Abstract
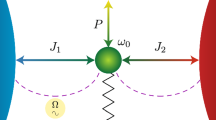
We present a study of the performance of endoreversible thermal machines optimized with respect to the thermodynamic force associated with the cold bath in the regime of small thermodynamic forces. These thermal machines can work either as an engine or as a refrigerator. We analyze how the optimal performances are determined by the dependence of the thermodynamic flux on the forces. The results are motivated and illustrated with a quantum model, the three level maser, and explicit analytical expressions of the engine efficiency as a function of the system parameters are given.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Carnot. Reflections on the Motive Power of Heat and on Machines Fitted to Develop that Power (Wiley, New York, 1890)
J. Yvon. Proceedings of the International Conference on Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy, Geneva, 1955 (United Nations, New York, 1955), p. 387
I.I. Novikov, Efficiency of an atomic power generating installation. At. Energy. 3, 1269–1272 (1957)
F.L. Curzon, B. Ahlborn, Efficiency of a Carnot engine at maximum power output. Am. J. Phys. 43, 22–24 (1975)
C. Van den Broeck, Thermodynamic efficiency at maximum power. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 190602 (2005)
M. Esposito, K. Lindenberg, C. Van den Broeck, Universality of efficiency at maximum power. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 130602 (2009)
E. Geva, R. Kosloff, A quantum-mechanical heat engine operating in finite time. A model consisting of spin-1/2 systems as the working fluid. J. Chem. Phys. 96, 3054–3067 (1992)
Y. Zhou, D. Segal, et al., Minimal model of a heat engine: Information theory approach. Phys. Rev. E. 82, 011120 (2010)
S. Abe, Maximum-power quantum-mechanical carnot engine. Phys. Rev. E. 83, 041117 (2011)
O. Abah, J. Roßnagel, G. Jacob, S. Deffner, F. Schmidt-Kaler, K. Singer, E. Lutz, Single-ion heat engine at maximum power. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 203006 (2012)
D. Gelbwaser-Klimovsky, R. Alicki, G. Kurizki, Minimal universal quantum heat machine. Phys. Rev. E. 87, 012140 (2013)
S. Velasco, J.M.M. Roco, A. Medina, A. Calvo Hernández, New performance bounds for a finite-time Carnot refrigerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3241–3244 (1997)
Y. Wang, M. Li, Z.C. Tu, A. Calvo-Hernández, J.M.M. Roco, Coefficient of performance at maximum figure of merit and its bounds for low-dissipation carnot-like refrigerators. Phys. Rev. E. 86, 011127 (2012)
A.E. Allahverdyan, K. Hovhannisyan, G. Mahler, Optimal refrigerator. Phys. Rev. E. 81, 051129 (2010)
L.A. Correa, J.P. Palao, G. Adesso, D. Alonso, Performance bound for quantum absorption refrigerators. Phys. Rev. E. 87, 042131 (2013)
L.A. Correa, Multistage quantum absorption heat pumps. Phys. Rev. E. 89, 042128 (2014)
L.A. Correa, J.P. Palao, D. Alonso, G. Adesso, Quantum-enhanced absorption refrigerators. Sci. Rep. 4, 3949 (2014)
L.A. Correa, J.P. Palao, G. Adesso, D. Alonso, Optimal performance of endoreversible quantum refrigerators. Phys. Rev. E. 90, 062124 (2014)
H.E.D. Scovil, E.O. Schulz-DuBois, Three-level masers as heat engines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2, 262–263 (1959)
R. Kosloff, Quantum thermodynamics, A dynamical viewpoint. Entropy. 15, 2100–2128 (2013)
R. Kosloff, A. Levy, Quantum heat engines and refrigerators: Continuous devices. Anual Rev. Phys. Chem. 65, 365–393 (2014)
H.P. Breuer, F. Petruccione. The Theory of Open Quantum Systems (Oxford University Press, New York, 2002)
M. Esposito, R. Kawai, K. Lindenberg, C. Van den Broeck, Efficiency at maximum power of low-dissipation Carnot engines. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 150603 (2010)
L.A. Correa, J.P. Palao, D. Alonso, Internal dissipation and heat leaks in quantum thermodynamics cycles. Phys. Rev. E. 92, 032136 (2015)
Acknowledgments
D. Alonso acknowledges the warm hospitality and support of the organizing committee of the Quantum Information and Thermodynamics workshop held in São Carlos in February 2015 and to Prof. Lucas C. Céleri for his kind assistance. We thank R. Kosloff, R. Uzdin, M Esposito, A del Campo, and I. de Vega for fruitful discussions in São Carlos. Financial support from Spanish MINECO (FIS2013-40627-P and FIS2013-41352-P), COST Action MP1209, and EU Collaborative Project TherMiQ (Grant Agreement 618074) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palao, J.P., Correa, L.A., Adesso, G. et al. Efficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal Machines. Braz J Phys 46, 282–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-015-0396-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-015-0396-x