles. Nature 195, 33–35 (1962)
D. Bouvard, F.F. Lange, Correlation between random dense parking and random dense packing for determining particle coordination number in binary systems. Phys. Rev. A 45, 5690–5693 (1992)
H. Chen, W. Liu, S. Li, Random loose packing of small particles with liquid cohesion. AIChE J. 65, 500–511 (2019)
Funding
This work is financially supported by China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgical Innovation Foundation (No. 202114). National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52304346) The Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. Chen wrote the main manuscript text, Z. Zheng provided supervision and funding acquisition. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zheng, Z. Binary Packing of Spherical Particles with Moderate Size Ratios in Viscous Fluid: A CFD-DEM Study. Braz J Phys 54, 110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-024-01476-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-024-01476-0