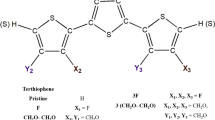
Abstract
There are fewer components in the nanoelectronics industry that do not use some kind of molecular junctions or interface. In general, many nanoelectronic devices have layered structures, and the behavior of the electron at the interface affects the electron properties of the final component, because the electron transfer mechanisms at the interface and multiple junctions are significantly different from the bulk material. Their junctions were studied. It was shown that to study the mechanisms of electron transfer and parameters affecting the conductivity of the junctions, various molecular junctions such as broken junctions can be used. It has been suggested that the solution temperature, shape, material, and spatial arrangement of the molecule used, the material, properties and surface nature of the metal electrodes, and the band structure of the junction’s components can affect the conductivity of these systems. Attempts have been made to introduce the salient features of each of these junctions and to discuss examples of real Nano electronic components and molecular junctions used in them. We will see that the conventional mechanisms for electron transfer in these devices strongly depend on the electronic structure of the molecules used and generally include direct tunneling, fullerene tunneling. Molecularly deals with the effects of various factors on it. controlling the conductivity of a molecular bond by changing its physical, chemical and mechanical properties and optimizing the electrical properties of the final nanoelectronic component. Organic molecular junctions, as a special form of molecular junction, are used in many organic nanoelectronic devices. Therefore, it is very important to study the nature of the interface between these junctions and their electron transfer mechanisms. Conductivity of junctions is analyzed based on the band structure of their components. Therefore, in this paper, organic molecular compounds are introduced and their electronic structure is discussed. As you will see, certain phenomena also occur in these junctions, the most important of which are the formation of organic dipoles at the interface of the organic molecule/metal and the CNL parameter. Attempts have been made to put these phenomena into plain language without addressing mathematical models and the heavy concepts of quantum physics, and to discuss their effect on charge transfer and the electronic structure of organic junctions.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
References
F. Chen, J. Hihath, Z. Huang, X. Li, N.J. Tao, Measurement of single-molecule conductance. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 58, 535–564 (2007)
J.R. Heath, M.A. Ratner, Molecular electronics. Phys. Today 56(5), 43 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1583533
R.M. Metzger (ed.), Unimolecular Supramolecular Electronics I: ChemistryPhysics Meet at Metal-Molecule Interfaces, Vol. 1. (Springer, 2012)
M. Kiguchia, K. Murakoshi, Highly conductive single molecular junctions by direct binding of π-conjugated molecule to metal electrodes. Thin Solid Films 518, 466–469 (2009)
B. Branchi, in UnimolecularSupramolecular Electronics II: ChemistryPhysics Meet at Metal-Molecule Interfaces, vol. 2, ed. by R.R.M. Metzger (Springer, 2012)
F. Léonard, A.A. Talin, Electrical contacts to one-and two-dimensional nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(11), 773–783 (2011)
G. Wang, S.-I. Na, T.-W. Kim, Y. Kim, S. Park, T. Lee, Effect of PEDOT:PSS–molecule interface on the charge transport characteristics of the large-area molecular electronic junctions. Org. Electron. 13, 771–777 (2012)
M.A. Reed, C. Zhou, C.J. Muller, T.P. Burgin, J.M. Tour, Conductance of a molecular junction. Science 278(5336), 252–254 (1997)
G.C. Solomon, C. Herrmann, T. Hansen, V. Mujica, M.A. Ratner, Exploring local currents in molecular junctions. Nat. Chem. 2(3), 223–228 (2010)
N.A. Zimbovskaya, Transport Properties of Molecular Junctions (Springer, 2013)
S.W. Wu et al., Control of Relative Tunneling Rates in Single Molecule Bipolar Electron Transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(23), 236–802 (2004)
E.G. Petrov, Tunneling through localized states of a single molecule. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst 426(1), 49–58 (2005)
J.P. Bourgoin, Molecular Electronics: A Review of Metal-Molecule-Metal Junctions, in Interacting electrons in nanostructures, (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2001), pp 105-124
W.Y. Kim et al., Application of quantum chemistry to nanotechnology: electronspin transport in molecular devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38(8), 2319–2333 (2009)
H. Vazquez, F. Flores, A. Kahn, Induced density of states model for weakly-interacting organic semiconductor interfaces. Org. Electron. 8(2), 241–248 (2007)
N.A. Zimbovskaya, Transport Properties of Molecular Junctions, vol. 254 (Springer, 2013)
I.L. Aleiner, P.W. Brouwer, L.I. Glazman, Quantum effects in Coulomb blockade. Phys. Rep. 358(5), 309–440 (2002)
L.P. Kouwenhoven, C.M. Marcus, P.L. McEuen, S. Tarucha, R.M. Westervelt, N.S. Wingreen, Electron transport in quantum dots , in Mesoscopic electron transport. (Springer Netherlands, 1997), pp. 105–214
S.M. Sze, The Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1981)
V. Balzani (ed.), Electron transfer in chemistry, chapter 4. (Vch Verlagsgesellschaft Mbh, 2001), p. 162
C. Martel, M. Plummer, J. Vignat et al., Worldwide burden of cancer attributable to HPV by site, 5Pan C, Issaeva N, Yarbrough WG. HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer: current knowledge of molecular biology and mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Cancers Head Neck 2018;3:12. country and HPV type. Int J Cancer 141:664– 670 (2017)
B.S. Chera, R.J. Amdur, R. Green et al., Phase II trial of de-intensified chemoradiotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 37, 2661–2669 (2019)
S. Cheraglou, P.K. Yu, M.D. Otremba et al., Treatment deintensification in human papillomavirus-positive oropharynx cancer: outcomes from the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer 124, 717–726 (2018)
H. Li, S.J. Torabi, W.G. Yarbrough et al., Association of human papillomavirus status at head and neck carcinoma subsites with overall survival. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144, 519–525 (2018)
M.L. Gillison, A.M. Trotti, J. Harris et al., Radiotherapy plus cetuximab or cisplatin in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (NRG Onclogy RTOG 1016): a randomised, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 393, 40–50 (2019)
F.O. Gleber-Netto, X. Rao, T. Guo et al., Variations in HPV function are associated with survival in squamous cell carcinoma. JCI Insight 4, pii: 124762 (2019)
I. Paiva, R.M. Gil da Costa, J. Ribeiro et al., A role for microRNA-155 expression in microenvironment associated to HPV-induced carcinogenesis in K14-HPV16 transgenic mice. PLoS One 10, e0116868 (2015)
I. Paiva, R.M. Gil da Costa, J. Ribeiro et al., MicroRNA-21 expression and susceptibility to HPVinduced carcinogenesis – role of microenvironment in K14-HPV16 mice model. Life Sci 128, 8–14 (2015)
V.F. Mestre, B. Medeiros-Fonseca, D. Estêvão, F. Casaca, S. Silva, A. Félix, F. Silva, B. Colaço, F. Seixas, M.M. Bastos, C. Lopes, R. Medeiros, P.A. Oliveira, R.M. Gil da Costa, HPV16 is sufficient to induce squamous cell carcinoma specifically in the tongue base in transgenic mice. J. Pathol. 251, 4–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5387
Z. Robison, J.P. Mosele, A. Gross, S. Lynch, Numerical Investigation of Turbulent Junction Flows. AIAA Journal 1–18 (2021)
C.L. Rumsey, J.R. Carlson, T.H. Pulliam, P.R. Spalart, Improvements to the quadratic constitutive relation based on nasa juncture flow data. AIAA Journal 58(10), 4374–4384 (2020)
I. Hnid, D. Frath, F. Lafolet, X. Sun, J.C. Lacroix, Highly efficient photoswitch in diarylethene-based molecular junctions. Journal of the American Chemical Society 142(17), 7732–7 (2020)
K. Wang, E. Meyhofer, P. Reddy, Thermal and thermoelectric properties ofmolecular junctions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(8), 1904534 (2020)
M.W. Gu, H.H. Peng, I.W.P. Chen, C.H. Chen, Tuning surface d bands withbimetallic electrodes to facilitate electron transport across molecular junctions. Nature Materials 20(5), 658–664 (2021)
S. Gunasekaran, J.E. Greenwald, L. Venkataraman, Visualizing quantuminterference in molecular junctions. Nano letters 20(4), 2843–2848 (2020)
S.K. Karuppannan, E.H.L. Neoh, A. Vilan, C.A. Nijhuis, Protective layers based on carbon paint to yield high-quality large-area molecular junctions with low contact resistance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(7), 3513–3524 (2020)
M. Supur, S.K. Saxena, R.L. McCreery, Ion-Assisted Resonant Injection andCharge Storage in Carbon-Based Molecular Junctions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(27), 11658–11662 (2020)
Q. Van Nguyen, U. Tefashe, P. Martin, M.L. Della Rocca, F. Lafolet, P. Lafarge, J.C. Lacroix, Molecular signature and activationless transport in cobalt-terpyridine-basedmolecular junctions. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6(7), 1901416 (2020)
R.B. Pontes, A.R. Rocha, S. Sanvito, A. Fazzio, A.J. da Silva, Ab initio calculations of structural evolution and conductance of benzene-1,4-dithiol on gold leads. ACS Nano 5(2), 795–804 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn101628w (Epub 2011 Jan 12. PMID: 21226481)
M. Salimi, V. Pirouzfar, E. Kianfar, Enhanced gas transport properties in silica nanoparticle filler-polystyrene nanocomposite membranes. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 295, 215–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3998-0
E. Kianfar, Synthesis and characterization of AlPO4/ZSM-5 catalyst for methanol conversion to dimethyl ether. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 91, 1711–1720 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427218100208
E. Kianfar, Ethylene to propylene conversion over Ni-W/ZSM-5 catalyst. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 92, 1094–1101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427219080068
E. Kianfar, Ethylene to propylene over zeolite ZSM-5: improved catalyst performance bytreatment with CuO. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 92, 933–939 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427219070085
E. Kianfar, M. Shirshahi, F. Kianfar et al., Simultaneous prediction of the density, viscosity and electrical conductivity of pyridinium-based hydrophobic ionic liquids using artificial neural network. Silicon 10, 2617–2625 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9798-z
M. Salimi, V. Pirouzfar, E. Kianfar, Novel nanocomposite membranes prepared withPVC/ABS and silica nanoparticles for C2H6/CH4 separation. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 59, 566–574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X17040071
F. Kianfar, E. Kianfar, Synthesis of isophthalic acid/aluminum nitrate thin film nanocomposite membrane for hard water softening. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 29, 2176–2185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01177-1
E. Kianfar, R. Azimikia, S.M. Faghih, Simple and strong dative attachment of α-diiminenickel (II) catalysts on supports for ethylene polymerization with controlled morphology. Catal Lett 150, 2322–2330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03116-z
E. Kianfar, Nanozeolites: synthesized, properties, applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 91, 415–429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05012-4
H. Liu, E. Kianfar, Investigation the synthesis of nano-SAPO-34 catalyst prepared by differenttemplates for MTO process. Catal Lett (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03333-6
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, S. Hajimirzaee, B. Koohestani, Methanol to gasoline conversion over CuO/ZSM-5 catalyst synthesized using sonochemistry method. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 17(2018)
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, V. Pirouzfar, B. Koohestani, Synthesis of modified catalyst andstabilization of CuO/NH4-ZSM-5 for conversion of methanol to gasoline. Int J Appl Ceram Technol. 15, 734–741 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12830
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, V. Pirouzfar, B. Koohestani, Synthesis and modification of zeolite ZSM-5 catalyst with solutions of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) for methanol to gasoline conversion. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 16(7), 20170229 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2017-0229
E. Kianfar, Comparison and assessment of zeolite catalysts performance dimethyl ether and light olefins production through methanol: a review. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 39, 157–177 (2019)
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, A review on the production of light olefins from hydrocarbons cracking and methanol conversion, in book: Advances in Chemistry Research, vol. 59, chapter 1, ed by J.C. Taylor (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020)
E. Kianfar, A. Razavi, Zeolite catalyst based selective for the process MTG: A review, in book: Zeolites: Advances in Research and Applications, chapter: 8, ed. A. Mahler (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020)
E. Kianfar, Zeolites: Properties, Applications, Modification and Selectivity, in book: Zeolites: Advances in Research and Applications, chapter: 1, ed. A. Mahler (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020)
E. Kianfar, S. Hajimirzaee, S.S. Musavian, A.S. Mehr, Zeolite-based catalysts for methanol to gasoline process: a review. Microchem. J. 104822 (2020)
E. Kianfar, M. Baghernejad, Y. Rahimdashti, Study synthesis ofvanadium oxide nanotubes with two template hexadecylamin and hexylamine. Biological Forum. 7, 1671–1685 (2015)
E. Kianfar, Synthesizing of vanadium oxide nanotubes using hydrothermal and ultrasonic method (Publisher: Lambert Academic Publishing, 2020), pp. 1–80. ISBN: 978-613-9-81541-8
E. Kianfar, V. Pirouzfar, H. Sakhaeinia, An experimental study on absorption/stripping CO2 using Mono-ethanol amine hollow fiber membrane contactor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 80, 954–962 (2017)
E. Kianfar, C. Viet, Polymeric membranes on base of polymethyl methacrylate forair separation: a review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 10, 1437–1461 (2021)
S. Nmousavian, P. Faravar, Z. Zarei, R. Zimikia, M.G. Monjezi, E. Kianfar, Modeling and simulation absorption of CO2 using hollow fiber membranes (HFM) with mono-ethanol amine with computational fluid dynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(4), 103946 (2020)
Z. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Zhou, H. Wang, L. Wen, E. Kianfar, Investigation of effective parameters on SAPO-34 nano catalyst the methanol-toolefin conversion process: A review. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 40(3), 91–105 (2020)
C. Gao, J. Liao, L. Jingqiong, J. Ma, E. Kianfar, The effect of nanoparticles on gas permeability with polyimide membranes and network hybrid membranes: a review. Rev. Inorg. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/revic-2020-0007
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, B. Koohestani, Zeolite catalyst: a review on the production of light olefins, (Publisher: Lambert Academic Publishing, 2020) p. 1-116. ISBN: 978-620-3-04259-7
E. Kianfar, Investigation on catalysts of “methanol to light olefins”, (Publisher: Lambert Academic Publishing, 2020) p. 1-168. ISBN: 978-620-3-19402-9
E. Kianfar, Application of nanotechnology in enhanced recovery oil and gas. Importance & Applications of Nanotechnology, 5, Chapter 3 (MedDocs Publishers, 2020), p. 16-21
E. Kianfar, Catalytic properties of nanomaterials and factors affecting it . Importance & Applications of Nanotechnology, 5, Chapter 4, (MedDocs Publishers, 2020), p. 22-25
E. Kianfar, Introducing the application of nanotechnology in lithium-ion battery. Importance & Applications of Nanotechnology, 4, Chapter 4, (MedDocs Publishers, 2020), p. 1-7
E. Kianfar, H. Mazaheri, Synthesis of nanocomposite (CAU-10-H) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for removal of color from the water. Fine Chemical Engineering 1, 83–91 (2020)
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, B. Koohestani, Methanol to gasoline conversionover CuO / ZSM-5 catalyst synthesized and influence of water on conversion. Fine Chemical Engineering 1, 75–82 (2020)
E. Kianfar, An experimental study PVDF and PSF hollow fiber membranes for chemical absorption carbon dioxide. Fine Chemical Engineering 1, 92–103 (2020)
Ehsan Kianfar; Sajjad Mafi, E. Kianfar, S. Mafi, Ionic liquids: properties, application, and synthesis. FineChemical Engineering 2, 22–31 (2020)
S.M. Faghih, E. Kianfar, Modeling of fluid bed reactor of ethylene dichloride production in Abadan Petrochemical based on three-phase hydrodynamic model. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 16, 1–14 (2018)
E. Kianfar, H. Mazaheri, Methanol to gasoline: a sustainable transport fuel, in book: Advances in Chemistry Research, chapter: 4, ed. by J.C. Taylor (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020), p. 66
Kianfar, A comparison and assessment on performance of zeolite catalyst based selective for the process methanol to gasoline: a review, in Advances in Chemistry Research, chapter 2 (NewYork: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., 2020), p. 63
E. Kianfar, M. Salimi, F. Kianfar et al., CO2/N2 separation using polyvinyl chloride isophthalic acid/aluminium nitrate nanocomposite membrane. Macromol. Res. 27, 83–89 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7009-4
E. Kianfar, Synthesis of characterization Nanoparticles isophthalic acid / aluminum nitrate (CAU-10-H) using method hydrothermal, in Advances in Chemistry Research, (Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020)
E. Kianfar, CO2 capture with ionic liquids: a review, in Advances in Chemistry Research, vol. 67 (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020)
E. Kianfar, Enhanced light olefins production via methanol dehydration over promoted SAPO-34, in Advances in Chemistry Research, chapter: 4 (Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020), p. 63
E. Kianfar, Gas hydrate: applications, structure, formation, separation processes, Thermodynamics, in Advances in Chemistry Research, chapter: 8, ed. J.C. Taylor (Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc., NY, USA, 2020), p. 62
M. Kianfar, F. Kianfar, E. Kianfar, The effect of nano-composites on themechanic and morphological characteristics of NBR/PA6 blends. American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies 4(1), 29–44 (2016)
F. Kianfar, S.R.M. Moghadam, E. Kianfar, Energy Optimization of Ilam Gas Refinery Unit 100 by using HYSYS Refinery Software (2015). Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8(S9), 431–436 (2015)
E. Kianfar, Production and identification of vanadium oxide nanotubes. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8(S9), 455–464 (2015)
F. Kianfar, S.R.M. Moghadam, E. Kianfar, Synthesis of Spiro Pyran by using silica-bonded N-propyldiethylenetriamine as recyclable basic catalyst. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8(11), 68669 (2015)
E. Kianfar, Recent advances in synthesis, properties, and applications of vanadium oxide nanotube. Microchem. J. 145, 966–978 (2019)
S. Hajimirzaee, A. Soleimani Mehr, E. Kianfar, Modified ZSM-5 zeolite for conversion of LPG to aromatics. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2020.1833048
E. Kianfar, Investigation of the effect of crystallization temperature and time in synthesis of SAPO-34 catalyst for the production of light olefins. Pet. Chem. 61, 527–537 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544121050030
X. Huang, Y. Zhu, E. Kianfar, Nano biosensors: properties, applicationsand Electrochemical Techniques. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12, 1649–1672 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.048
E. Kianfar, Protein nanoparticles in drug delivery: animal protein, plant proteins and proteincages, albumin nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 19, 159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00896-3
E. Kianfar, Magnetic nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery: a review. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05932-9
R. Syah, M. Zahar, E. Kianfar, Nanoreactors: properties, applicationsand characterization. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2021-0069
I. Raya, H.H. Kzar, Z.H. Mahmoud, A. Al Ayub Ahmed, A.Z. Ibatova, E. Kianfar, A review of gas sensors based on carbon nanomaterial. Carbon Letters (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-021-00276-9
Y. Sun, Y. Yang, X. Shi, G. Suo, H. Chen, X. Hou, ..., Z. Chen, Self-standingfilm assembled using SnS–Sn/multiwalled carbon nanotubes encapsulated carbon fibers: apotential large-scale production material for ultra-stable sodium-ion battery anodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(24), 28359–28368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c07152
X. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Zhang, C. Lee, A novel aluminum-graphite dual-ionbattery. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(11), 1502588 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201502588
X. Tong, F. Zhang, B. Ji, M. Sheng, Y. Tang, Carbon-coated porousaluminum foil anode for high-rate, long-term cycling stability, and high energy density dual-ionbatteries. Advanced materials (Weinheim) 28(45), 9979–9985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603735
M. Wang, C. Jiang, S. Zhang, X. Song, Y. Tang, ..., H. Cheng, Reversiblecalcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with ahigh discharge voltage. Nat. Chem. 10(6), 667–672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0045-4
Z. Zhang, R. Xun, L. Wang, Z. Meng, Construction of pseudocapacitive Li.sub.2-xLa.sub.xZnTi.sub.3O.sub.8 anode for fast and super-stable lithium storage. Ceram. Int. 47(1), 62 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.174
C. He, H. Wang, L. Fu, J. Huo, Z. Zheng, C. Zhao, ..., M. An, Principles fordesigning CO2 adsorption catalyst: Serving thermal conductivity as the determinant forreactivity. Chin. Chem. Lett. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.09.049
L. Li, Y. Shan, F. Wang, X. Chen, Y. Zhao, D. Zhou, ..., W. Cui, Improvingfast and safe transfer of lithium ions in solid-state lithium batteries by porosity and channelstructure of polymer electrolyte. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c11489
L. Zhang, M. Cong, X. Ding, Y. Jin, F. Xu, Y. Wang, ..., L. Zhang, A JanusFe-SnO2 catalyst that enables bifunctional electrochemical nitrogen fixation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(27), 10888–10893 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202003518
L. Jiang, Y. Wang, X. Wang, F. Ning, S. Wen, Y. Zhou, ..., F. Zhou, Electrohydrodynamic printing of a dielectric elastomer actuator and its application in tunable lenses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 147(106461)(2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106461
W. Yan, K. Liang, Z. Chi, T. Liu, M. Cao, S. Fan, ..., J. Su, Litchi-likestructured MnCo2S4@C as a high capacity and long-cycling time anode for lithium-ionbatteries. Electrochim. Acta 376, 138035 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138035
R. Syah, M. Zahar, E. Kianfar, Nanoreactors: properties, applications and characterization. Int J Chem React Eng 19(10), 981–1007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2021-0069
T.C. Chen, R. Rajiman, M. Elveny, J.W.G. Guerrero, A.I. Lawal, N.K.A. Dwijendra, ..., Y. Zhu, Engineering of novel Fe-based bulk metallic glasses using a machine learning-based approach. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(12), 12417–12425 (2021)
C. Fu, A. Rahmani, W. Suksatan, S.M. Alizadeh, M. Zarringhalam, S. Chupradit, D. Toghraie, Comprehensive investigations of mixed convection of Fe–ethylene-glycolnanofluid inside an enclosure with different obstacles using lattice Boltzmann method. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–16 (2021)
T. Tjahjono, M. Elveny, S. Chupradit, D. Bokov, H.T. Hoi, M. Pandey, Role of cryogenic cycling rejuvenation on flow behavior of ZrCuAlNiAg metallic glass at relaxation temperature. Trans. Indian Inst. Metals , 1–17 (2021)
S.G. Al-Shawi, N. Andreevna Alekhina, S. Aravindhan, L. Thangavelu, A. Elena, N. Viktorovna Kartamysheva, R. Rafkatovna Zakieva, Synthesis of NiO nanoparticles and sulfur, and nitrogen co doped-graphene quantum Dots/NiO nanocomposites for antibacterial application. Journal of Nanostructures 11(1), 181–188 (2021)
S. Hutapea, S. Ghazi Al-Shawi, T.C. Chen, X. You, D. Bokov, W.K. Abdelbasset, W. Suksatan, Study on food preservation materials based on nano-particle reagents. Food Science and Technology (2021)
M.A. Sina, M.A. Adeel, Assessment of stand-alone photovoltaic system and mini-grid solar system as solutions to electrification of remote villages in Afghanistan. International Journal of Innovative Research and Scientific Studies 4(2), 92–99 (2021). https://doi.org/10.53894/ijirss.v4i2.62
Y.-P. Xu, P. Ouyang, S.-M. Xing, L.Y. Qi, H. Jafari, Optimal structuredesign of a PV/FC HRES using amended Water Strider Algorithm. Energy Rep. 7, 2057–2067 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.04.016
J. Khan, S. Norfarhani, R.K. Sahu, S. Ruhi, M. Kaleemullah, S. Al-Dhalli, E. Yusuf, Development and evaluation of topical emulgel of aspirin using different polymericbases. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 13(12), 6300–6304 (2020)
Z. Othman, H.R.H. Khalep, A.Z. Abidin, H. Hassan, S. Fattepur, The Anti-Angiogenic Properties of Morinda citrifolia. L (Mengkudu) Leaves using chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Pharmacognosy Journal 11(1), (2019)
S. Mazraedoost, R. Masoumzade, Z. Javidi, Y. Ashoori, The role of nanoparticles for reactive oxygen species (ROS) in biomedical engineering. Advances in Applied NanoBio-Technologies 2(4), 24–36 (2021)
Acknowledgements
Department of Chemical Engineering, Arak Branch, Islamic Azad University, Arak, Iran. Young Researchers and Elite Club, Gachsaran Branch, Islamic Azad University, Gachsaran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Saade Abdalkareem Jasim, Mustafa M. Kadhim, Venu KN, Indah Raya: investigation, concept and design, experimental studies, writing—original draft, reviewing and editing. Sarah Jawad Shoja, Wanich Suksatan, Muneam Hussein Ali, Ehsan kianfar: investigation, concept and design, data curation, conceptualization, writing—original draft, reviewing, and editing.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jasim, S.A., Kadhim, M.M., KN, V. et al. Molecular Junctions: Introduction and Physical Foundations, Nanoelectrical Conductivity and Electronic Structure and Charge Transfer in Organic Molecular Junctions. Braz J Phys 52, 31 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-01033-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-01033-z