Abstract
Purpose
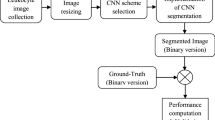
Microscopic examination of stained blood slides is an indispensable technique for hematological disease recognition. Diagnosis based on human visual interpretation is often subjected to inter and intra observer variations, slowness, tiredness and operator experience. Accurate and authentic diagnosis of hematological neoplasia is essential in the planning of suitable surgery and chemotherapy. This paper aims at proposing a fast and simple framework for lymphocyte image segmentation.
Methods
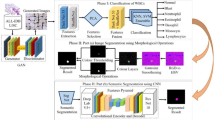
Accurate segmentation of lymphocyte is essential as it facilitates automated leukemia detection in blood microscopic images. In this paper image segmentation is considered as a pixel classification problem and a novel neural architecture is employed to classify each pixel into cytoplasm, nucleus or background region. The network tuned for a set of images works well for other similar stained blood images.
Results
Comparative analysis with other standard techniques reveals that the proposed scheme outperforms its counterparts in terms of nucleus and cytoplasm extraction.
Conclusions
In this work, a neural network based lymphocyte image segmentation scheme is designed for automated leukemia detection. Desired segmentation accuracy in terms of nucleus and cytoplasm extraction is always high in automated disease recognition system and is achieved through the proposed scheme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theml H, Diem H, Haferlach T. Color atlas of hematology: practical microscopic and clinical diagnosis. Thieme; 2004.
Tkachuk CD, Hirschmann JV. Wintrobe’s atlas of clinical hematology. 1st ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007.
Angulo J, Klossa J, Flandrin G. Ontology based lymphocyte population description using mathematical morphology on colour blood images. Cell Mol Biol. 2006; 52(6):2–15.
Ghosh M, Das D, Chakraborty C, Ray AK. Automated leukocyte recognition using fuzzy divergence. Micron. 2010; 41(7):840–846.
Ko BC, Gim J, Nam J. Automatic white blood cell segmentation using stepwise merging rules and gradient vector flow snake. Micron. 2011; 42(7):695–705.
Chakravarti GK, Bhattacharya K. A Handbook of clinical pathology: technique and interpretation. 5th ed. Academic Publishers; 2005.
Zamani F, Safabakhsh R. An unsupervised gvf snake approach for white blood cell segmentation based on nucleus. Proc 8th Int Conf Signal Pr. 2006; volume 2.
Piuri V, Scotti F. Morphological classification of blood leucocytes by microscope images. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Intell Meas Syst Appl. 2004; 103–108.
Park JS, Keller JM. Fuzzy patch label relaxation in bone marrow cell segmentation. Proc IEEE Int Conf Syst Man Cybern. 1997; 2:1133–1138.
Montseny E, Sobrevilla P, Romani S. A fuzzy approach to white blood cells segmentation in color bone marrow images. Proc IEEE Int Conf Fuzzy Syst. 2004; 1:173–178.
Jiang K, Liao QM, Dai SY. A novel white blood cell segmentation scheme using scalespace filtering and watershed clustering. Proc IEEE Int Conf Mach Learn Cybern. 2003; 5:2820–2825.
Liao Q, Deng Y. An accurate segmentation method for white blood cell images. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imag. 2002; 245–248.
Angulo J, Flandrin G. Microscopic image analysis using mathematical morphology: application to haematological cytology. 2003; 1:304–312.
Sinha N, Ramakrishnan AG. Blood cell segmentation using em algorithm. Proc Indian Conf Comput Vis Graph Im Proc. 2002.
Umpon NT. Patch based white blood cell nucleus segmentation using fuzzy clustering. ECTI T Electr Electron Commun. 2005; 3(1):5–10.
Dorini LB, Minetto R, Leite NJ. White blood cell segmentation using morphological operators and scale-space analysis. Proc Brazilian Symp Comput Graph Image Proc. 2007; 294–304.
Comaniciu D, Meer P. Cell image segmentation for diagnostic pathology in advanced algorithmic approaches to medical image segmentation: State-of-the-art applications in cardiology, neurology, mammography and pathology. Springer; 2001.
Yang L, Meer P, Foran DJ. Unsupervised segmentation based on robust estimation and color active contour models. IEEE T Inform Tech Biomed. 2005; 9(3):475–486.
Yi F, Chongxun Z, Chen P, Li L. White blood cell image segmentation using on-line trained neural network. Proc 27th Annu Int Conf The IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005; 6476–6479.
Shitong W, Min W. A new detection algorithm based on fuzzy cellular neural networks for white blood cell detection. IEEE T Inform Technol Biomed. 2006; 10(1):5–10.
Chinwaraphat S, Sanpanich A, Pintavirooj C, Sangworasil M, Tosranon P. A modified fuzzy clustering for white blood cell segmentation. Proc Third Int Symp Biomed Eng. 2008; 6:2259–2261.
Meurie C, Lezoray O, Charrier C, Elmoataz E. Combination of multiple pixel classifiers for microscopic image segmentation. IASTED Int J Robot Autom. 2005; 20(2):63–69. Special Issue on Colour Image Processing and Analysis for Machine Vision.
Ghosh M, Das D, Chakraborty C, Pala M, Maity AK, Pal SK, Ray AK. Statistical pattern analysis of white blood cell nuclei morphometry. Proc IEEE Students Technol Symp. 2010; 59–66.
“Clemex Technologies Inc. Website”. “http://www.clemexhemato.com”.
Swolin B, Simonsson P, Backman S, Lofqvist I, Bredin I, Johnsson M. Differential counting of blood leukocytes using automated microscopy and a decision support system based on artificial neural networks evaluation of diffmastertm octavia. Clin Lab Haematol. 2003; 25(3):139–147.
Swolin B, Simonsson P, Backman S, Lofqvist I, Bredin I, Johnsson M. Performance evaluation of the cellavision dm96 system: wbc differentials by automated digital image analysis supported by an artificial neural network. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 124(5):770–780.
Clarke LP, Velthuizen RP, Camacho MA, Heine JJ, Vaidyanathan M, Hall LO, Thatcher RW, Silbiger ML. Mri segmentation: methods and applications. Magn Reson Imaging. 1995; 13(3):343–368.
Lawson SW, Parker GA. Intelligent segmentation of industrial radiographic images using neural networks. Proc SPIE Mach Vis Appl Architectures Syst Integration III. SPIE. 1994; 2347:245–255.
Silverman RH, Noetzel AS. Image processing and pattern recognition in ultrasonograms by backpropagation. Neural Networks. 1990; 3(5):593–603.
Oshio K, Singh M. Automatic segmentation of magnetic resonance head images using neural nets. Proc IEEE Nucl Sci Symp. 1990; 1430–1434.
Ozkan M, Dawant BM, Maciunas RJ. Neural-network-based segmentation of multi-modal medical images: a comparative and prospective study. IEEE T Med Imaging, 1993; 12(3):534–544.
Blanz WE, Gish SL. A connectionist classifier architecture applied to image segmentation. Proc 10th Int Conf Pattern Recogn. 1990; 2:272–277.
Babaguchi N, Yamada K, Kise K, Tezuka Y. Connectionist model binarization. Proc 10th Int Conf Pattern Recogn. 1990; 2:51–56.
Hall, LO, Bensaid AM, Clarke LP, Velthuizen RP, Silbiger MS, Bezdek JC. A comparison of neural network and fuzzy clustering techniques in segmenting magnetic resonance images of the brain. IEEE T Neural Networ. 1992; 3(5):672–682.
Ozkan M, Dawant BM, Maciunas RJ. Neural-network-based segmentation of multi-modal medical images: a comparative and prospective study. IEEE T Med Imaging. 1993; 12(3):534–544.
Phukpattaranont P, Boonyaphiphat P. Segmentation of cancer cells in microscopic images using neural network and mathematical morphology. Proc Int Joint Conf SICE-ICASE. 2006; 2312–2315.
Meftah B, Lezoray O, Lecluse M, Benyettou A. Cell microscopic segmentation with spiking neuron networks. Proc 20th Int Conf Artif Neural Networ. 2010; 117–126.
Rodrigues P, Ferreira M, Monteiro J. Segmentation and classification of leukocytes using neural networks: a generalization direction. 2008; 83:373–396.
Macqueen J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Proc Fifth Berkeley Symp Math Stat Probab. 1967; 1:281–297.
Mohapatra S, Patra D. Automated leukemia detection using hausdorff dimension in blood microscopic images. Proc Int Conf Emerg Trends Robot Commun Technol. 2010; 64–68.
Russ JC. The Image Processing Handbook. 5th ed. Taylor and Francis; 2007.
Charrier C, Lebrun G, Lezoray O. Evidential segmentation of microscopic color images with pixel classification posterior probabilities. J Multimedia. 2007; 2(3).
Demirkaya O, Asyali MH, Sahoo PK. Image Processing with MATLAB: applications in Medicine and Biology. Taylor and Francis. 2009.
Robertson AR. The cie 1976 color difference formulae. Color Res Appl. 1977; 2:7–11.
Mohapatra S, Sa PK, Majhi B. Adaptive threshold selection for impulsive noise detection in images using coefficient of variance. Neural Comput Appl. 21(2):281–288.
Haykin S. Neural Networks. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall; 1999.
Patra JC, Pal RN, Chatterji BN, Panda G. Identification of nonlinear dynamic systems using functional link artificial neural networks. IEEE T Syst Man Cyb. 1999; 29(2):254–262.
Patra JC, Panda G, Baliarsingh R. Artificial neural networkbased nonlinearity estimation of pressure sensors. IEEE T Instrum Meas. 1994; 43(6):874–881.
Mohapatra S. Developmant of impulse noise detection schemes for selective filtering. Master’s thesis, National Institute of Technolgy Rourkela. 2008.
Panda S. Color image segmentation using markov random field model. PhD thesis, National Institute of Technolgy Rourkela. 2011.
Sinha N, Ramakrishnan AG. Automation of differential blood count. Proc Conf Convergent Technol Asia Pac Reg. 2003; 2:547–551.
Mohapatra S, Patra D, Kumar K. Blood microscopic image segmentation using rough sets. Proc Int Conf Image Inform Proc. 2011; 1–6.
Tu K, Yu H, Guo Z, Li X. Learnability-based further prediction of gene functions in gene ontology. Genomics. 2004; 84(6):922–928.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, S., Patra, D., Kumar, S. et al. Lymphocyte image segmentation using functional link neural architecture for acute leukemia detection. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2, 100–110 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-012-0056-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-012-0056-9