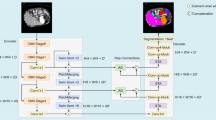
Abstract
Deep learning-based methods have recently shown great promise in medical image segmentation task. However, CNN-based frameworks struggle with inadequate long-range spatial dependency capture, whereas Transformers suffer from computational inefficiency and necessitate substantial volumes of labeled data for effective training. To tackle these issues, this paper introduces CI-UNet, a novel architecture that utilizes ConvNeXt as its encoder, amalgamating the computational efficiency and feature extraction capabilities. Moreover, an advanced attention mechanism is proposed to captures intricate cross-dimensional interactions and global context. Extensive experiments on two segmentation datasets, namely BCSD, and CT2USforKidneySeg, confirm the excellent performance of the proposed CI-UNet as compared to other segmentation methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Senthilkumaran N, Vaithegi S. Image segmentation by using thresholding techniques for medical images. Comput Sci Eng Int J. 2016;6(1):1–13.
Manikandan S, Ramar K, Iruthayarajan MW, Srinivasagan K. Multilevel thresholding for segmentation of medical brain images using real coded genetic algorithm. Measurement. 2014;47:558–68.
Ng H, Ong S, Foong K, Goh P-S, Nowinski W. Medical image segmentation using k-means clustering and improved watershed algorithm. In 2006 IEEE southwest symposium on image analysis and interpretation; 2006. pp. 61–65. IEEE.
Masulli F, Schenone A. A fuzzy clustering based segmentation system as support to diagnosis in medical imaging. Artif Intell Med. 1999;16(2):129–47.
Pohle R, Toennies KD. Segmentation of medical images using adaptive region growing. In: medical imaging 2001: Image Processing, vol. 4322; 2001. pp. 1337–1346. SPIE.
Pan Z, Lu J. A bayes-based region-growing algorithm for medical image segmentation. Comput Sci Eng. 2007;9(4):32–8.
Chalana V, Kim Y. A methodology for evaluation of boundary detection algorithms on medical images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1997;16(5):642–52.
Aslam A, Khan E, Beg MS. Improved edge detection algorithm for brain tumor segmentation. Proced Comput Sci. 2015;58:430–7.
Heimann T, Meinzer H-P. Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: a review. Med Image Anal. 2009;13(4):543–63.
Shen T, Li H, Huang X. Active volume models for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;30(3):774–91.
Mitchell SC, Lelieveldt BP, Van Der Geest RJ, Bosch HG, Reiver J, Sonka M. Multistage hybrid active appearance model matching: segmentation of left and right ventricles in cardiac mr images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2001;20(5):415–23.
Khalifa F, El-Baz A, Gimel’farb G, Ouseph R, El-Ghar MA. Shape-appearance guided level-set deformable model for image segmentation. In: 2010 20th International conference on pattern recognition; 2010. pp. 4581–4584. IEEE.
Chen X, Udupa JK, Bagci U, Zhuge Y, Yao J. Medical image segmentation by combining graph cuts and oriented active appearance models. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2012;21(4):2035–46.
Chen X, Williams BM, Vallabhaneni SR, Czanner G, Williams R, Zheng Y. Learning active contour models for medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2019. pp. 11632–11640.
Zhou S, Wang J, Zhang S, Liang Y, Gong Y. Active contour model based on local and global intensity information for medical image segmentation. Neurocomputing. 2016;186:107–18.
Hemalatha R, Thamizhvani T, Dhivya AJA, Joseph JE, Babu B, Chandrasekaran R. Active contour based segmentation techniques for medical image analysis. Med Biol Image Anal. 2018;4(17):2.
Liu A-A, Li K, Kanade T. A semi-Markov model for mitosis segmentation in time-lapse phase contrast microscopy image sequences of stem cell populations. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2011;31(2):359–69.
Besbes A, Komodakis N, Langs G, Paragios N. Shape priors and discrete mrfs for knowledge-based segmentation. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2009; pp. 1295–1302. IEEE.
Wimmer A, Soza G, Hornegger J. A generic probabilistic active shape model for organ segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2009: 12th international conference, London, Sept 20–24, 2009; proceedings, Part II 12; 2009. pp. 26–33. Springer.
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2015; pp. 3431–3440.
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, Oct 5-9, 2015, proceedings, Part III 18; 2015; pp. 234–241. Springer.
Dai J, Qi H, Xiong Y, Li Y, Zhang G, Hu H, Wei Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2017; pp. 764–773.
Alam M S, Wang D, Liao Q, et al. A Multi-scale Context aware Attention Model for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022;27(8):3731–3739.
Li D, Dharmawan DA, Ng BP, Rahardja S. Residual u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP); 2019; pp. 425–1429. IEEE.
Yu W, Fang B, Liu Y, Gao M, Zheng S, Wang Y. Liver vessels segmentation based on 3D residual u-net. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP); 2019; pp. 250–254. IEEE.
Li D, Rahardja S. Bseresu-net: an attention-based before-activation residual u-net for retinal vessel segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;205:106070.
Zhang J, Jin Y, Xu J, Xu X, Zhang Y. Mdu-net: Multi-scale densely connected u-net for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.00352; 2018.
Zhang Z, Wu C, Coleman S, Kerr D. Dense-inception u-net for medical image segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;192:105395.
Wang K, Zhang X, Zhang X, Lu Y, Huang S, Yang D. Eanet: iterative edge attention network for medical image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2022;127:108636.
Cheng J, Tian S, Yu L, Gao C, Kang X, Ma X, Wu W, Liu S, Lu H. Resganet: residual group attention network for medical image classification and segmentation. Med Image Anal. 2022;76:102313.
Gu R, Wang G, Song T, Huang R, Aertsen M, Deprest J, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T, Zhang S. Ca-net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020;40(2):699–711.
Li C, Tan Y, Chen W, Luo X, He Y, Gao Y, Li F. Anu-net: Attention-based nested u-net to exploit full resolution features for medical image segmentation. Comput Graph. 2020;90:11–20.
Huang H, Lin L, Tong R, Hu H, Zhang Q, Iwamoto Y, Han X, Chen Y-W, Wu J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In: ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP); 2020; pp. 1055–1059. IEEE.
Valanarasu JMJ, Oza P, Hacihaliloglu I, Patel VM. Medical transformer: gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th international conference, Strasbourg, France, Sept 27–Oct 1, 2021, proceedings, Part I 24; 2021; pp. 36–46. Springer.
Hatamizadeh A, Tang Y, Nath V, Yang D, Myronenko A, Landman B, Roth HR, Xu D. Unetr: Transformers for 3D medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision; 2022; pp. 574–584.
Xie Y, Zhang J, Shen C, Xia Y. Cotr: Efficiently bridging CNN and transformer for 3D medical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th international conference, Strasbourg, France, Sept 27–Oct 1, 2021, proceedings, Part III 24; 2021. p. 171–180. Springer.
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929; 2020.
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European conference on computer vision; 2020; pp. 213–229. Springer.
Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C-Y, Feichtenhofer C, Darrell T, Xie S. A convnet for the 2020s. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2022; pp. 11976–11986.
Zhou Z, Rahman Siddiquee MM, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Deep learning in medical image analysis and multimodal learning for clinical decision support: 4th international workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th international workshop, ML-CDS 2018, held in conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, Sept 20, 2018, proceedings 4; 2018; pp. 3–11. Springer.
Xiao X, Lian S, Luo Z, Li S. Weighted res-unet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In: 2018 9th international conference on information technology in medicine and education (ITME); 2018; pp. 327–331. IEEE.
Jha D, Riegler MA, Johansen D, Halvorsen P, Johansen HD. Doubleu-net: a deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE 33rd international symposium on computer-based medical systems (CBMS); 2020; pp. 558–564. IEEE.
Tomar NK, Jha D, Riegler MA, Johansen HD, Johansen D, Rittscher J, Halvorsen P, Ali S. Fanet: A feedback attention network for improved biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2022; 34(11):9375–9388.
Wang S-H, Lv Y-D, Sui Y, Liu S, Wang S-J, Zhang Y-D. Alcoholism detection by data augmentation and convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling. J Med Syst. 2018;42:1–11.
Wang S-H, Sun J, Phillips P, Zhao G, Zhang Y-D. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image segmentation by convolutional neural network using graphical processing units. J Real-Time Image Proc. 2018;15:631–42.
Zhao X, Zhang P, Song F, Fan G, Sun Y, Wang Y, Tian Z, Zhang L, Zhang G. D2a u-net: automatic segmentation of Covid-19 CT slices based on dual attention and hybrid dilated convolution. Comput Biol Med. 2021;135:104526.
Liu J, Dong B, Wang S, Cui H, Fan D-P, Ma J, Chen G. Covid-19 lung infection segmentation with a novel two-stage cross-domain transfer learning framework. Med Image Anal. 2021;74:102205.
Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Adeli E, Wang Y, Lu L, Yuille AL, Zhou Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306; 2021.
Jha A, Kumar A, Pande S, Banerjee B, Chaudhuri S. Mt-unet: a novel u-net based multi-task architecture for visual scene understanding. In: 2020 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP); 2020; pp. 2191–2195. IEEE.
Zhang Y, Liu H, Hu Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and CNNS for medical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention–MICCAI 2021: 24th international conference, Strasbourg, France, Sept 27–Oct 1, 2021, proceedings, Part I 24; 2021; pp. 14–24. Springer.
Li Z, Wang W, Xie E, Yu Z, Anandkumar A, Alvarez JM, Luo P, Lu T. Panoptic segformer: delving deeper into panoptic segmentation with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2022; pp. 1280–1289.
Pinkus A. Approximation theory of the MLP model in neural networks. Acta Numer. 1999;8:143–95.
Deng W, Wang H, Huang J, Ju H, Geng Y, Lin CT, Pedrycz W. Ftranscnn: fusing transformer and a CNN based on fuzzy logic for uncertain medical image segmentation. Inform Fus. 2023;99:101880.
Luo X, Hu M, Song T, Wang G, Zhang S. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via cross teaching between cnn and transformer. In: International conference on medical imaging with deep learning; 2022; pp. 820–833. PMLR.
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS. Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV); 2018; pp. 3–19.
Misra D, Nalamada T, Arasanipalai AU, Hou Q. Rotate to attend: convolutional triplet attention module. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision; 2021; pp. 3139–3148.
Song Y, Zheng J, Lei L, Ni Z, Zhao B, Hu Y. Ct2us: cross-modal transfer learning for kidney segmentation in ultrasound images with synthesized data. Ultrasonics. 2022;122:106706.
Deponker Sarker Depto MMH. Shazidur Rahman: blood cell segmentation dataset. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/jeetblahiri/bccd-dataset-with-mask 2023.
Funding
This work was supported in Tianjin Research Innovation Project for Postgraduate Students (2022SKY126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study utilized publicly available datasets, and therefore, ethical review and approval were not required in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Competing Interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wen, Y., Zhang, X. et al. CI-UNet: melding convnext and cross-dimensional attention for robust medical image segmentation. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 14, 341–353 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-023-00341-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-023-00341-4